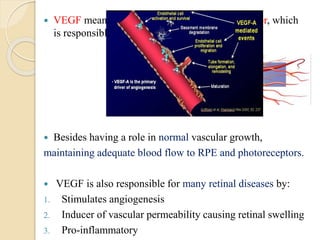
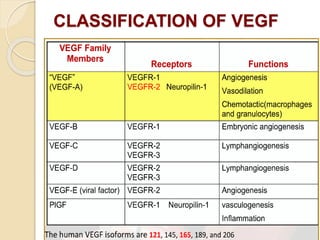
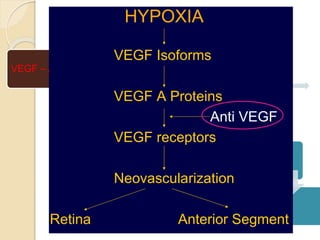
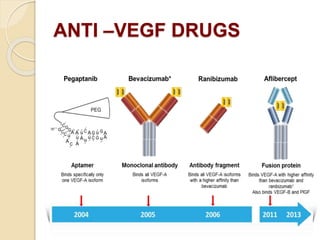
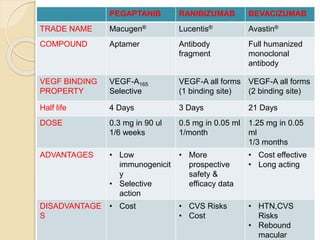
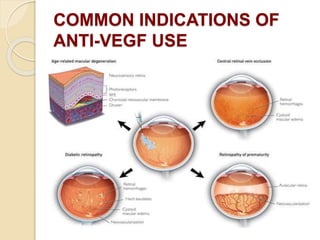
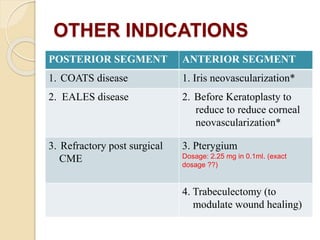
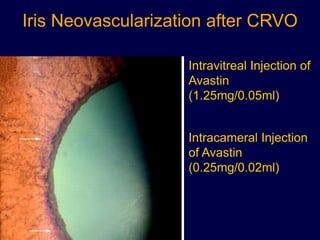
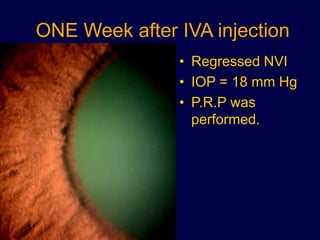
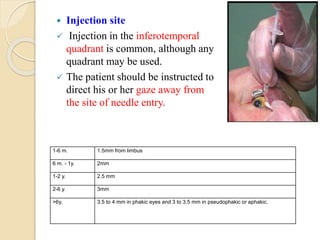
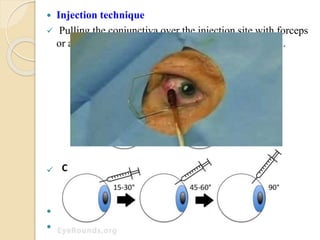
This document discusses anti-VEGF drugs used to treat retinal diseases caused by abnormal blood vessel growth stimulated by VEGF. It begins by explaining what VEGF is and its role in normal and abnormal angiogenesis in the retina. It then covers the major anti-VEGF drugs - pegaptanib, bevacizumab, ranibizumab, aflibercept - comparing their mechanisms of action, dosages, and indications. The document also discusses common adverse reactions and complications of intravitreal injections, as well as criteria for determining treatment response and failure. Overall, the document provides an overview of anti-VEGF drugs for retinal diseases, how they work, and their clinical use and monitoring.














![31
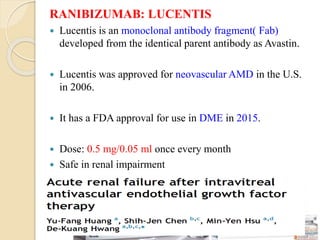
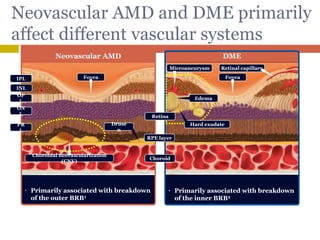
Structural changes observed1,2
• Retinal thickening
• Subretinal fluid accumulation
• Cystoid spaces
• Pigment epithelial detachment
• CNV
OCT of neovascular AMD
Structural changes observed3,4
• Retinal swelling (thickening)
• Cystoid macular edema
• Serous retinal detachment
• Vitreomacular traction
• Hard exudates
OCT of DME
Differences in neovascular AMD and
DME are evident from OCT images
1. Liakopoulos S et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008;49:5048–5054
2. The Royal College of Ophthalmologists. AMD: guidelines for management. 2009.
http://www.rcophth.ac.uk/docs/publications/AMD_GUIDELINES_FINAL_VERSION_Feb_09.pdf [accessed Sep 2009]
3. Bhagat N et al. Surv Ophthalmol 2009;54:1–32
4. Lang GE. In Developments in ophthalmology. 2007. p31–47
Retina
RPE layer
Choroid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anti-vegf-170509120304/85/Anti-VEGF-Facts-Myths-31-320.jpg)