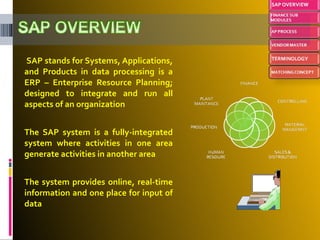
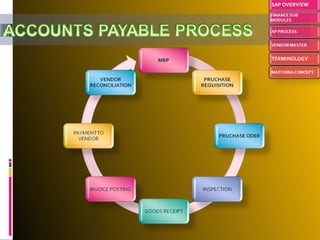
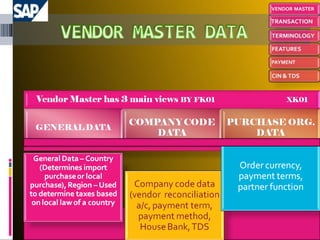
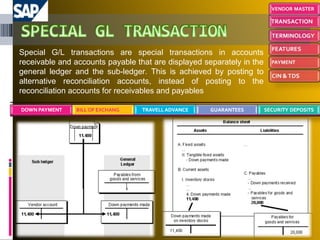
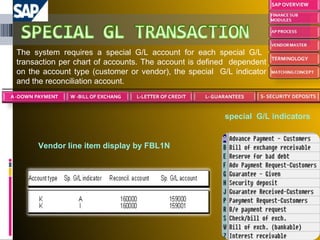
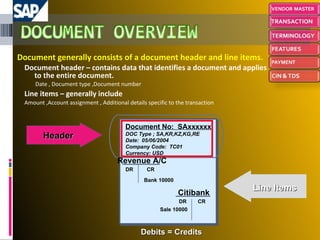
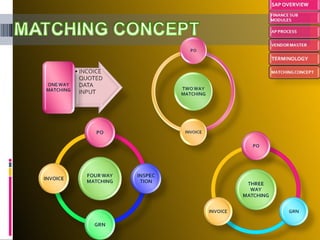
The document provides an introduction to SAP, an ERP system that integrates all aspects of an organization. It discusses how the general ledger is reconciled with subsidiary ledgers when items are posted. It also describes features like alternate payees, clearing open items between vendors and customers, and special general ledger transactions that post to alternative reconciliation accounts. Finally, it discusses document types, headers, line items, and posting keys that control which side of an account can be posted to and which account types.