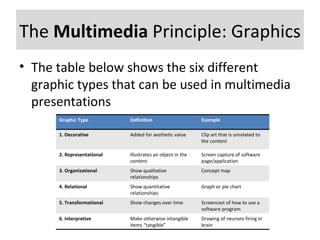
The document discusses the multimedia and contiguity principles, which highlight that individuals learn more effectively when both words and graphics are used in educational materials. It describes different graphic types utilized in multimedia presentations and emphasizes that printed and spoken words should be positioned near their corresponding graphics for optimal learning. The content aims to educate learners on how to implement these principles to promote active learning in multimedia formats.