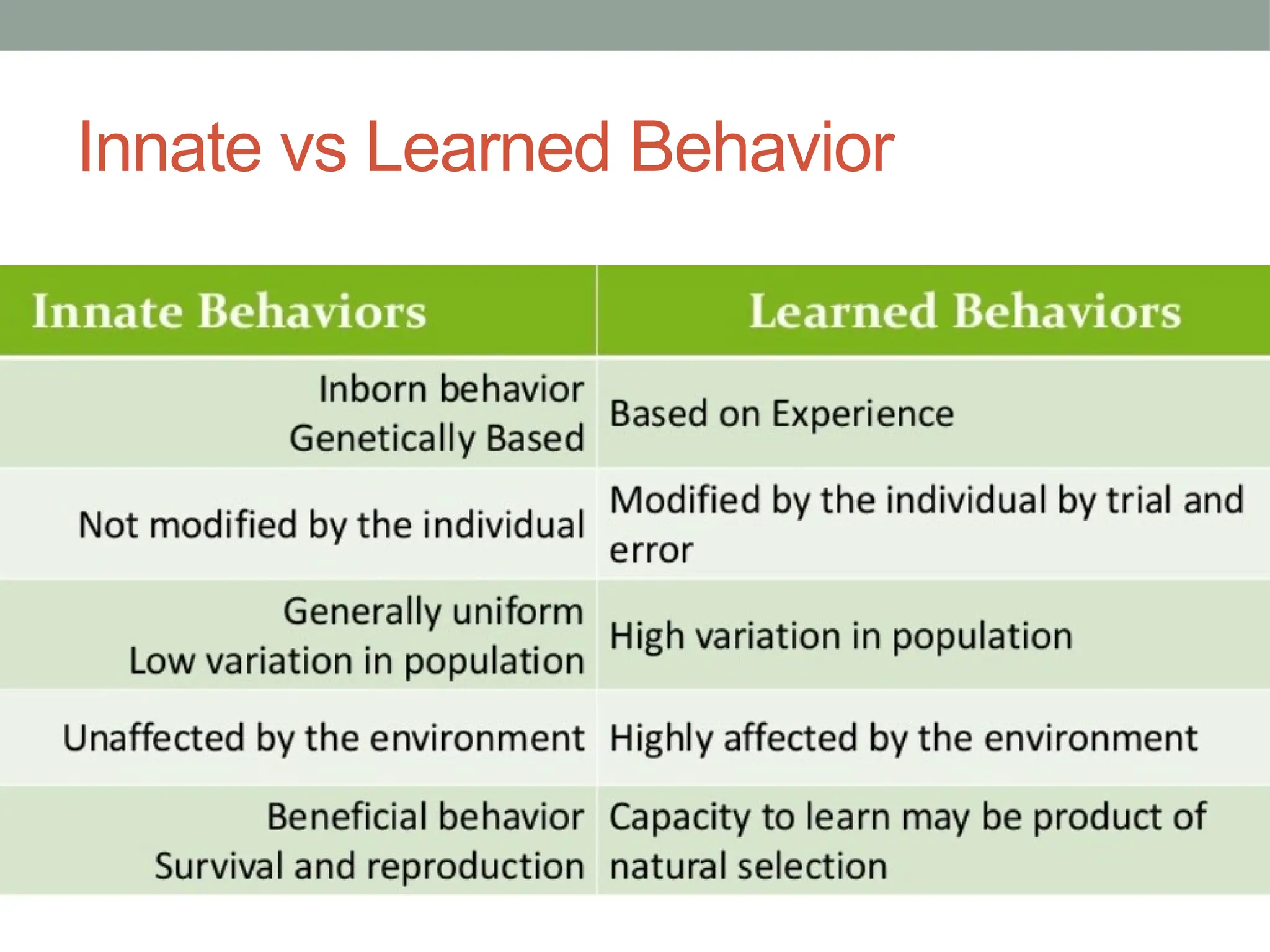
There are two main types of animal behavior: innate behavior, which is instinctive and genetically hardwired, and learned behavior, which develops through experience. Innate behaviors, such as web-making in spiders or nest-building in birds, occur naturally in all species members without prior learning and include categories like kinesis, taxis, reflexes, and fixed action patterns. Examples of innate behavior demonstrate how animals instinctively respond to stimuli, like baby turtles heading for the sea or honeybees performing a 'dance' to communicate food sources.