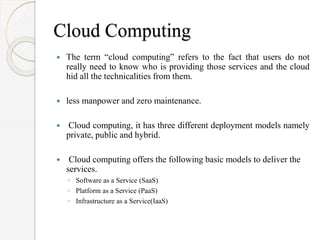
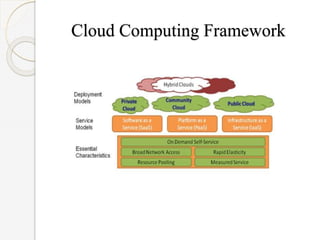
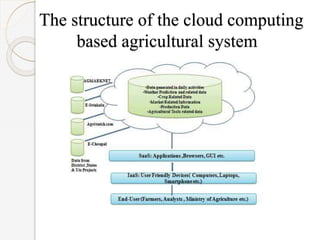
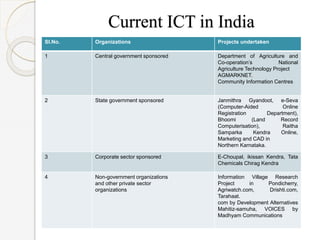
The document discusses the application of cloud computing in agriculture, highlighting its role in addressing challenges like poor knowledge of weather, pests, and insufficient ICT infrastructure among farmers. It outlines cloud computing's advantages, including reduced costs, improved efficiency, and easier access to agricultural information and techniques. The conclusion emphasizes the transformative potential of cloud computing for agricultural practices, but also notes the need for careful planning to navigate technical and business challenges.






![References
[1] Cloud computing and emerging IT platforms: Vision, hype, and
reality for delivering computing as the 5th utility R Buyya et al. /
Future Generation Computer Systems 25 (2009) 599_616.
[2] Cloud Security Alliance. Security best practices for cloud
computing, 2010b http://www.cloudsecurityalliance.org
[Accessed: July 2013].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofcloudcomputingtoagriculture1-150615052403-lva1-app6891/85/Application-of-cloud-computing-to-agriculture-11-320.jpg)
