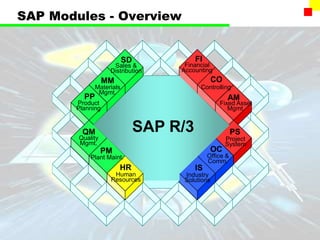
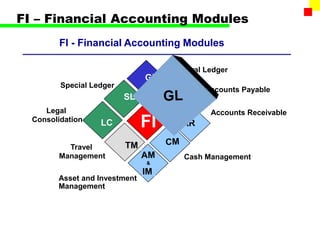
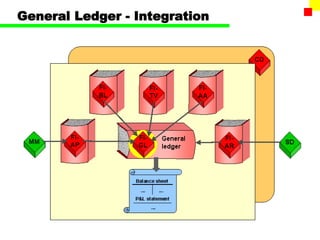
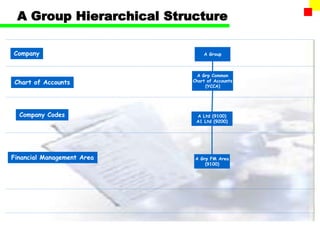
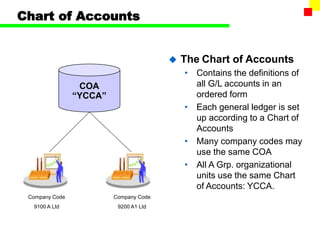
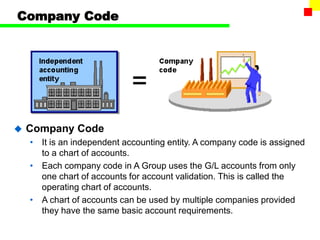
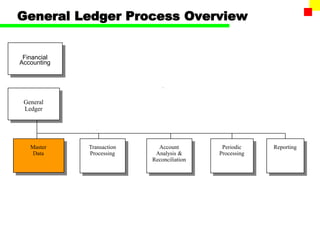
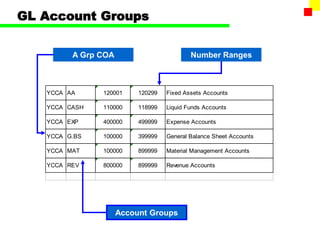
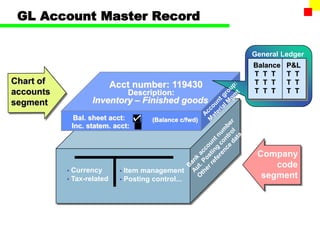
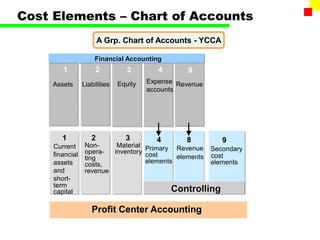
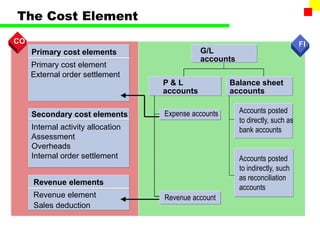
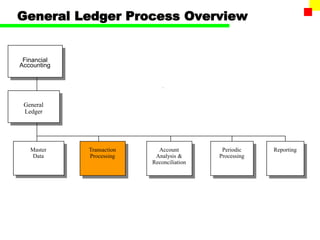
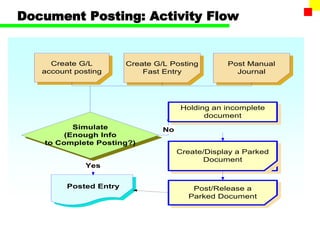
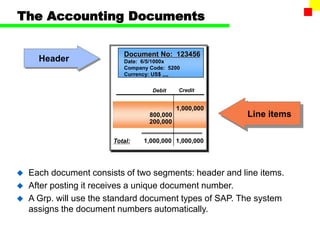
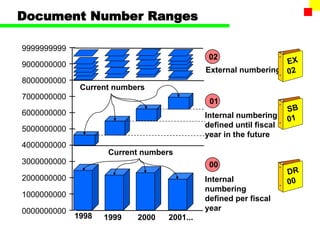
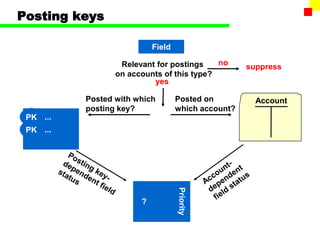
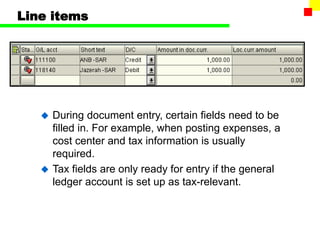
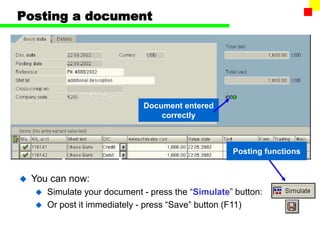
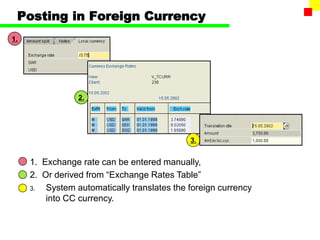
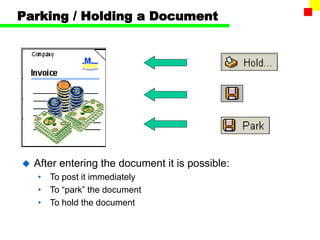
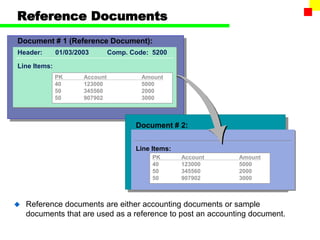
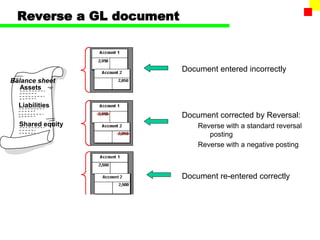
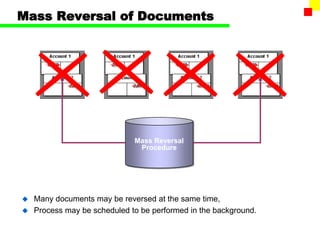
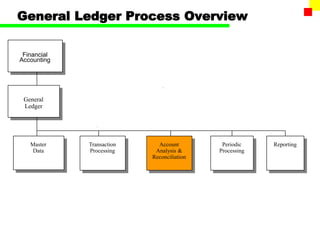
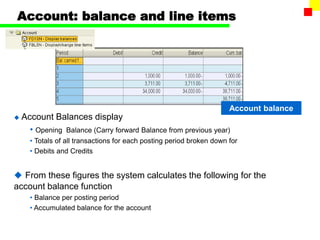
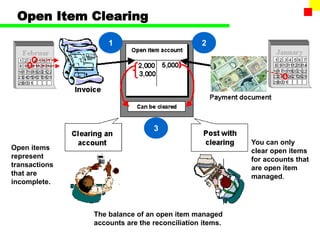
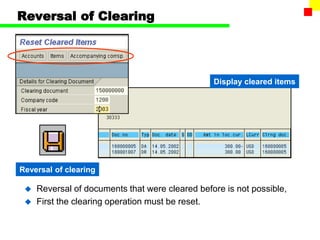
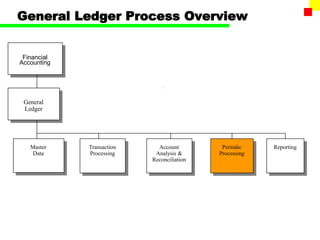
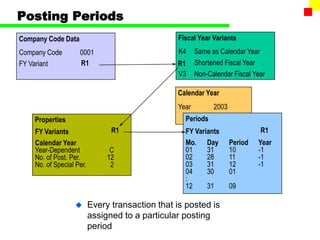
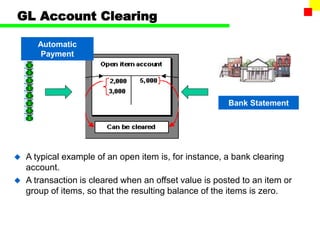
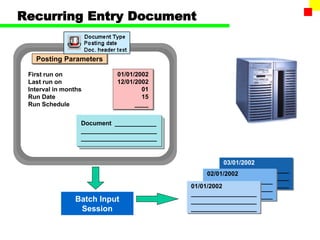
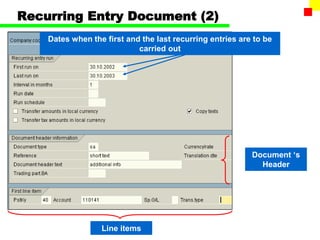
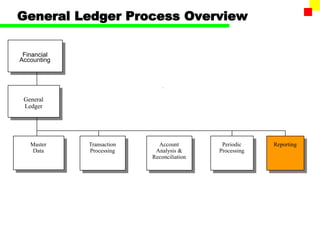
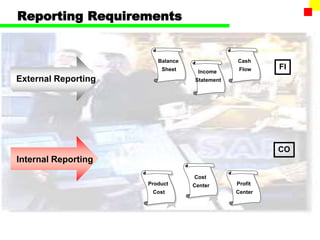
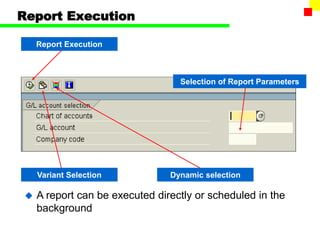
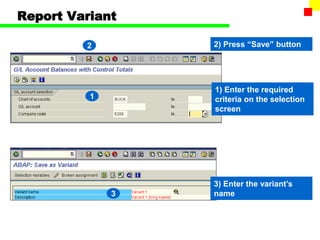
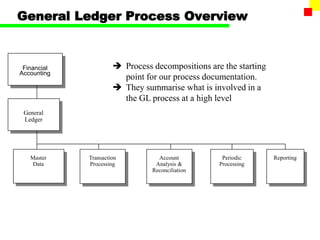
The document outlines the SAP FI General Ledger's structure and processes, including transaction processing, master data maintenance, and reporting functionalities. It describes key components such as the chart of accounts, company codes, account types, and the integration between financial accounting and controlling. Additionally, it details the various types of financial transactions supported, along with procedures for document posting, account analysis, and periodic processing activities.