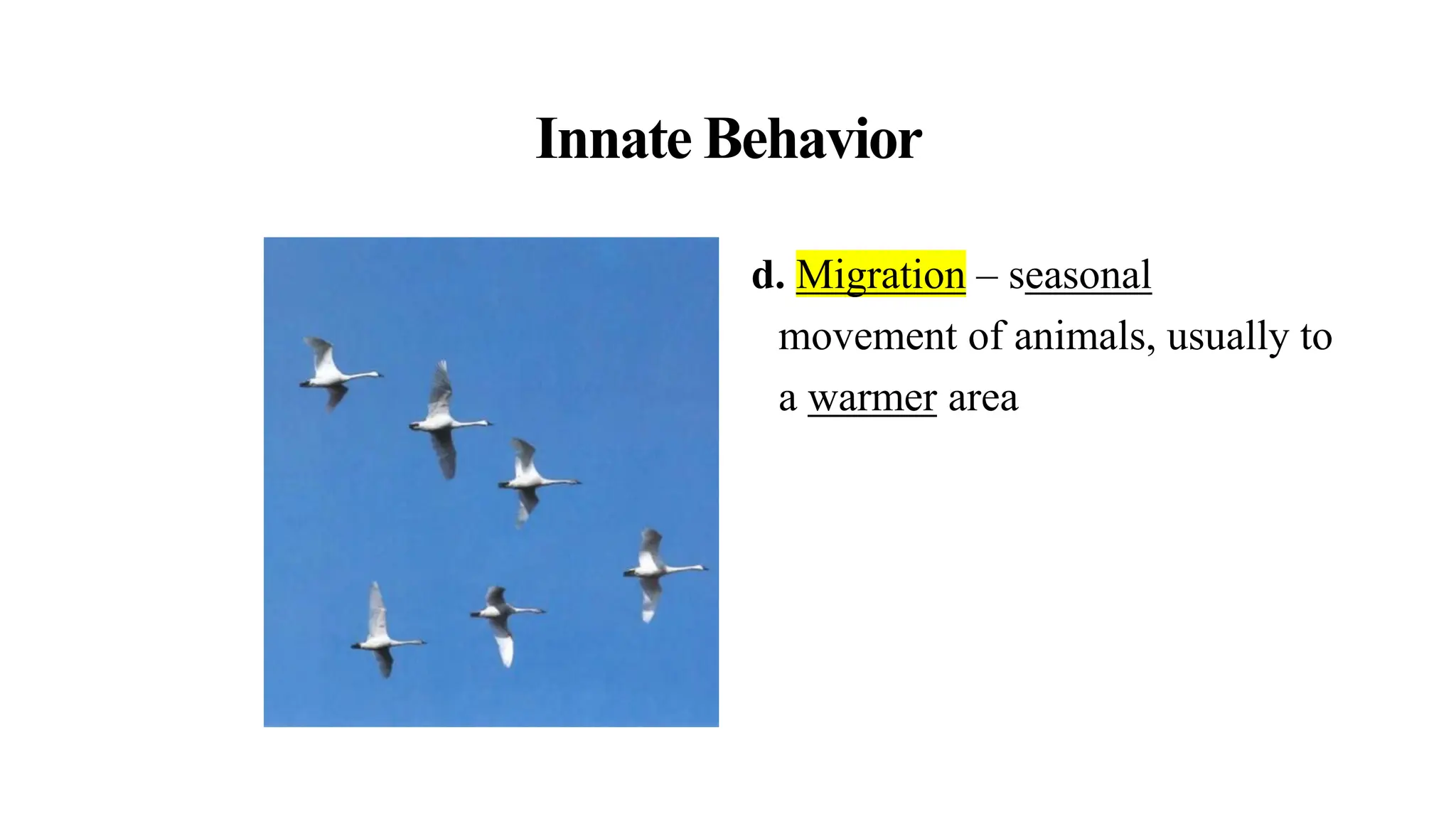
This document discusses animal behavior and defines it as actions performed by animals in response to stimuli. It describes three main types of behavior: innate behaviors that are genetically determined, learned behaviors acquired through experience, and social behaviors related to communication and interactions within a species. Innate behaviors include reflexes, instincts, taxes, migration, estivation and hibernation. Learned behaviors involve habituation, imprinting, classical conditioning, and trial and error. Social behaviors encompass communication through pheromones, courtship dances, and territorial defense.