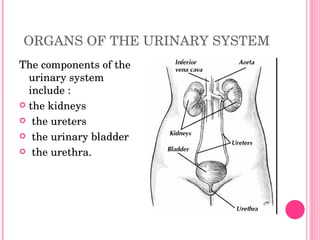
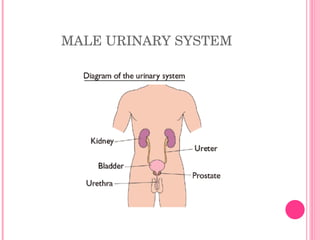
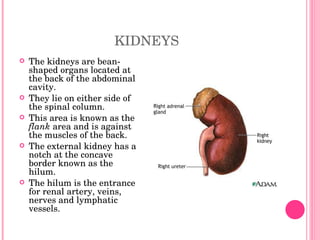
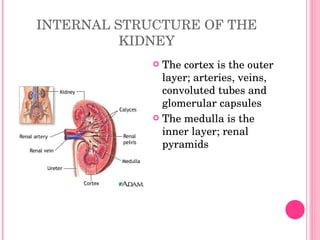
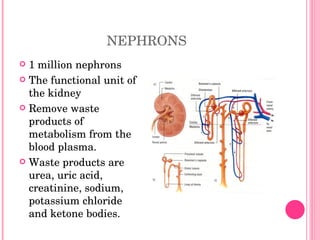
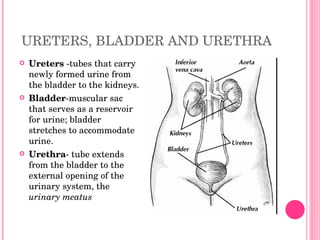
The urinary system consists of organs that produce and excrete urine from the body, including the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine and are located in the abdominal cavity. Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys that filter waste products from the blood to produce urine. Urine is stored in the bladder and exits the body through the urethra. Common disorders of the urinary system include cystitis, kidney stones, and urinary tract infections. The functions and structures of the urinary system change over the lifespan from childhood to older age.