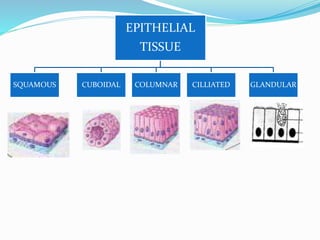
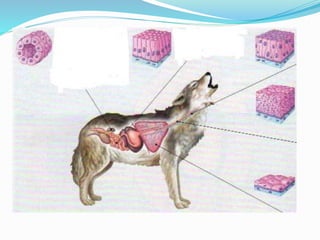
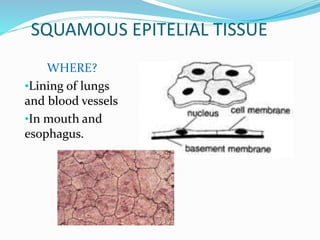
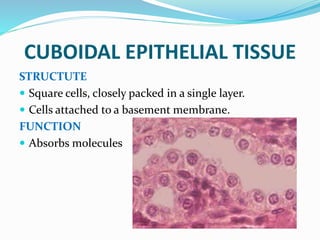
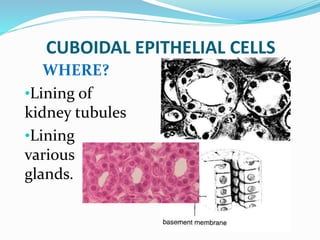
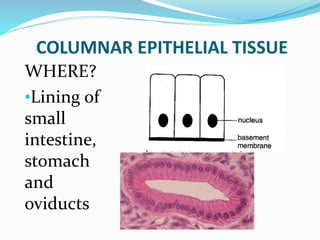
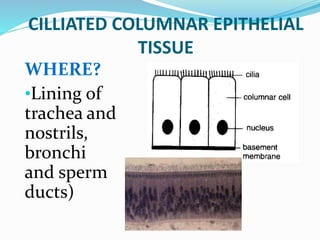
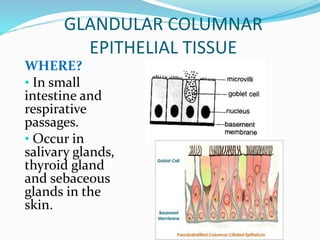
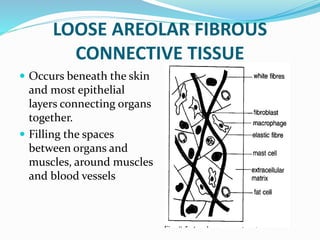
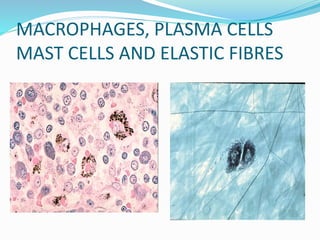
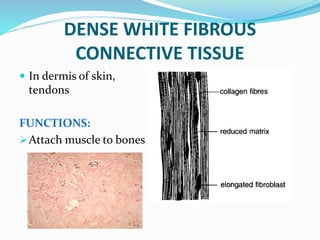
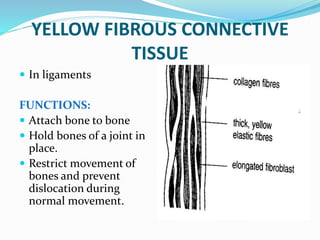
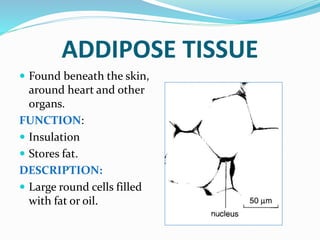
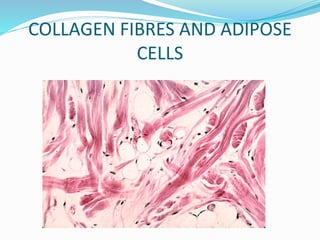
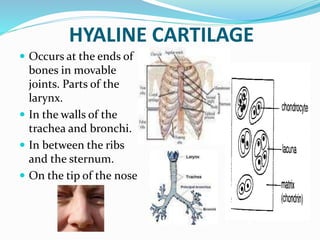
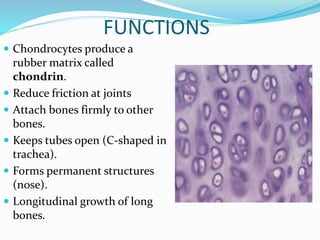
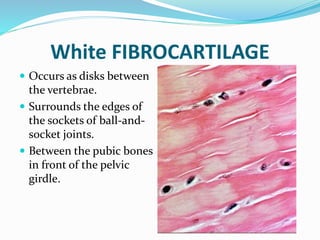
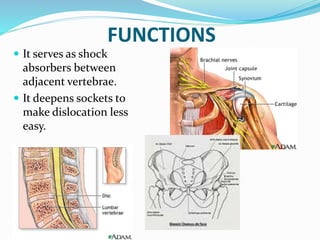
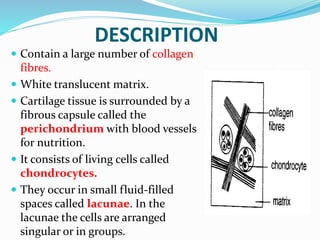
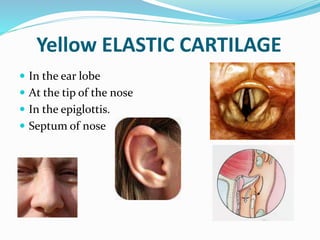
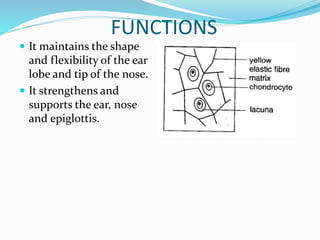
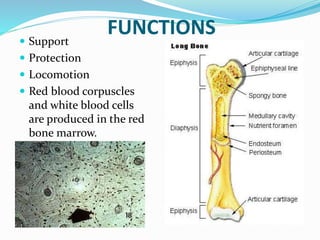
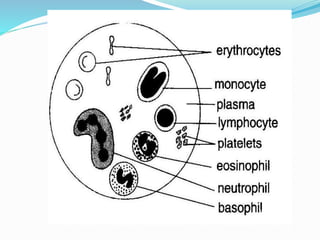
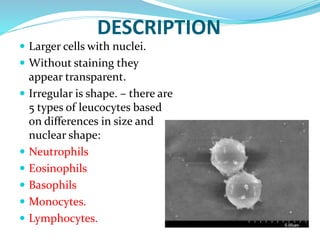
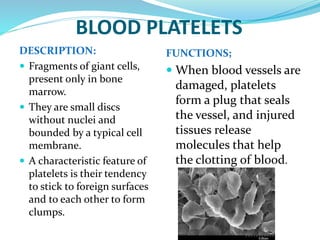
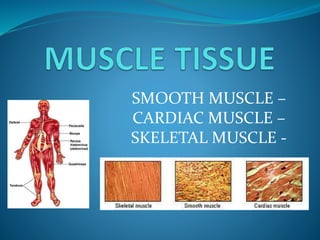
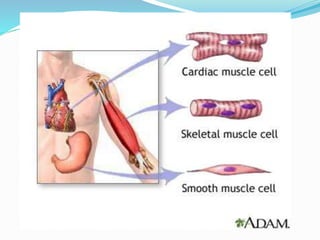
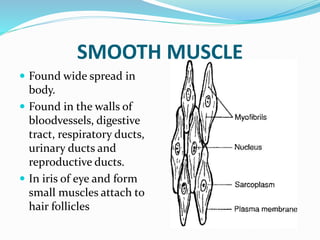
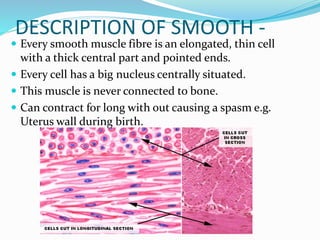
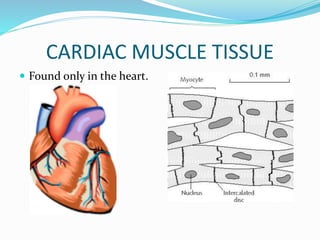
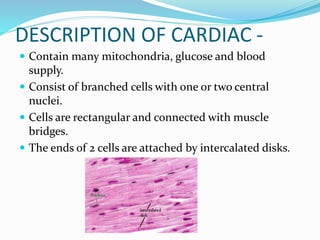
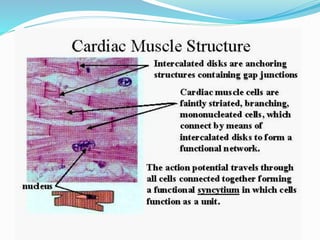
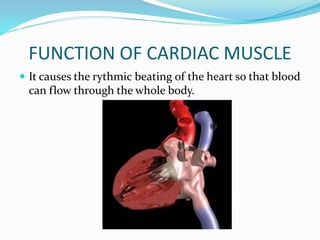
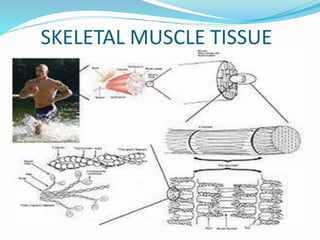
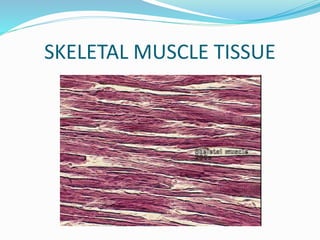
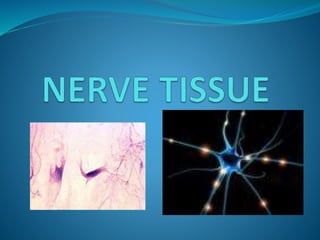
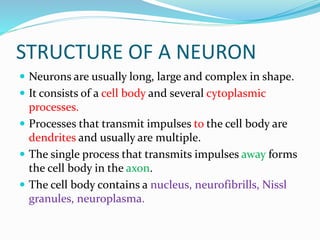
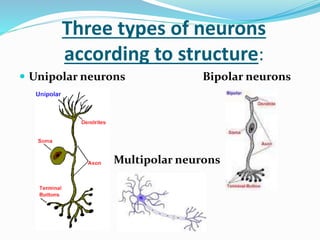
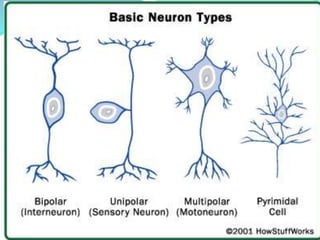
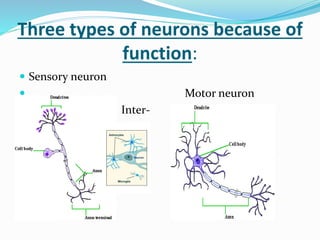
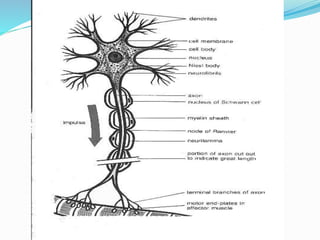
This document provides information about animal tissues. It begins by explaining how tissues fit into the hierarchy of living organisms, from single cells to complex multicellular organisms. The major types of tissues - epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue - are then introduced. The remainder of the document delves into specific examples of each tissue type, describing their structure, location in the body, and functions. Key tissue examples discussed include squamous, cuboidal, columnar and glandular epithelial tissues, as well as areolar, dense and adipose connective tissues, cartilage, bone and the three main muscle tissues.