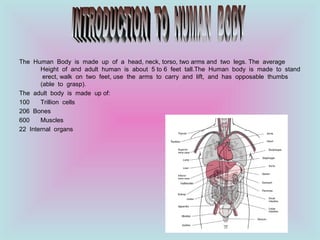
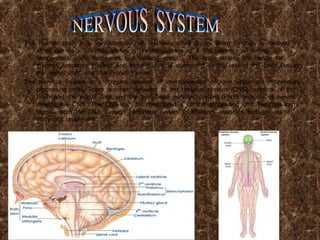
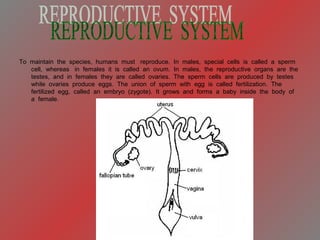
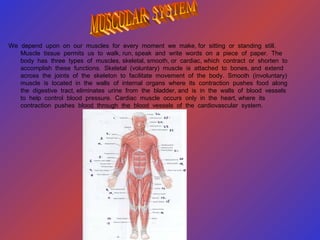
The document provides an overview of the human body, including its structure, functions, and major systems such as the circulatory, respiratory, nervous, reproductive, skeletal, and muscular systems. It highlights key components like the cells and their functions, the digestive process, and the significance of organs, along with explanations of how these systems interact to sustain life. Additionally, it includes questions and answers related to human anatomy and physiology.