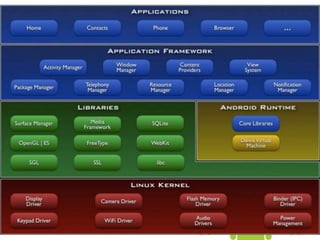
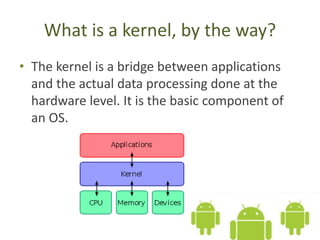
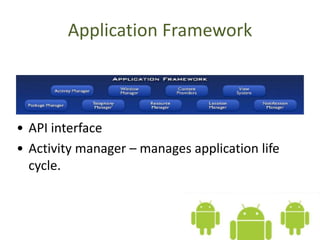
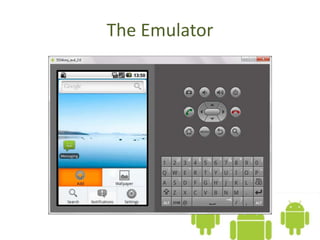
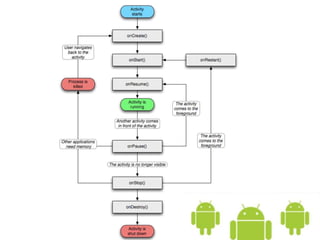
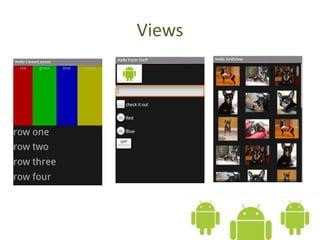
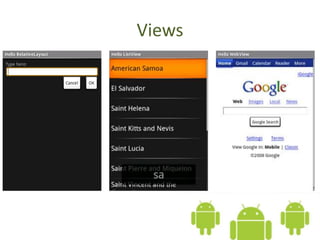
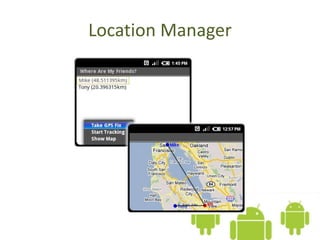
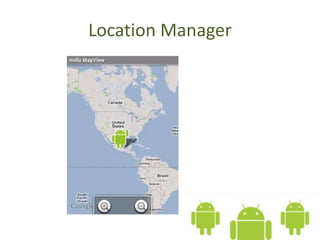
The document introduces the Android platform, describing its architecture including the Linux kernel, libraries, Android runtime, and application framework. It also discusses the basics of developing Android applications, covering tools like the emulator, building user interfaces with views and layouts, and key services like the notification and location managers. The document provides an overview of developing for Android and some of its core components.