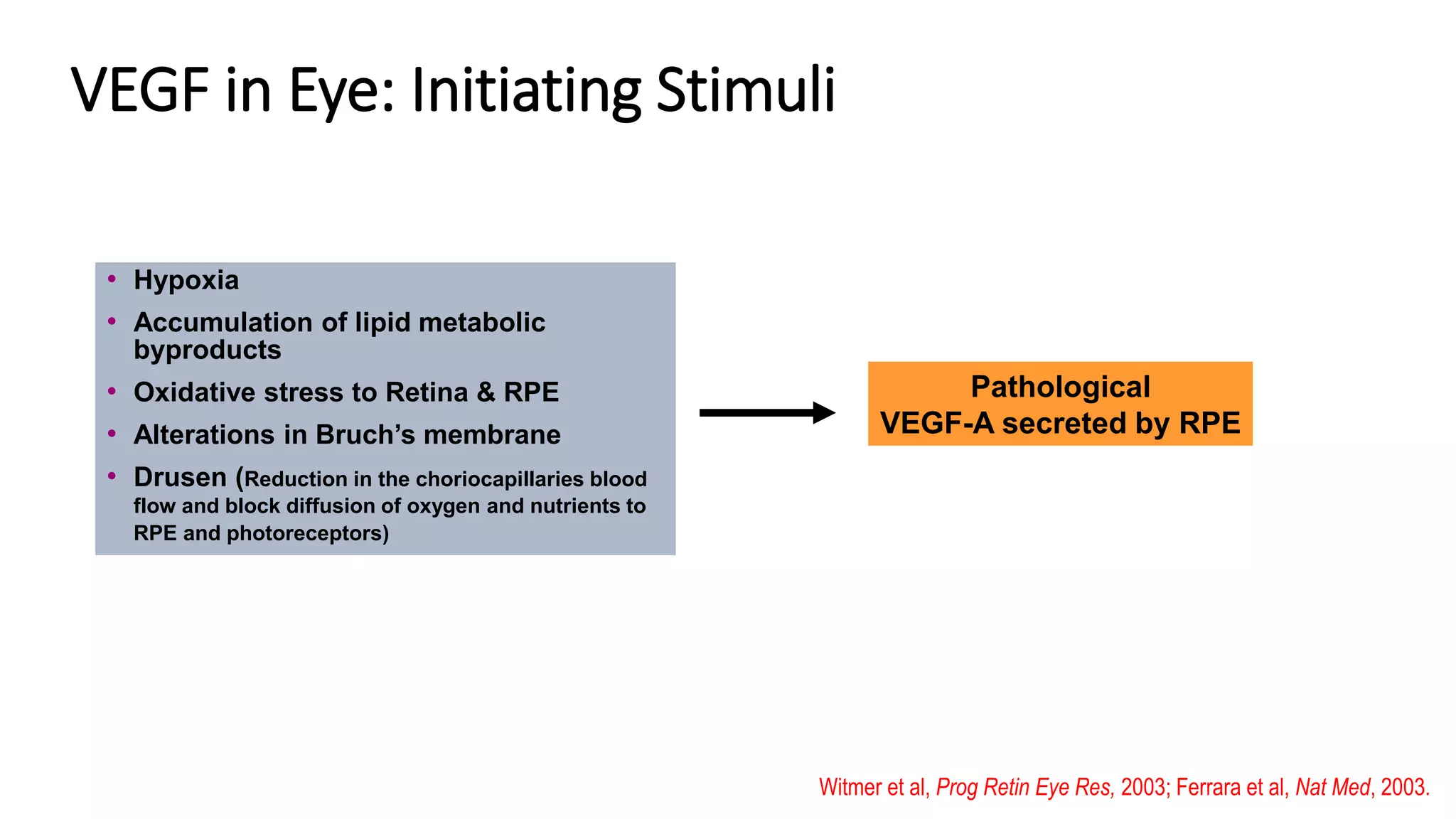
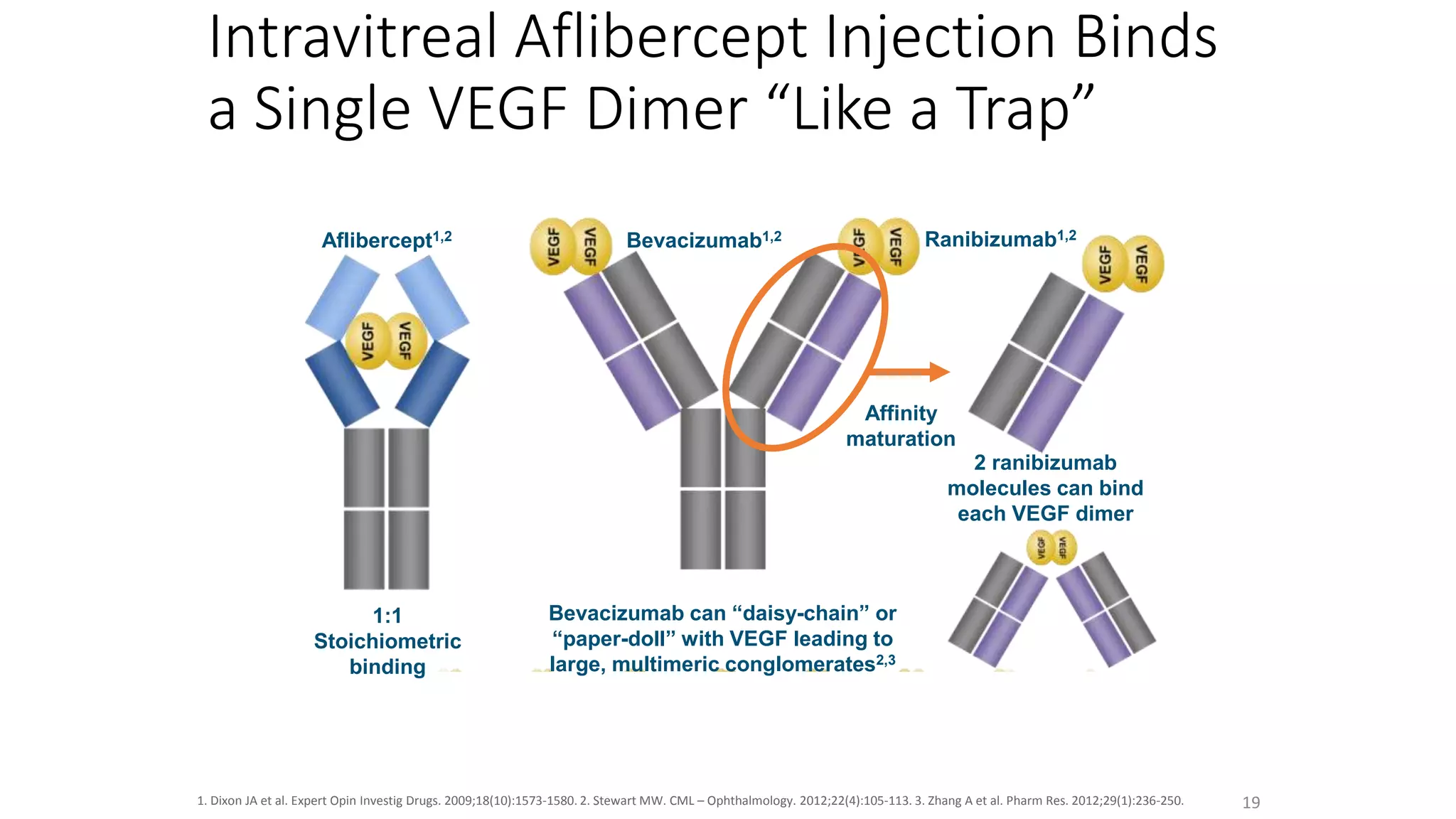
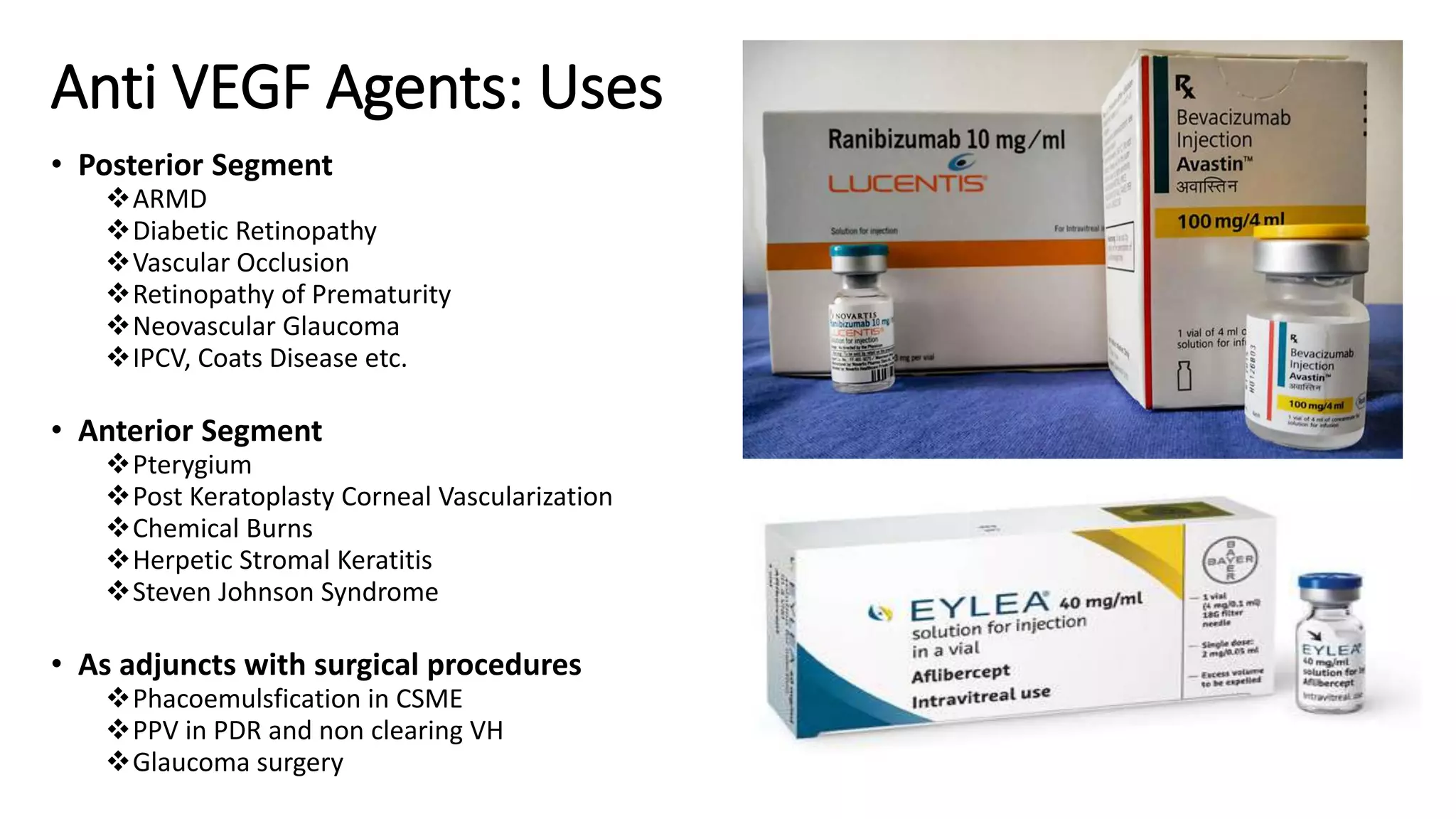
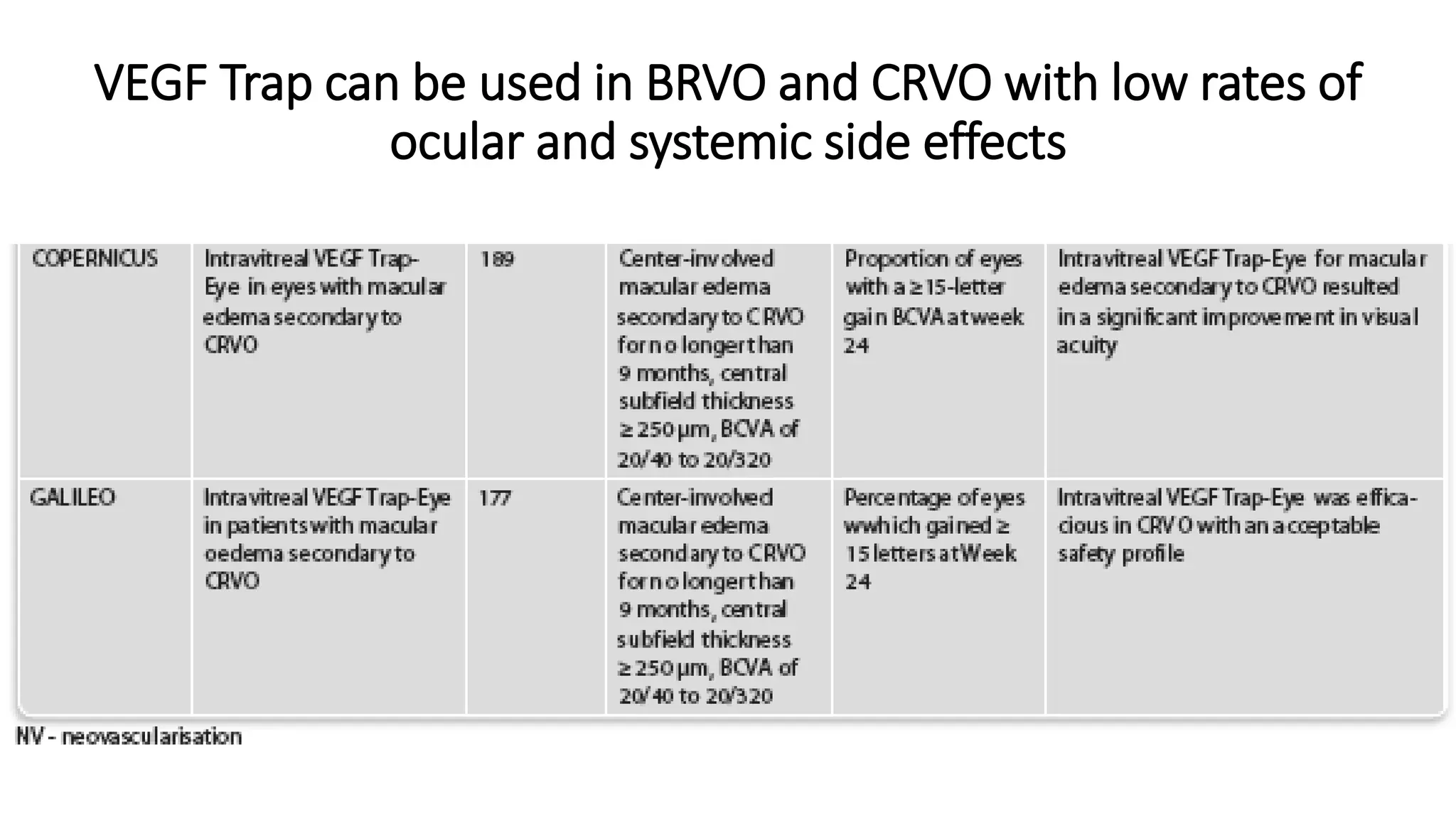
Anti-VEGF agents such as bevacizumab, ranibizumab, pegaptanib, and aflibercept are used to treat retinal diseases caused by abnormal blood vessel growth due to VEGF overexpression. They work by inhibiting VEGF to prevent new blood vessel proliferation and leakage. Common uses include treating wet age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusions, and retinopathy of prematurity. Ranibizumab and aflibercept are approved by the FDA, while bevacizumab is commonly used off-label. Monthly intravitreal injections are typically required initially, then treatments are extended based on disease response. Adverse events include inflammation, increased intraocular pressure, and