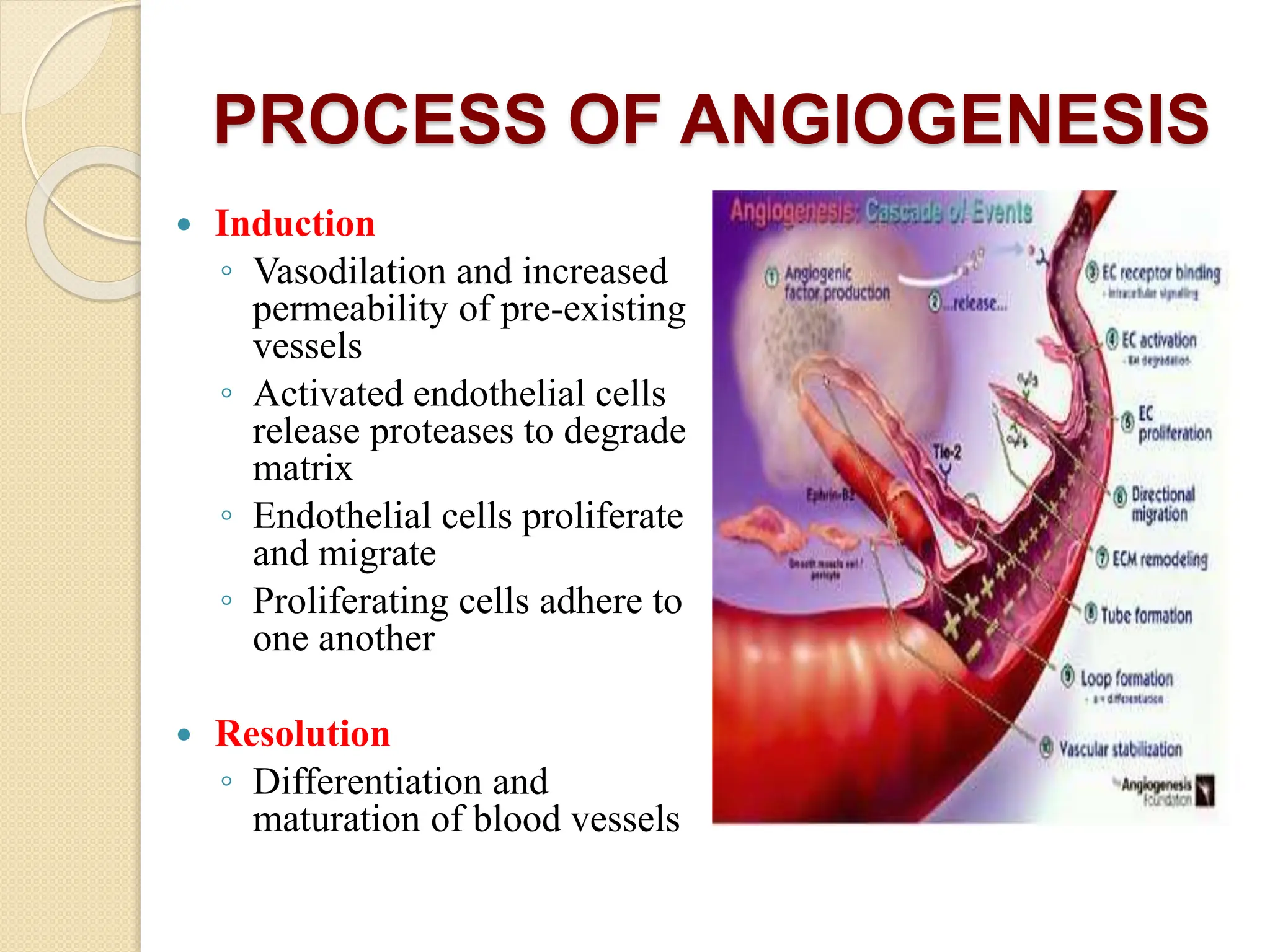
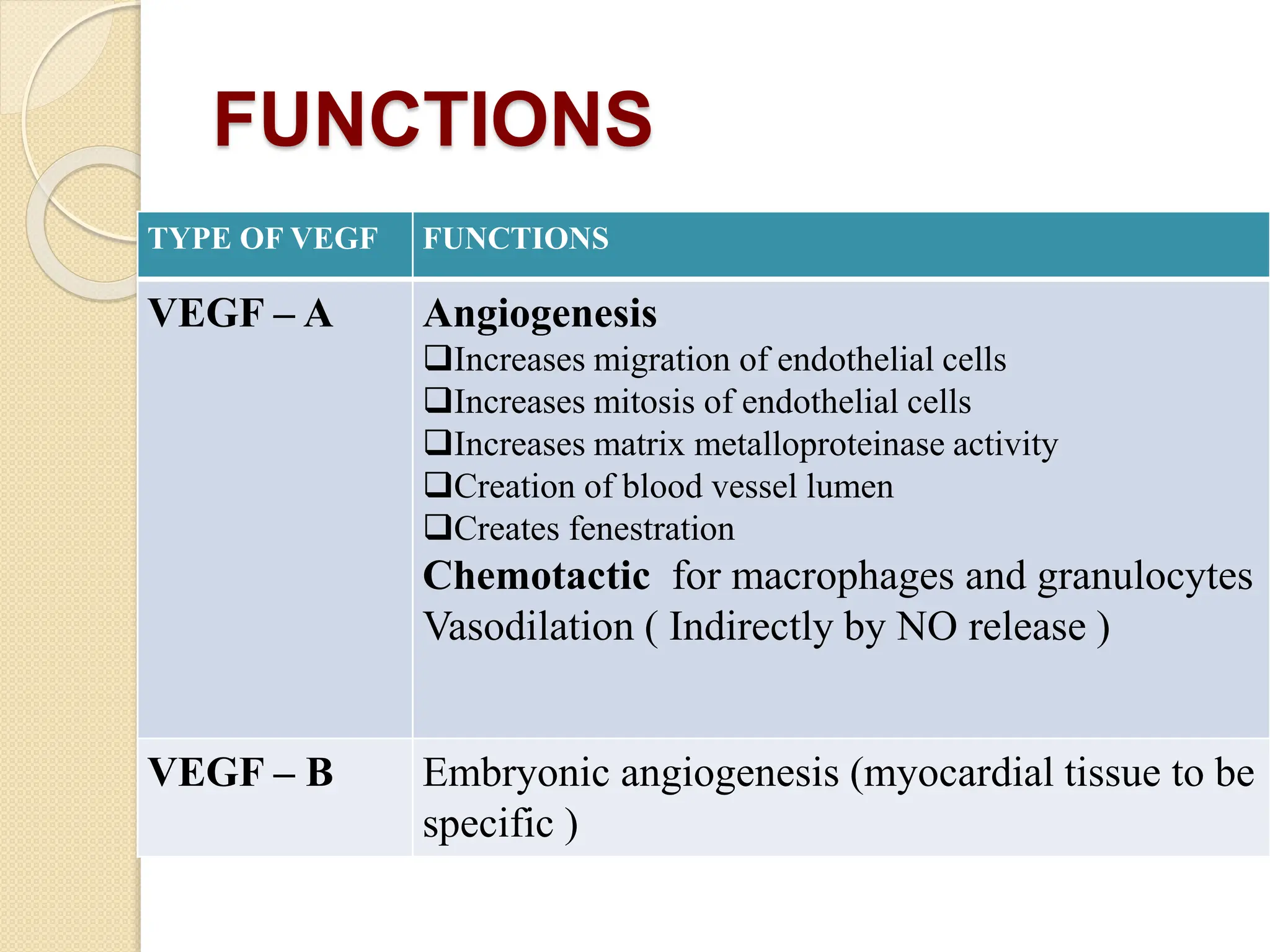
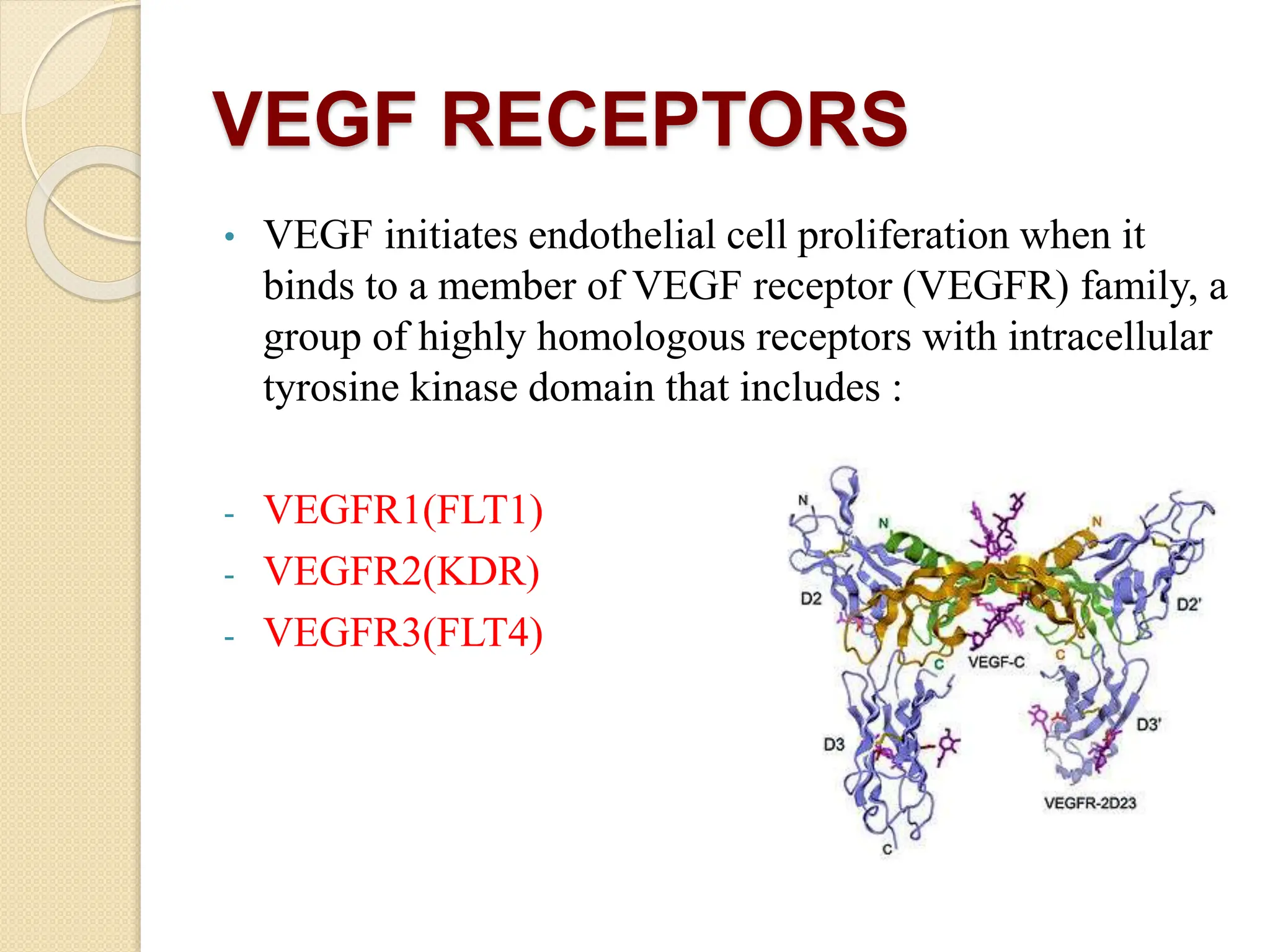
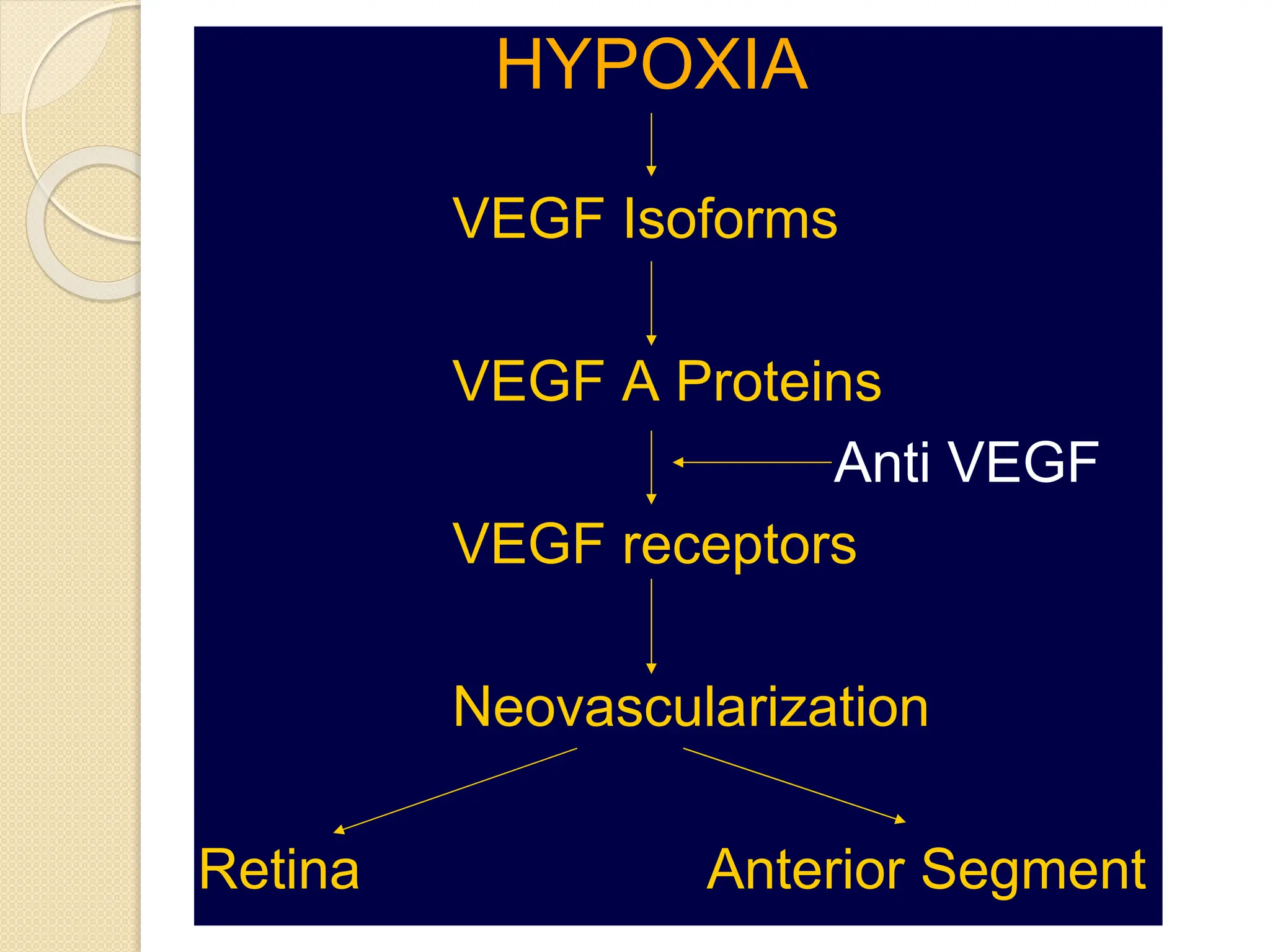
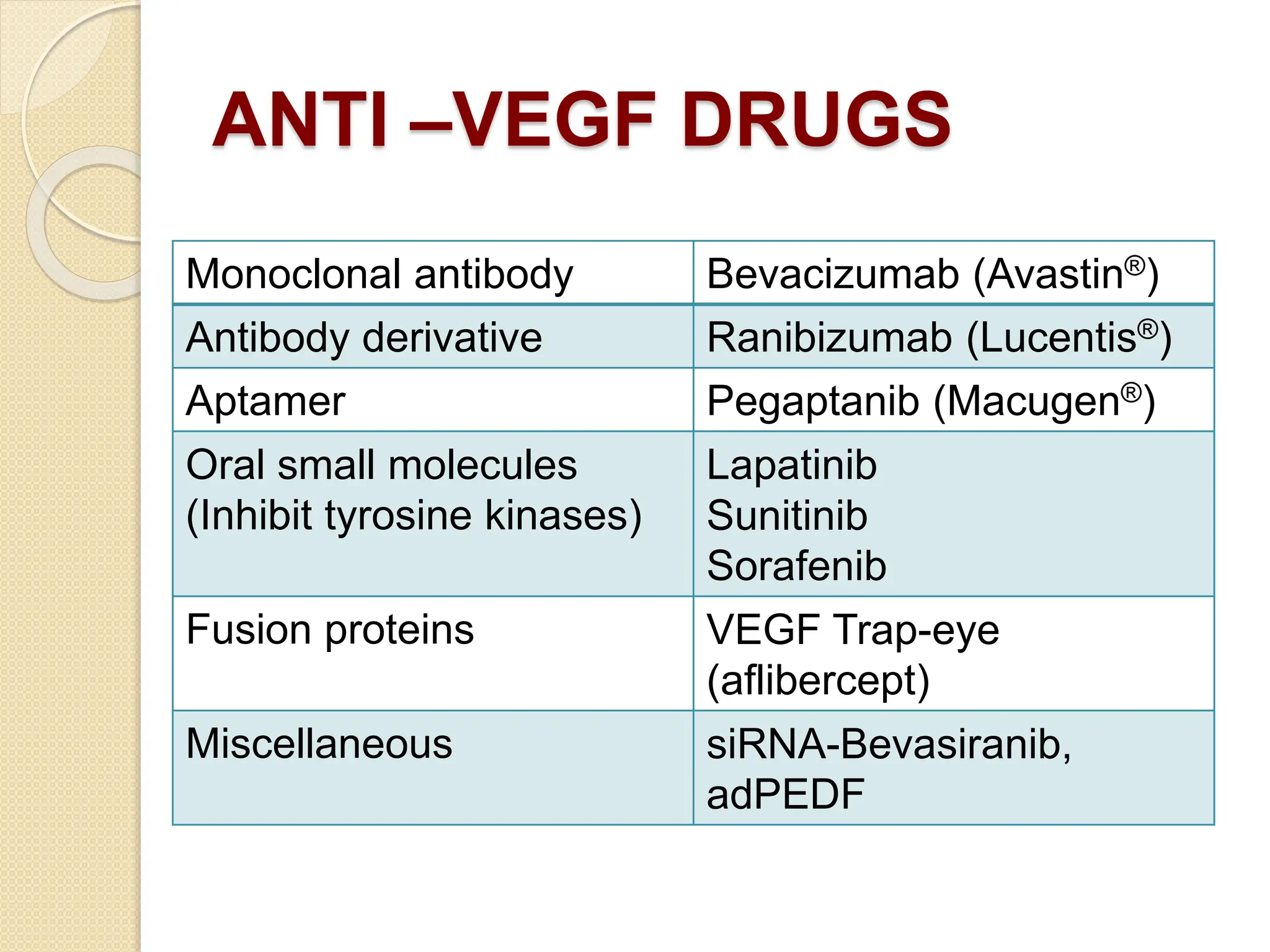
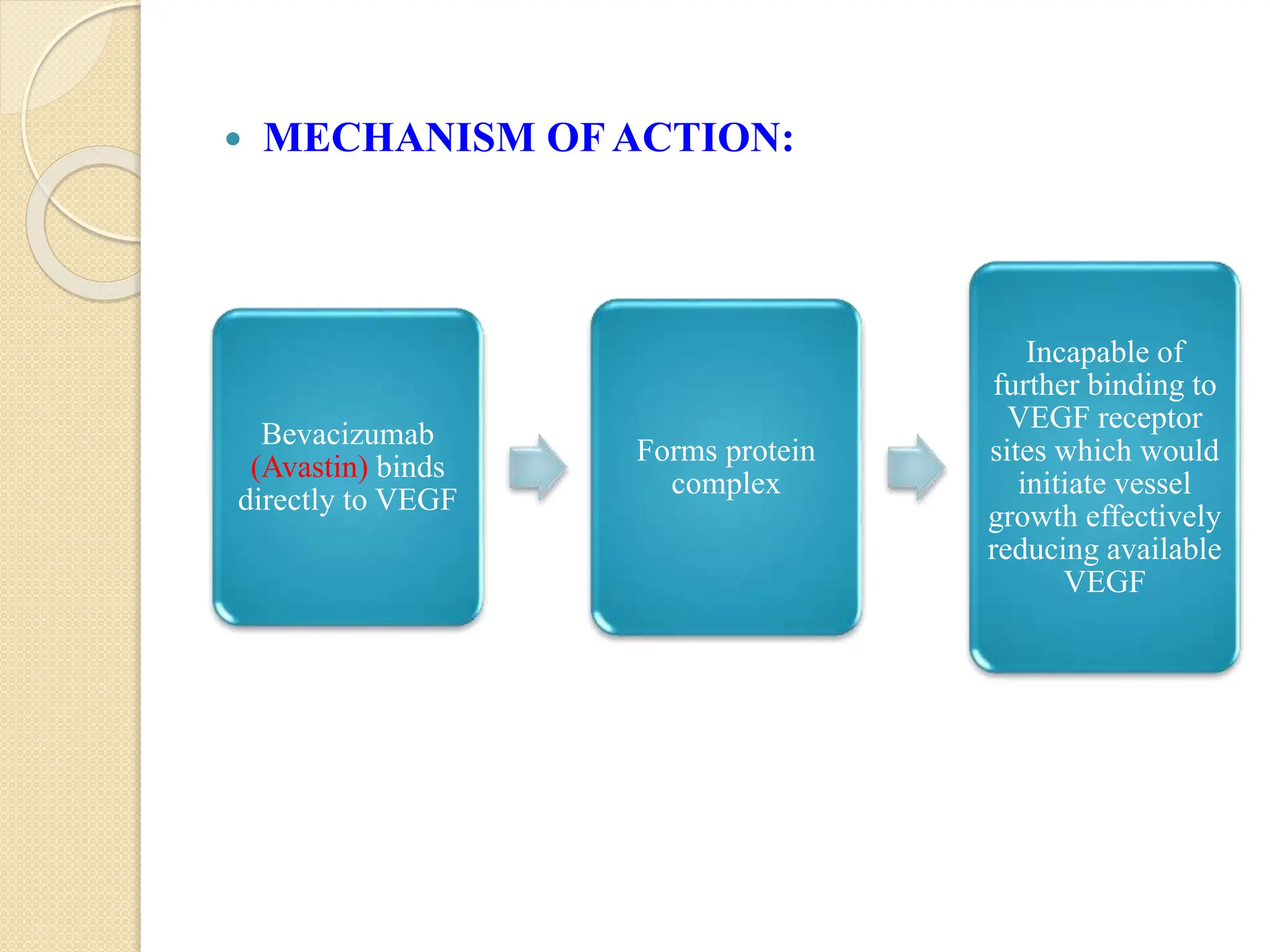
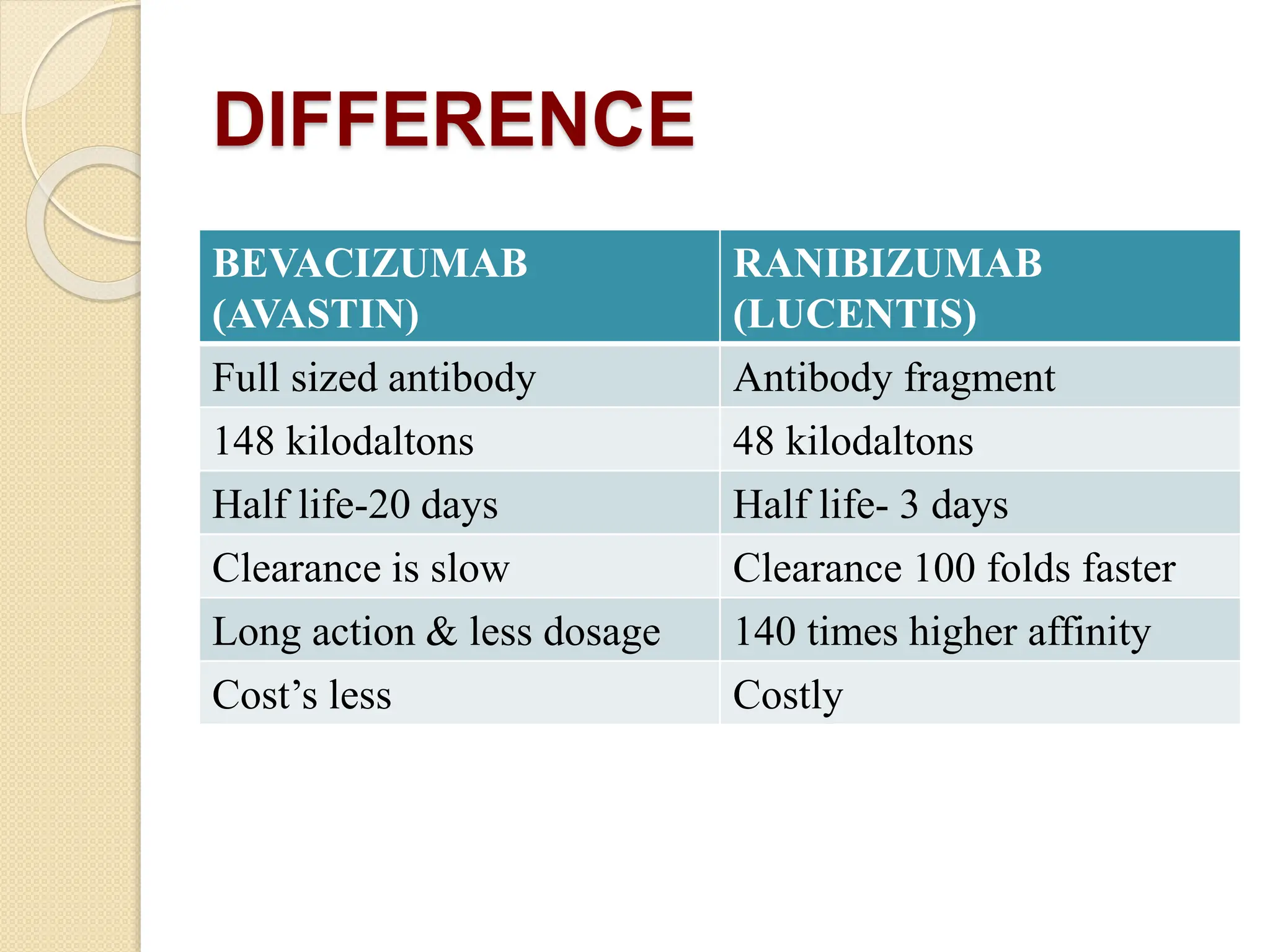
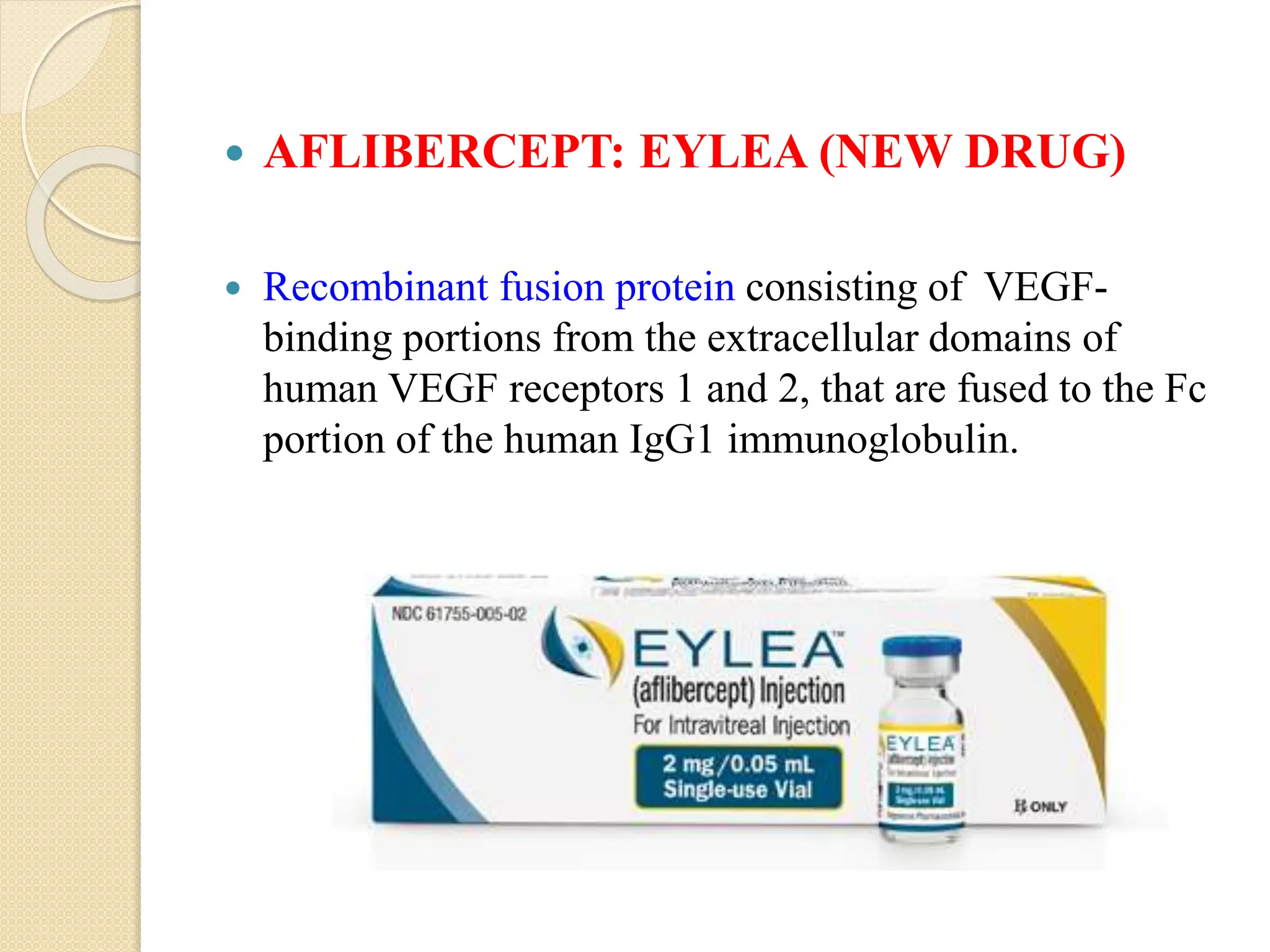
VEGF is a protein that stimulates blood vessel growth and increases permeability. It plays a role in retinal diseases by causing abnormal new vessel growth and retinal swelling. Anti-VEGF drugs work by blocking VEGF, thereby reducing vessel growth and leakage. Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits VEGF and is commonly used off-label via intravitreal injection to treat wet age-related macular degeneration and other retinal conditions associated with abnormal vessel growth and leakage. While effective, it carries risks of adverse events like bleeding and high blood pressure.