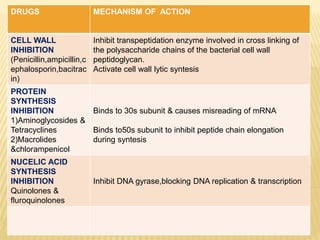
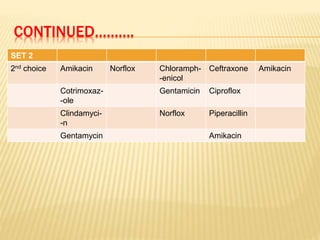
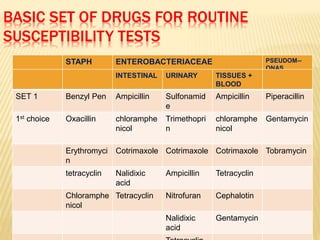
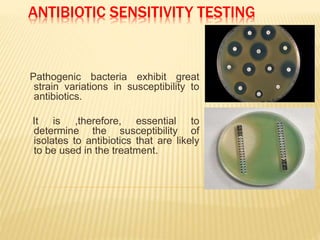
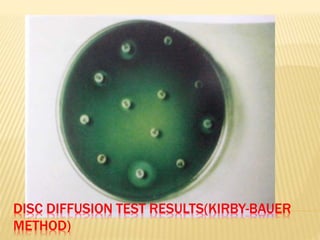
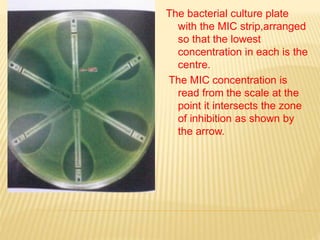
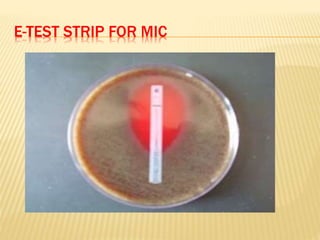
This document discusses antimicrobial therapy and drug sensitivity testing. It begins with the historical discoveries of antimicrobial drugs by Ehrlich, Domagk, and Fleming. It then describes the properties of antimicrobial drugs and their mechanisms of action, which include inhibiting cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis, and disrupting cell membranes. Common methods for determining drug sensitivity are also summarized, such as diffusion methods like Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion and dilution methods involving broth or agar. Control strains, testing mediums, and interpreting zone sizes are also outlined. The document provides an overview of the evaluation of antimicrobial sensitivity.