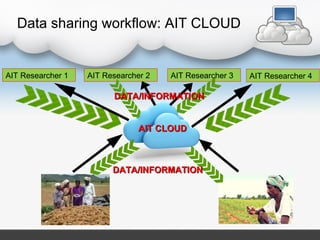
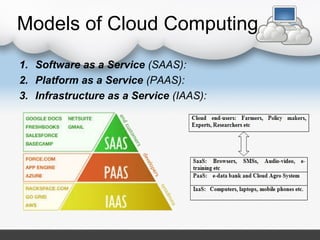
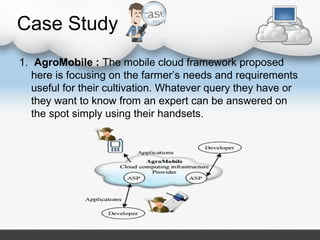
The document discusses how cloud computing can be used in Indian agriculture. It provides examples of existing cloud-based agricultural applications and services, including AgroMobile which provides farmers information on crops, weather, and expert advice via mobile devices. Other examples are a traceability software for food safety and security, an automatic irrigation control system, and land record automation in the cloud. The document also covers the types of clouds, cloud computing models, advantages and limitations, and potential future applications in agriculture like databases for crop, market, production, and tool information.





![Case Study (con..)
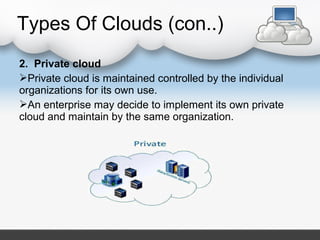
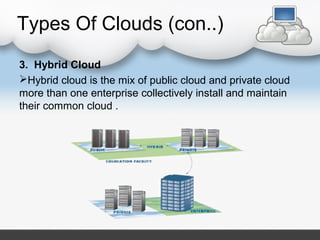
3. Cloud Computing to Control Automatic Irrigation Systems
This system uses an ethernet module to provide
the microcontroller an interface for internet
connection. The Ethernet module has been
mapped with a cloud connector Near-Bus
[an open source cloud connector] which allows
us to integrate our MCU [microcontroller unit]
platform with cloud.
4. Land record automation:
Cloud computing storage facility store the record of land with the
description related to that particular land like soil analysis result and production
history etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing-171205114308/85/Cloud-computing-in-Agriculture-13-320.jpg)