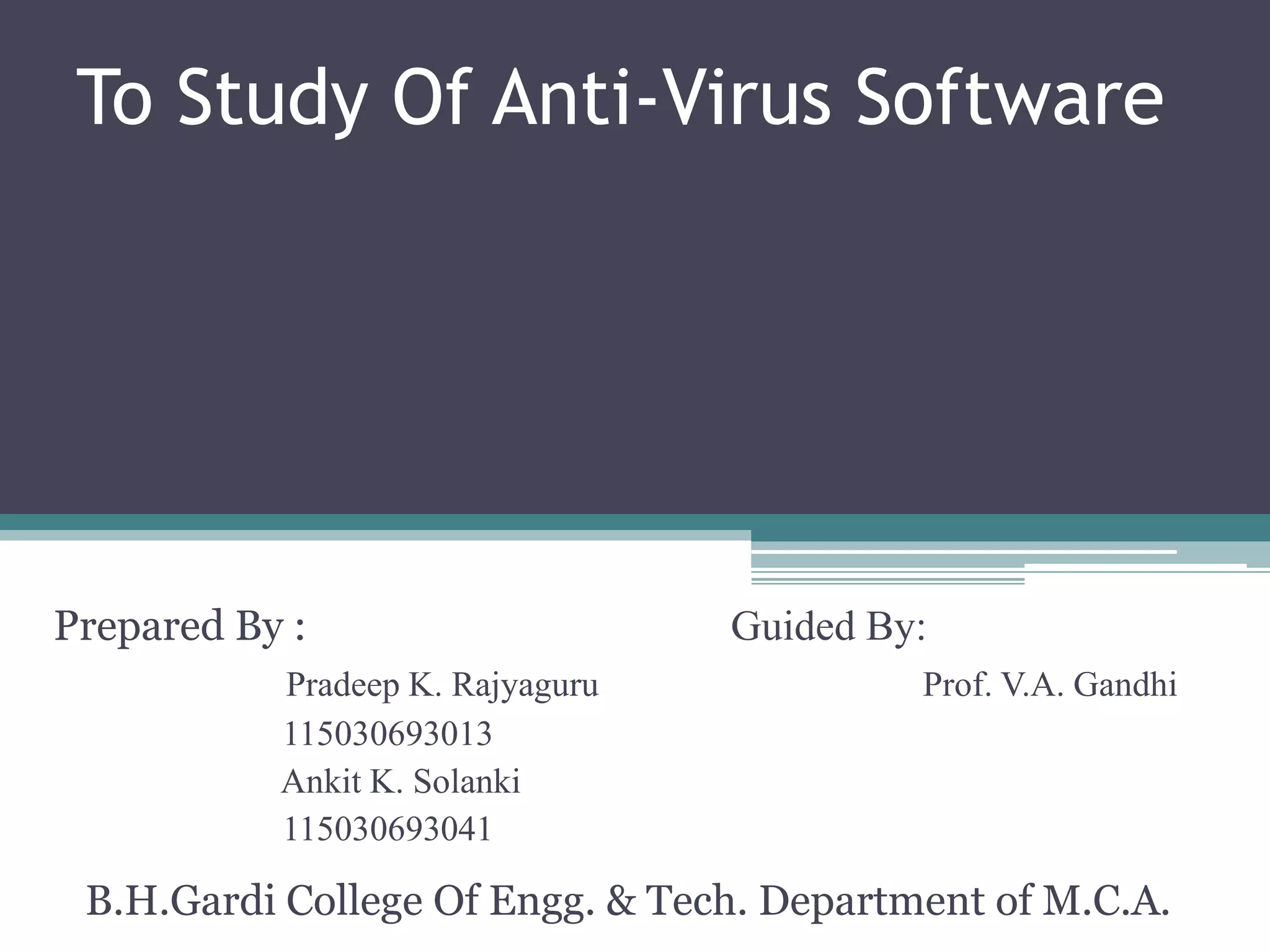
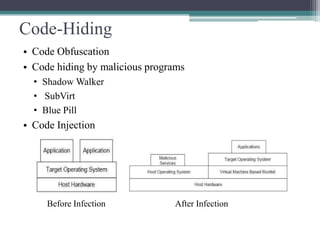
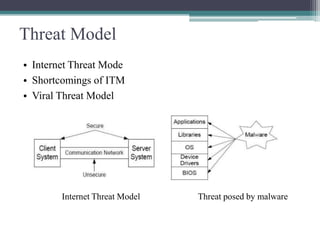
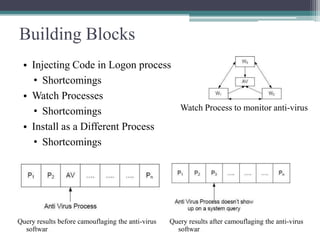
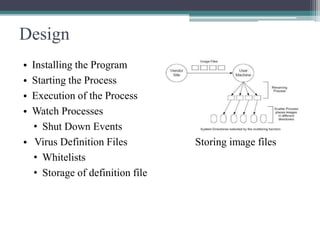
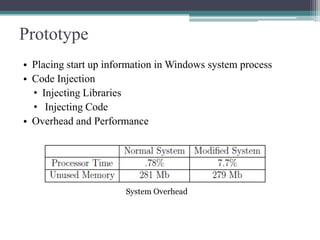
This document summarizes a study on anti-virus software. It discusses various types of malware threats like viruses, worms, and trojans. It also covers different types of attacks and how anti-virus software works using techniques like signature detection, emulation, and heuristics. The document outlines the design of a prototype that aims to improve anti-virus reliability by hiding its presence on a system through techniques like code injection, changing file names and registry entries, and migrating processes to avoid detection. The goal is to create an anti-virus that can evade malware and continue running even if a system is compromised.