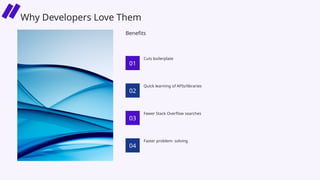
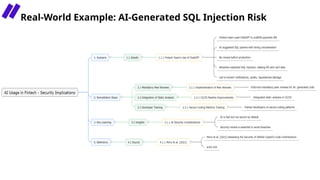
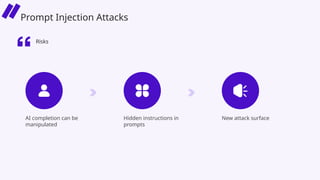
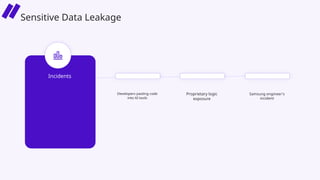
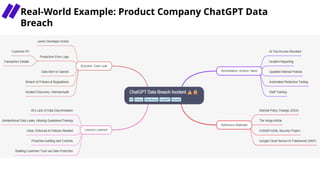
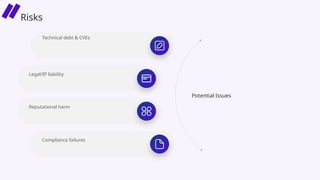
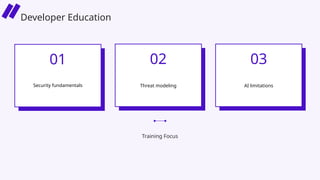
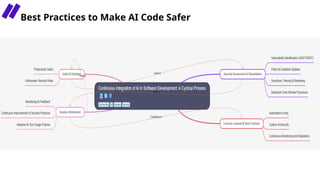
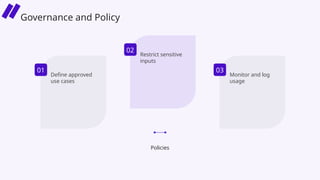
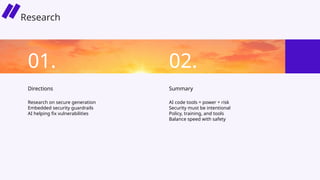
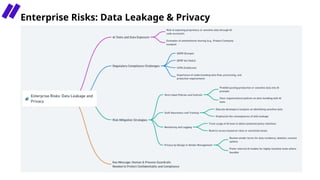
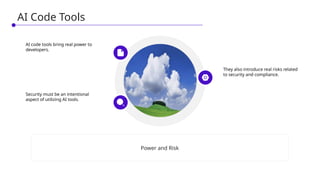
In this session, we’ll explore how security leaders can navigate the risks of AI-generated code, implement secure development guardrails, and strike the right balance between innovation and security. AI is prediction, not understanding — making security review essential. We’ll also discuss the importance of having the right policies, training, and tooling in place to manage trust, validate outputs, and prepare for emerging threats.