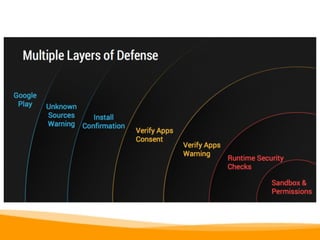
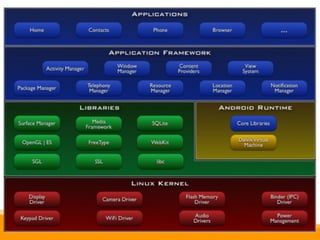
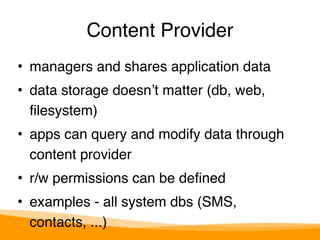
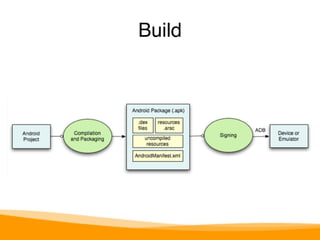
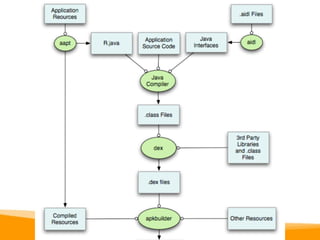
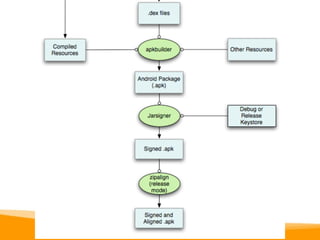
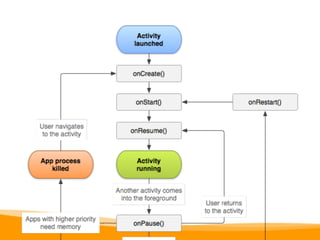
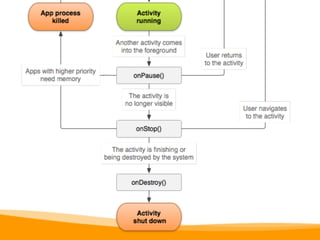
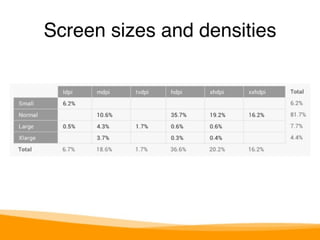
This document provides an overview of Android development, including:
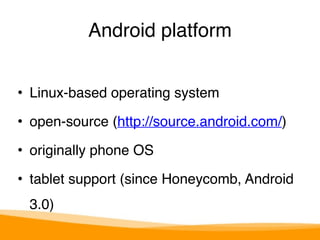
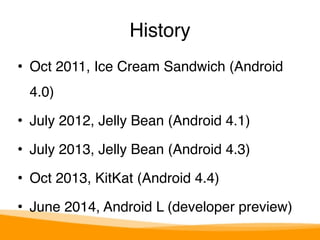
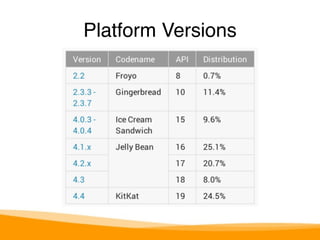
- The basics of the Android platform, ecosystem, and history
- Tools for Android development like Android Studio and SDK
- Key Android app components like Activities, Services, and Broadcast Receivers
- Building a basic "Hello World" Android app
- Designing user interfaces with widgets and handling configuration changes