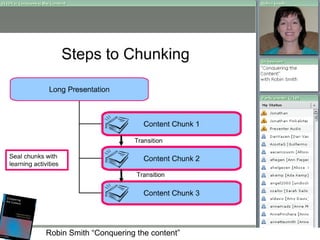
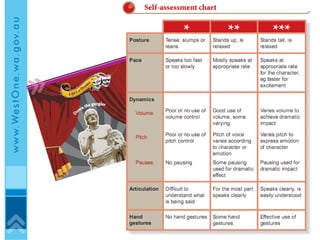
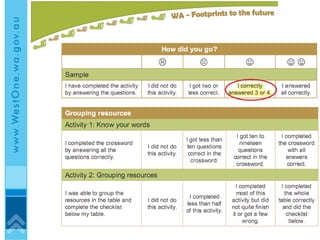
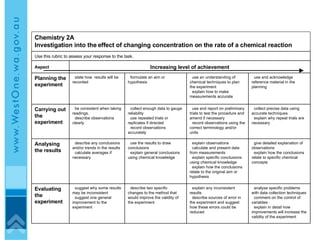
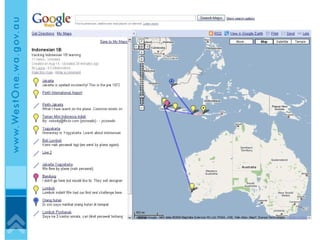
The document discusses effective eLearning design and the I.D.E.A framework. It introduces Darren Entwistle, Julie Bettenay and Jonathan Bromage who work in curriculum and education. The framework includes four stages: Introduce, Discover, Engage and Apply. Content should build on prior knowledge and be chunked into modes suited to learners. Student interaction and reflection are important. Assessment should be embedded throughout and allow self-evaluation. Effective online learning requires addressing schools' lack of technology infrastructure.