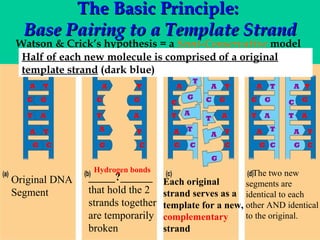
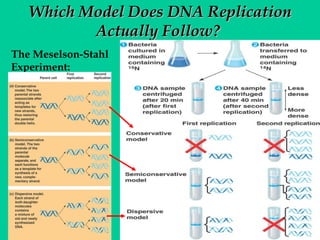
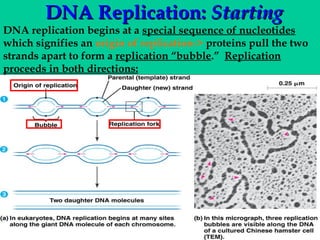
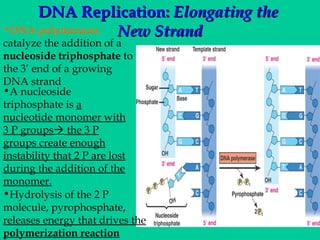
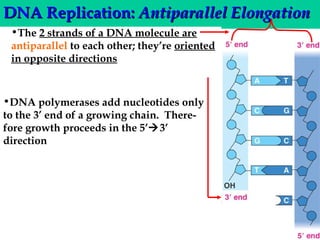
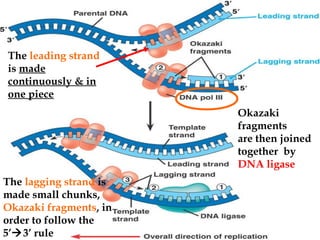
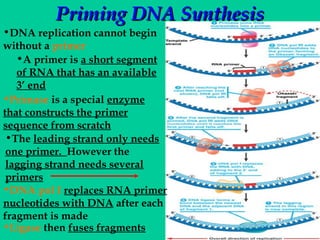
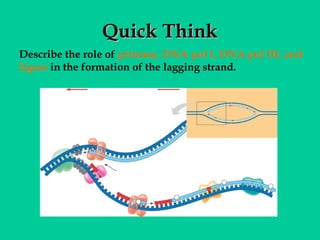
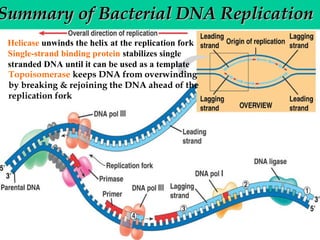
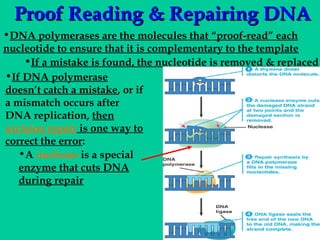
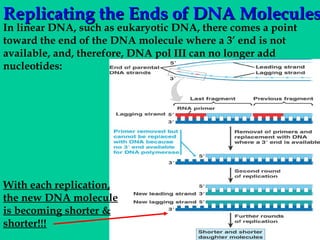
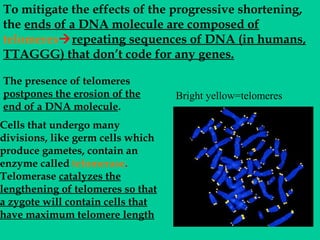
DNA replication involves several key proteins working together. The DNA double helix unwinds and each strand serves as a template to produce two new identical DNA molecules. Semi-conservative replication means each new molecule contains one original and one new strand. The lagging strand is replicated in fragments that are later joined together. DNA repair proteins proofread and correct any errors that occur during replication to maintain fidelity of the genetic code.