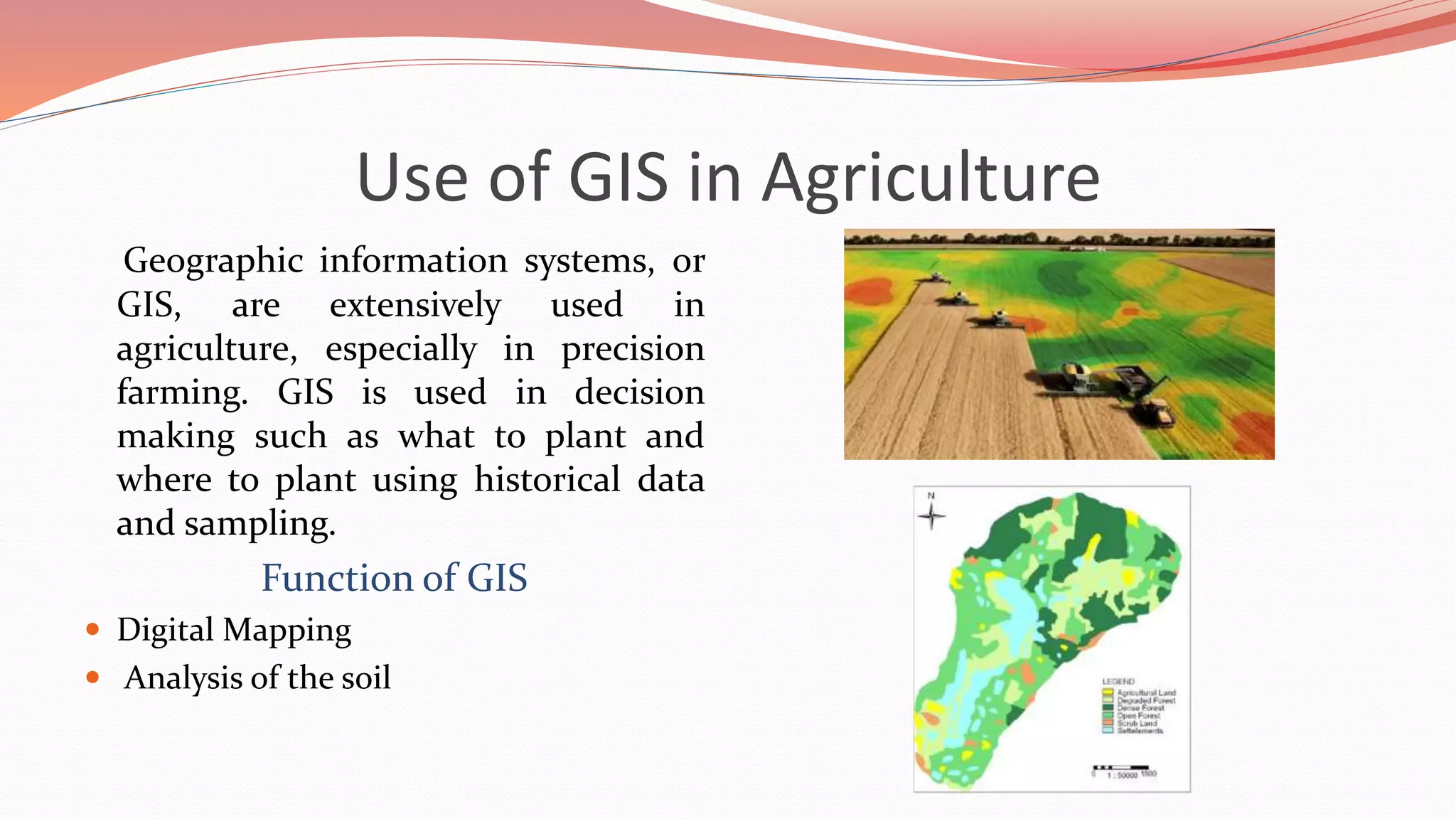
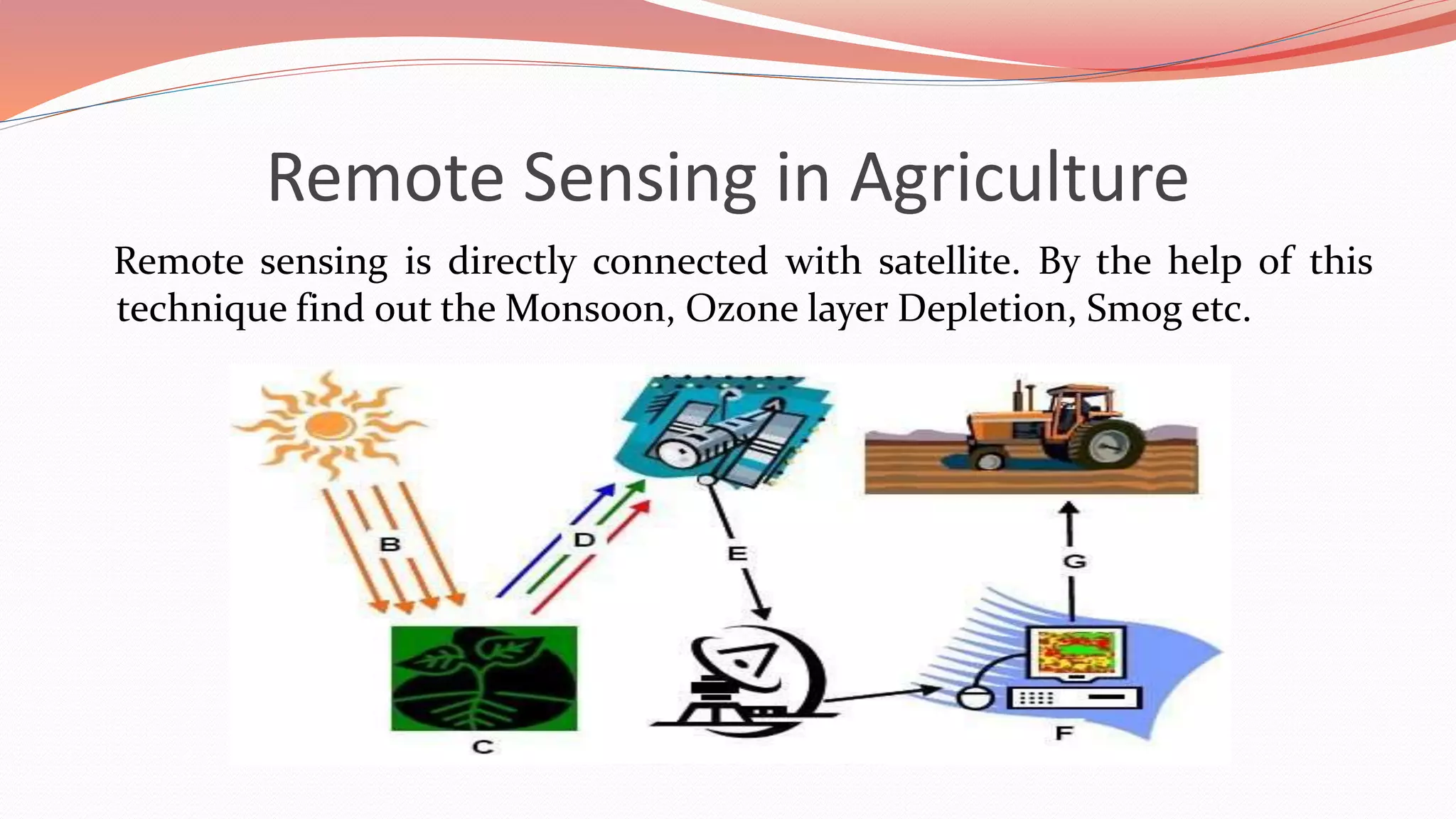
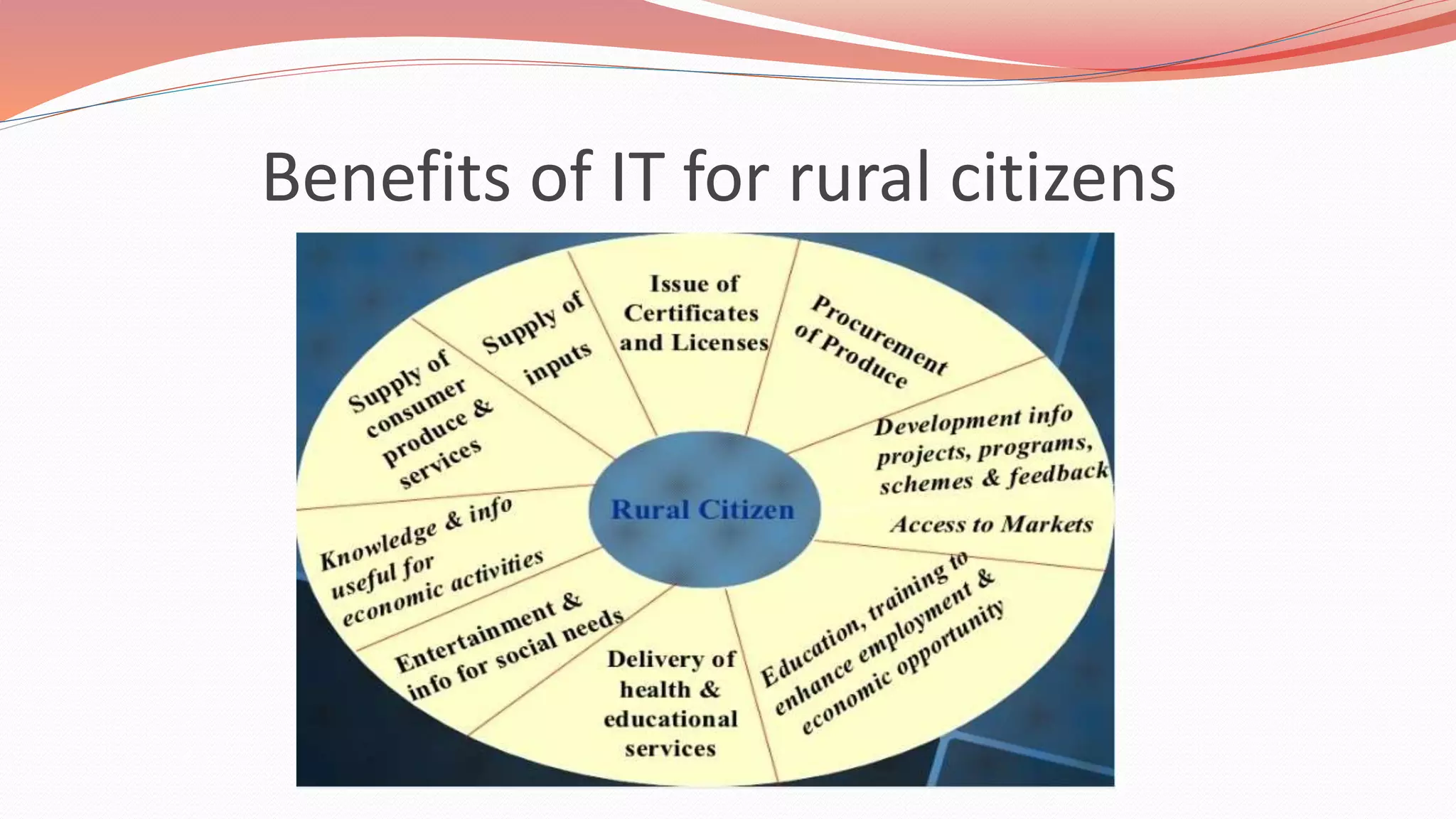
This document discusses the role of information technology in Indian agriculture. It outlines how IT can increase food production and productivity through tools like weather forecasting, digital marketplaces, mobile advisory services, greenhouse monitoring technologies, and GPS/GIS systems. The document also examines IT initiatives in India, benefits of IT for farmers, and challenges to expanding agricultural IT, with the goal of improving decision making and farm management through information access.