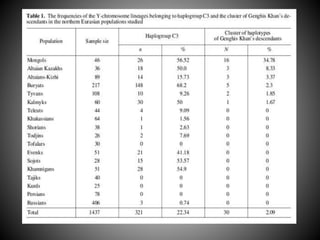
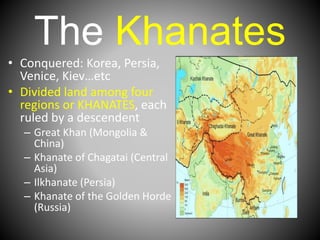
The Mongols, a nomadic people from the Mongolian steppe, conquered much of Asia under the leadership of Genghis Khan in the 13th century. Genghis Khan united the Mongol tribes and built a powerful military force that allowed the Mongols to establish the largest contiguous land empire in world history. After Genghis Khan's death, the Mongol Empire was divided into four khanates that were ruled by his descendants and continued expanding the empire's territories to include regions like Korea, Persia, Russia, and parts of Eastern Europe. The Mongol Empire promoted trade and interaction between different peoples during a period of stability known as the Pax Mongolica.