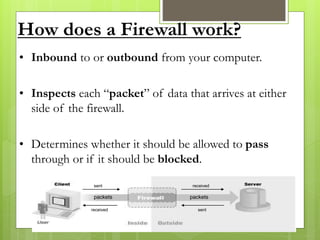
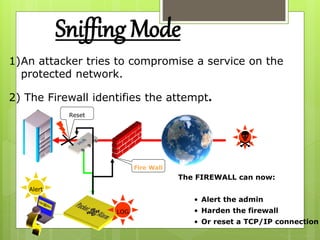
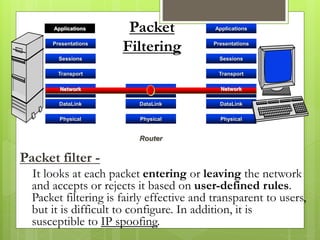
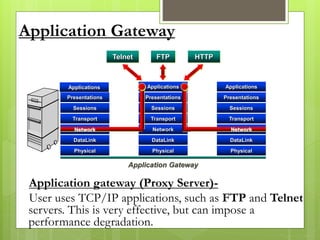
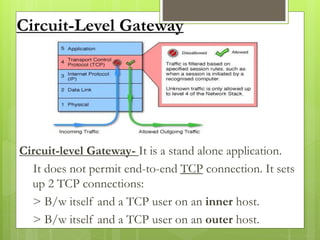
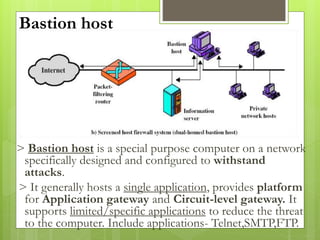
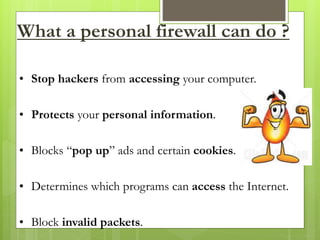
The document provides an overview of computer viruses, describing what they are, their history, types, and methods of spreading, including macro and polymorphic viruses. It also discusses antivirus software, its functionality, and notable programs like Norton and McAfee, alongside how firewalls work to secure networks from unauthorized access. Furthermore, it delineates the capabilities and limitations of personal firewalls and antivirus software, emphasizing the need for continual updates and vigilance against potential threats.