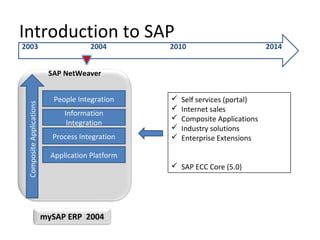
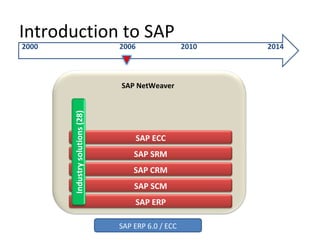
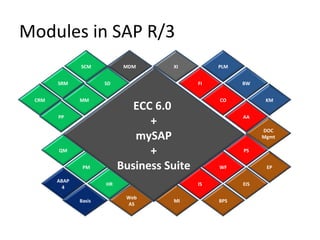
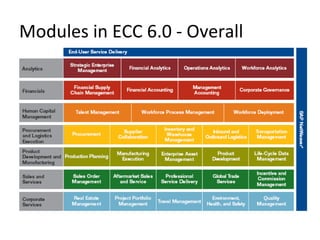
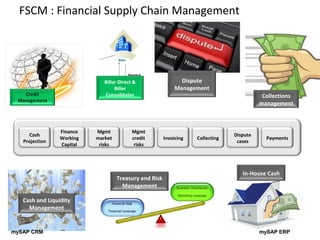
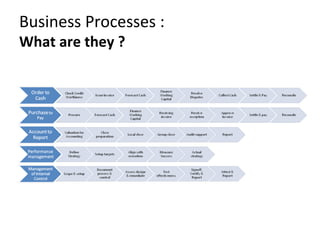
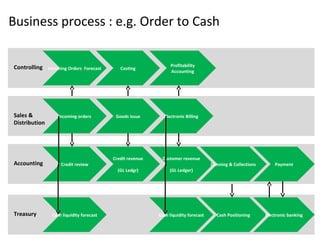
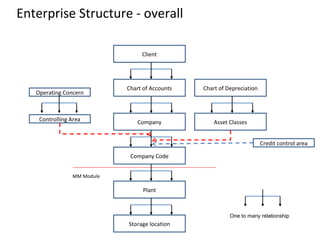
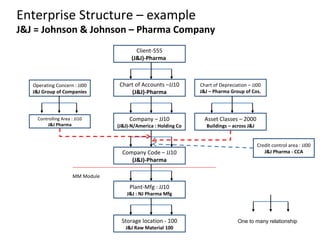
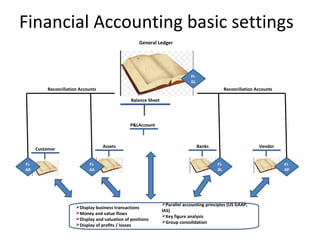
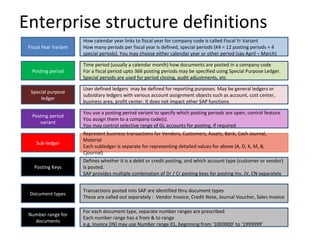
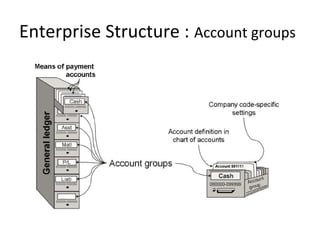
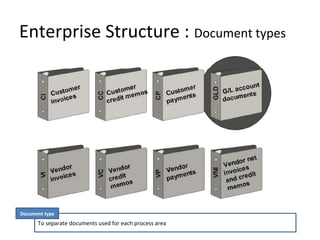
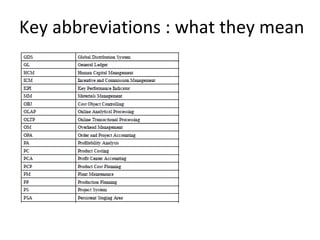
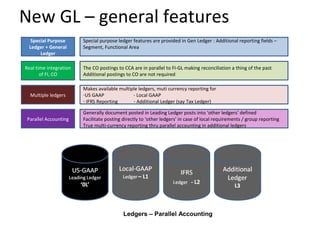
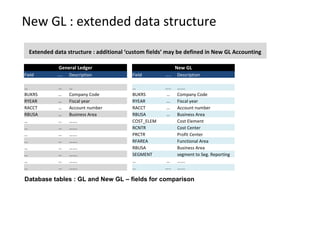
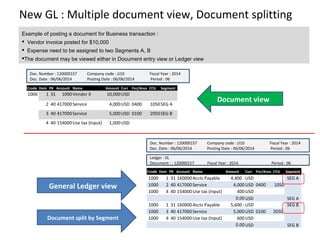
The document provides an agenda and overview for a training session on SAP FI-CO (financial accounting and controlling) modules. It includes sections on introducing SAP R/3 and its evolution, modules in SAP R/3 with a focus on FI-CO submodules, business processes, enterprise structure definitions, financial accounting basic settings, and new features in the SAP general ledger including document splitting. The training aims to provide participants with foundational knowledge on SAP financial modules and configurations.