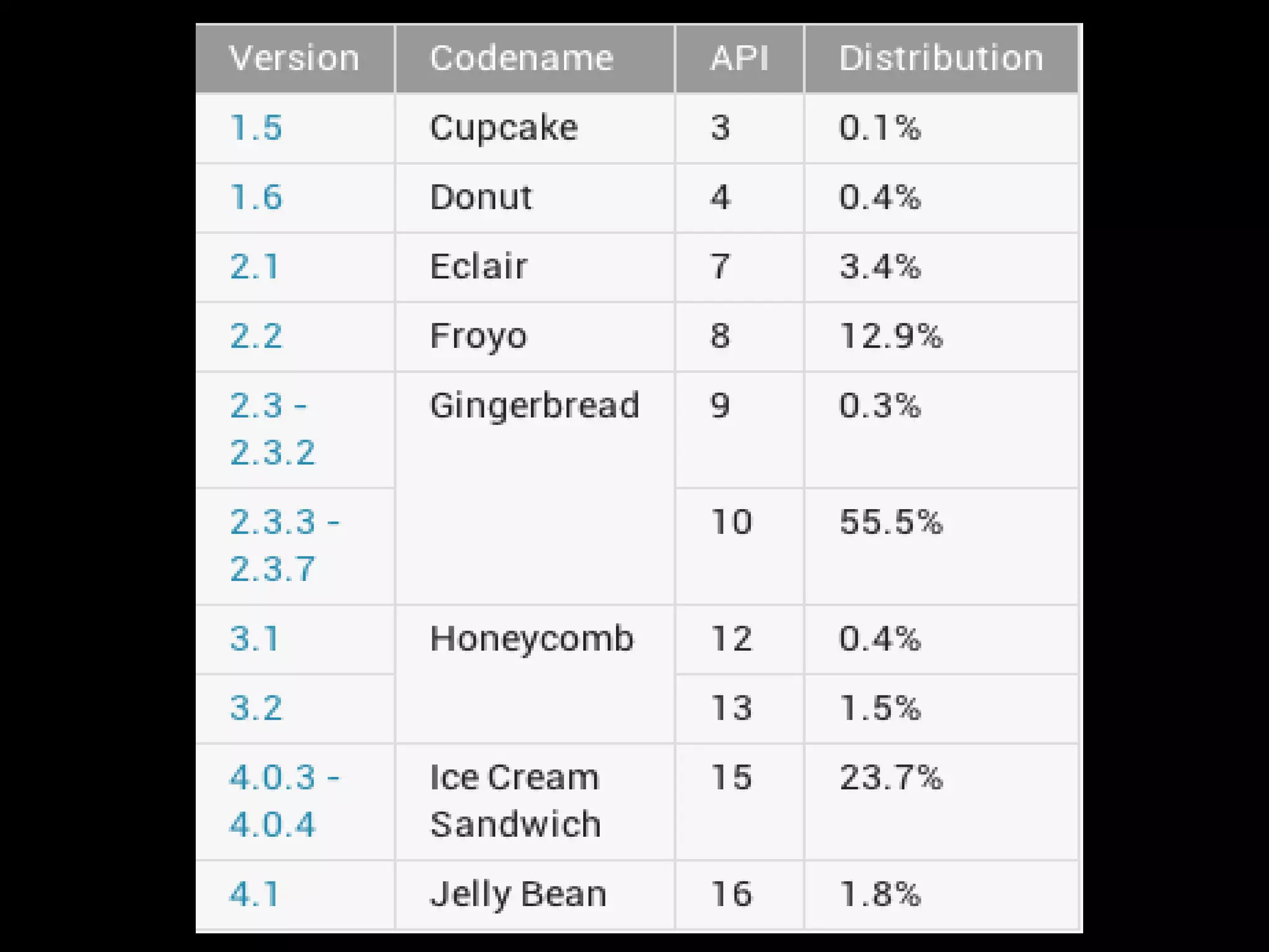
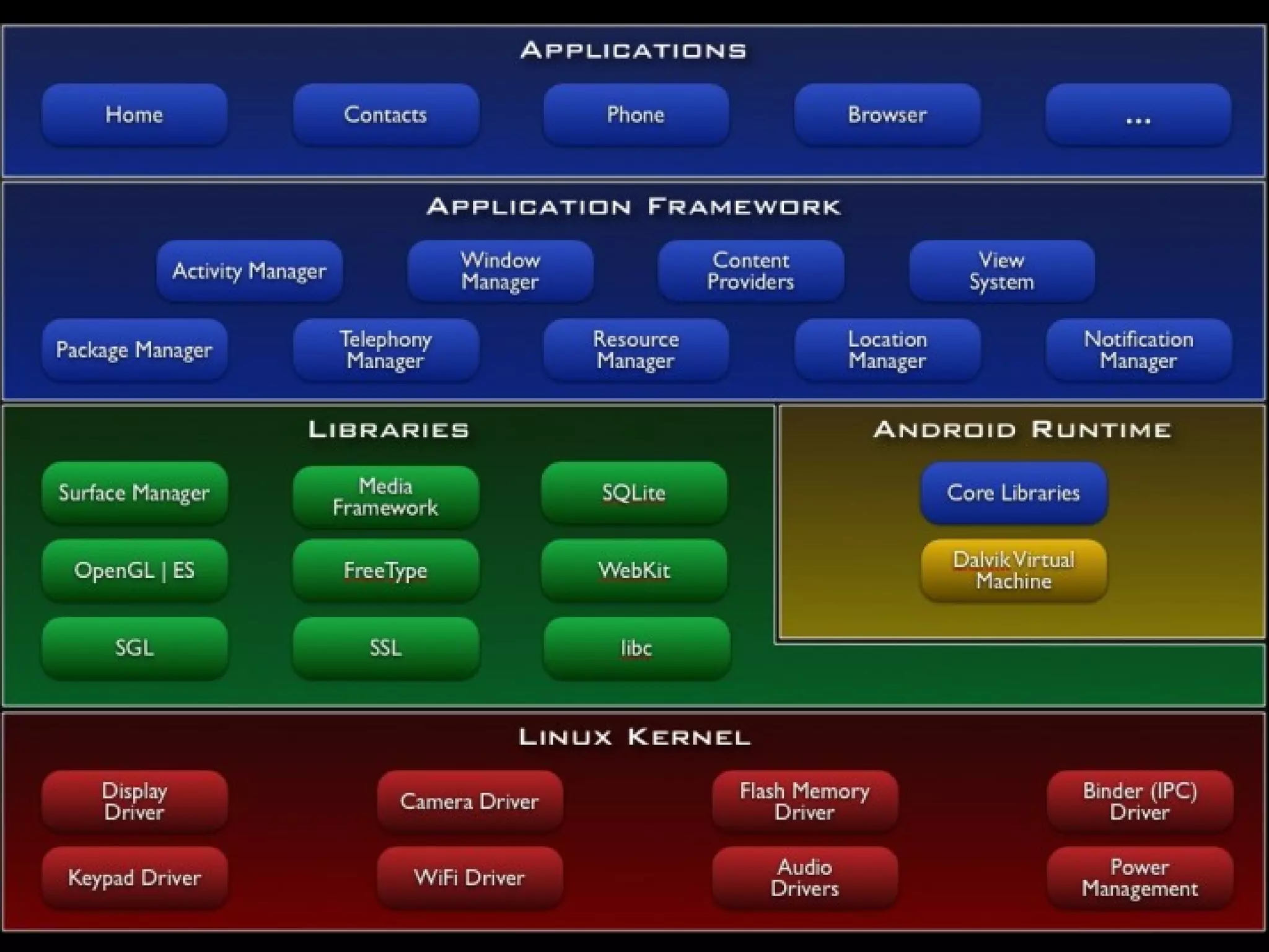
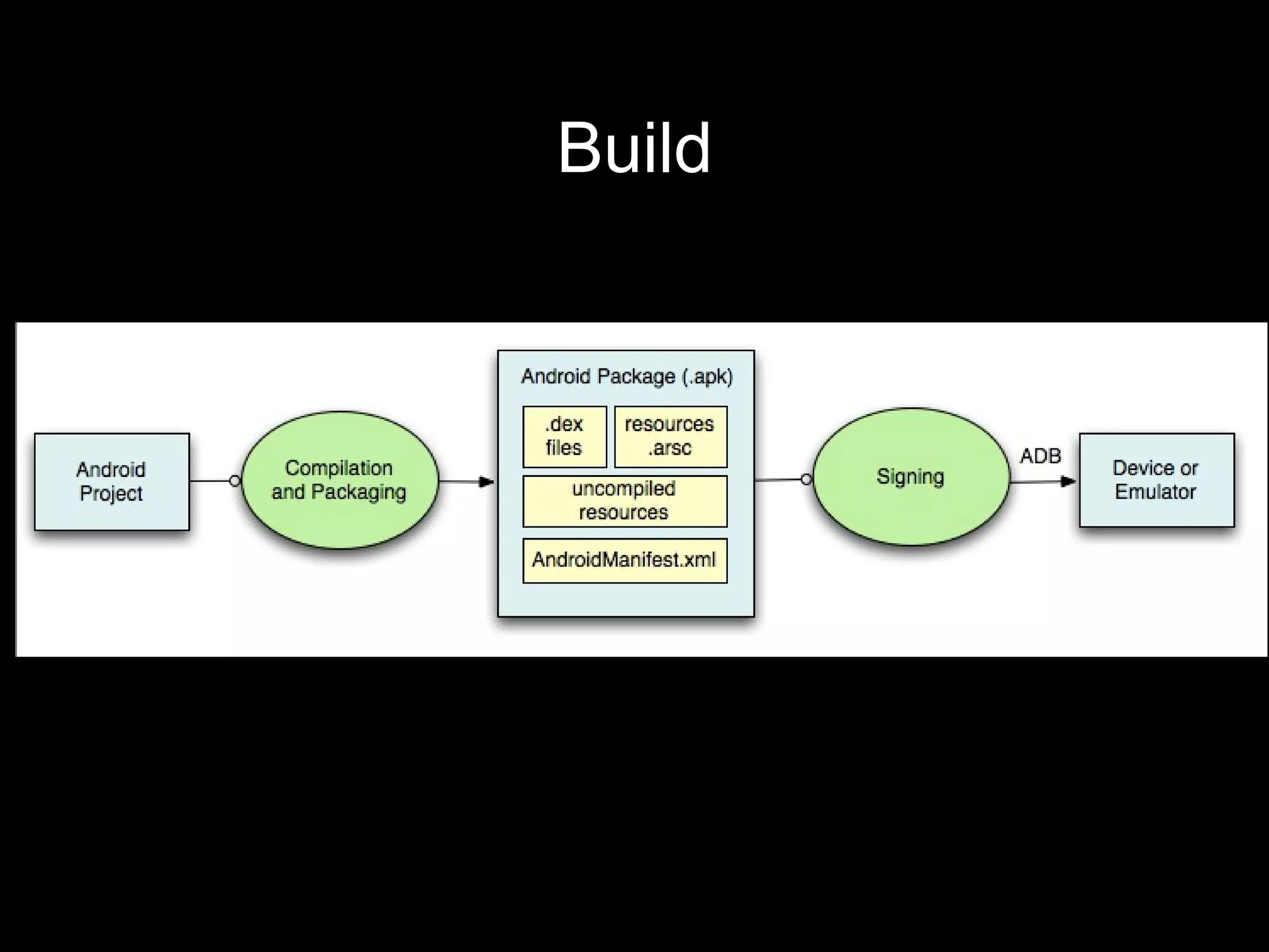
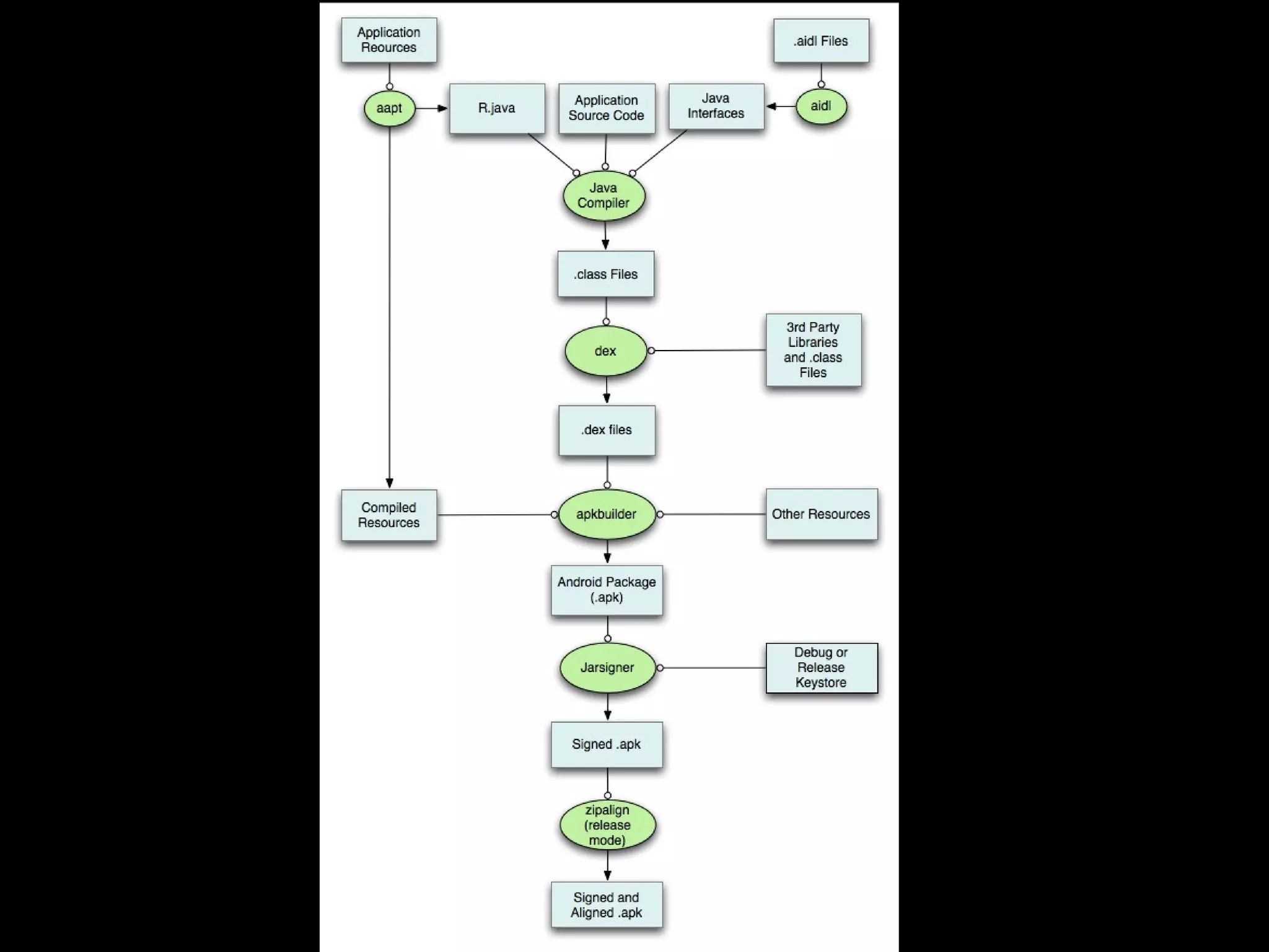
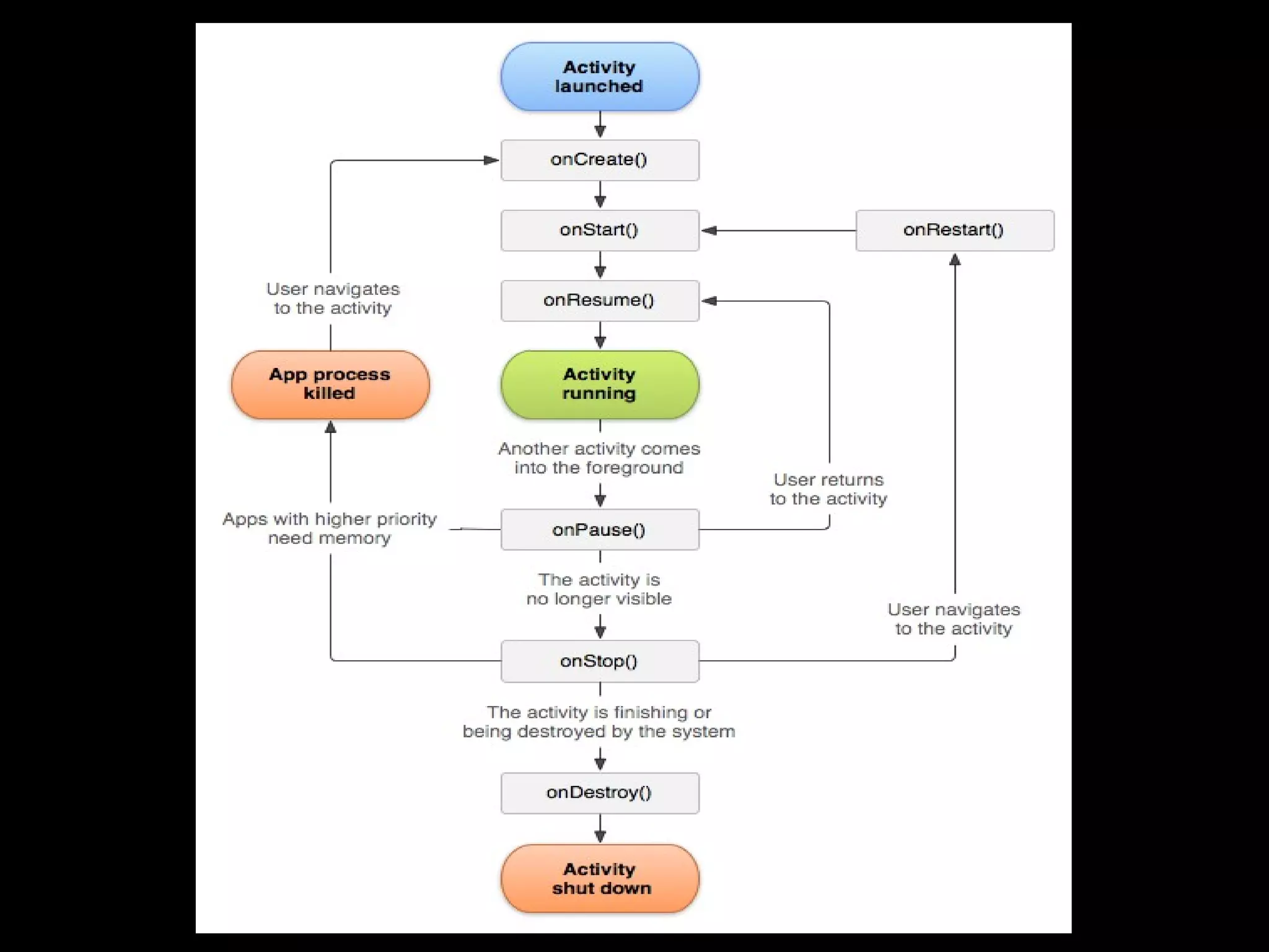
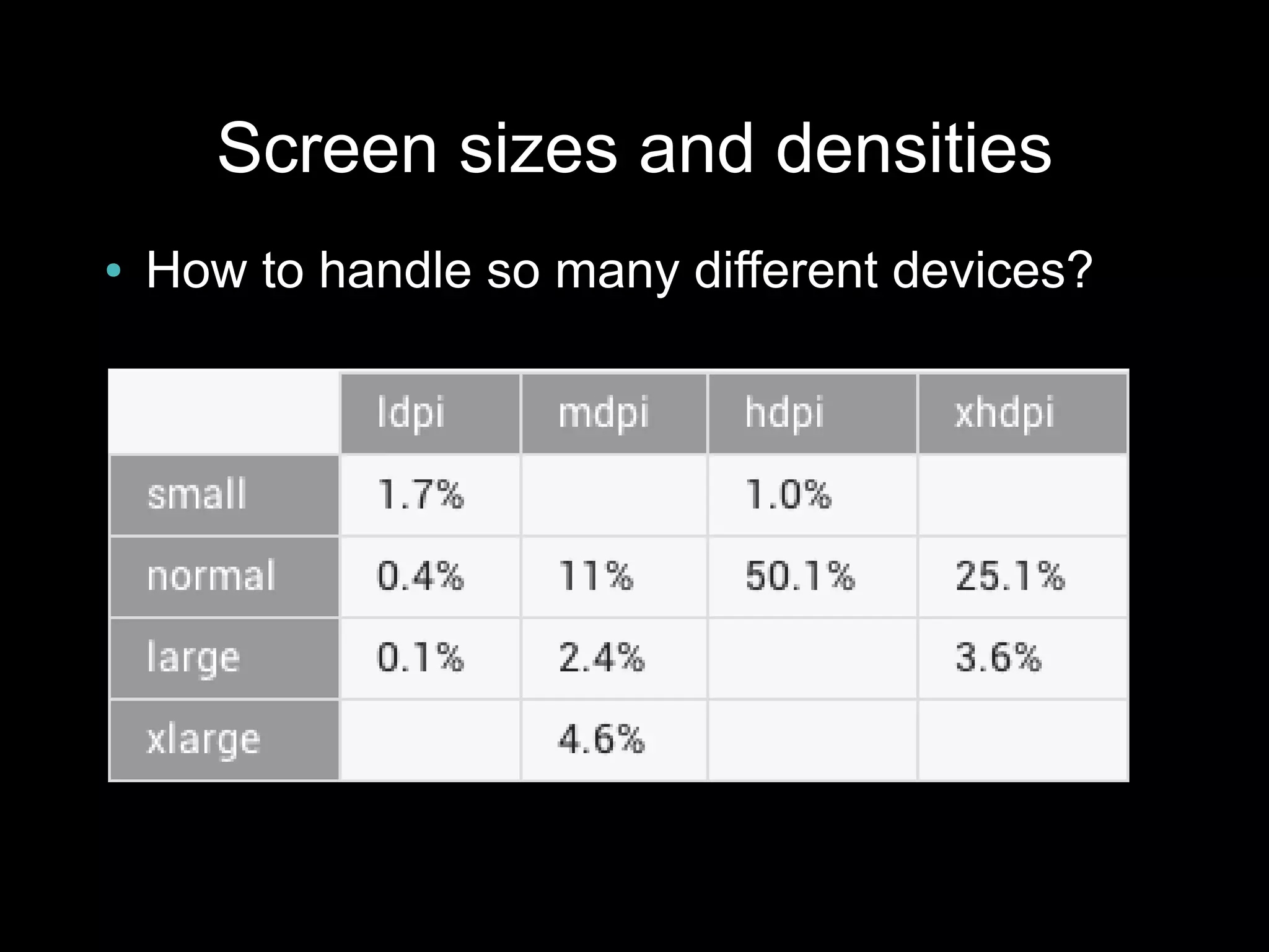
This document provides an overview of Android development basics. It discusses the Android platform, ecosystem, and SDK tools. It describes key Android concepts like activities, services, content providers, and broadcasts. It also covers user interface components, resources, handling different device configurations, fragments, threads, menus, dialogs, notifications and more. The document is intended as an introduction to the fundamentals of Android development.