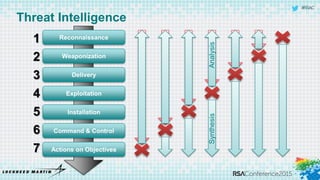
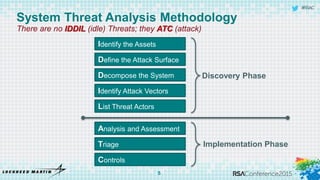
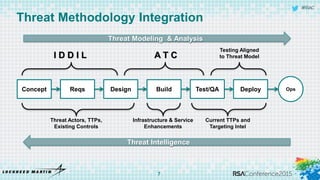
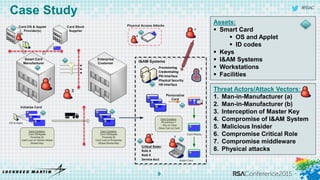
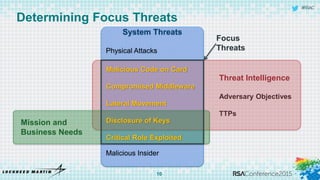
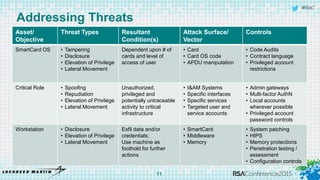
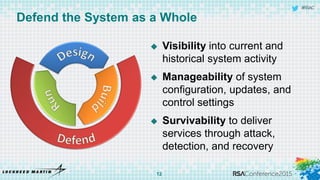
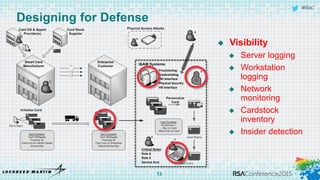
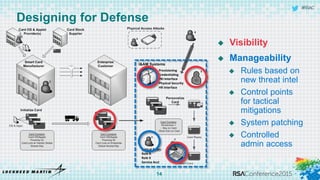
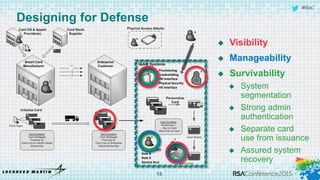
The document discusses using threat-driven methodologies to achieve defendable system architectures. It describes a threat analysis methodology that involves identifying assets, attack vectors, threat actors, and controls. A case study applies this methodology to analyze threats to a smart card system. Key threats are identified and addressed through controls that focus on visibility, manageability, and survivability of the system. The presentation emphasizes starting with threat intelligence and analysis to select appropriate protections and designing systems to be defended.