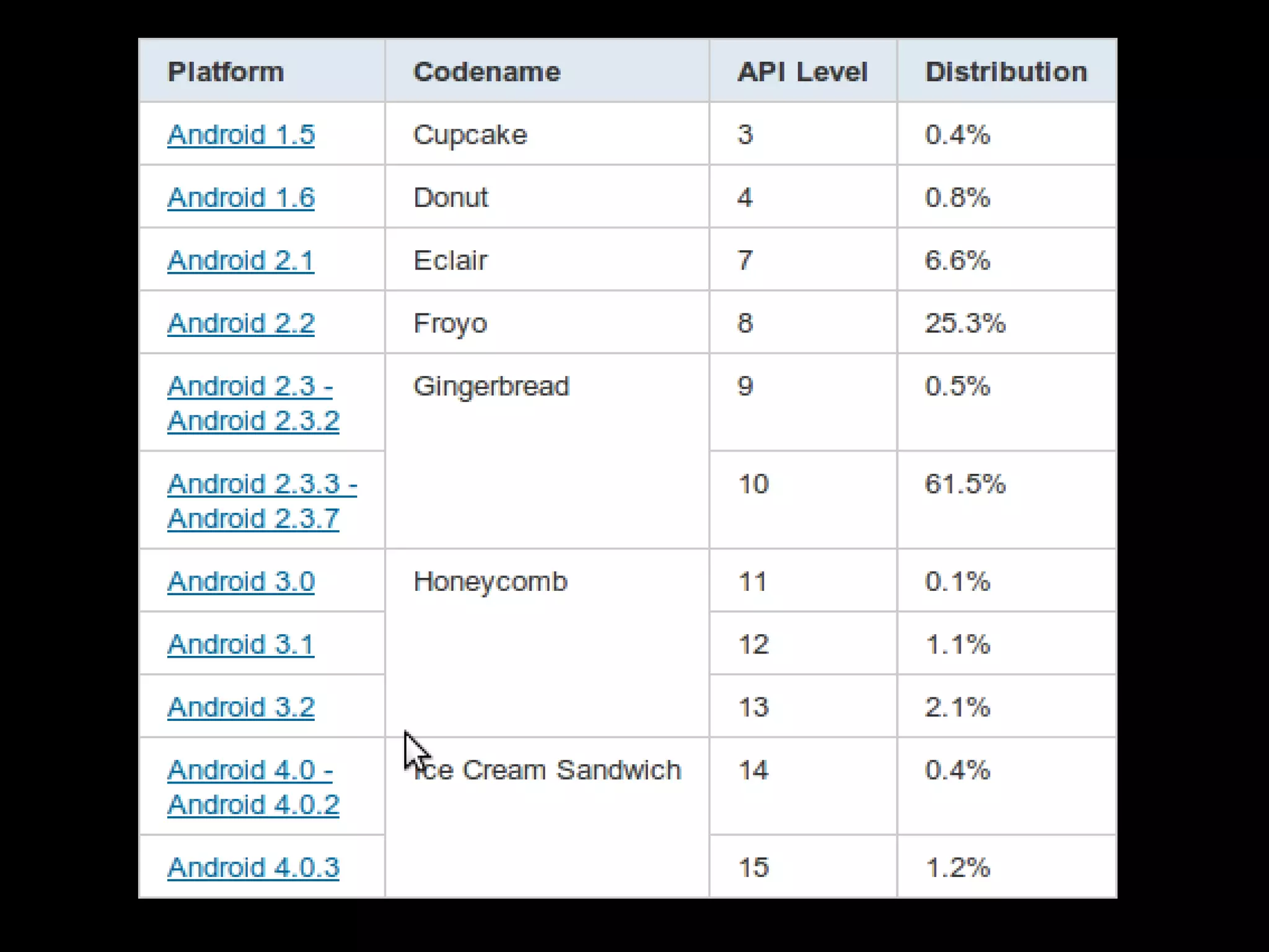
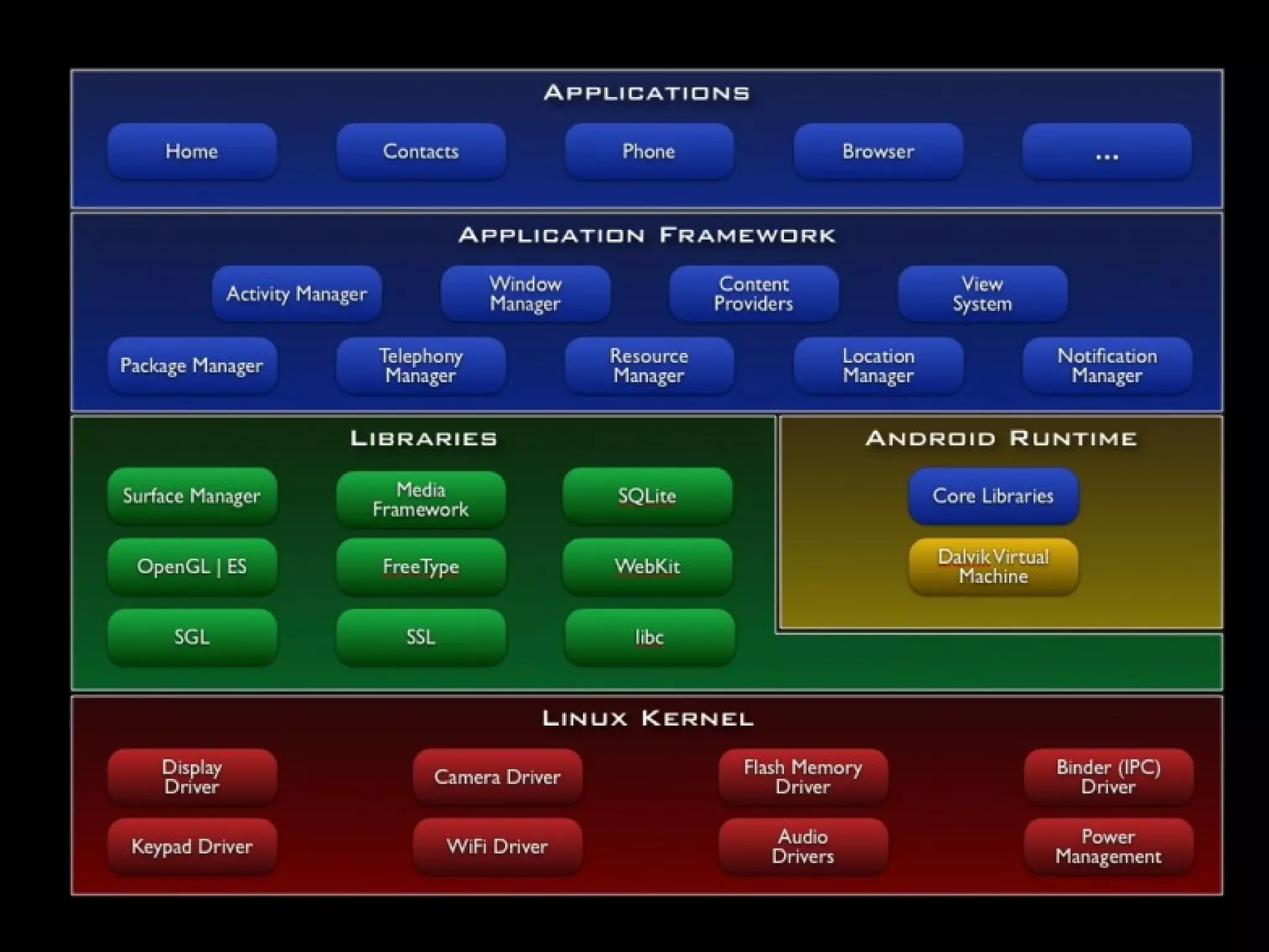
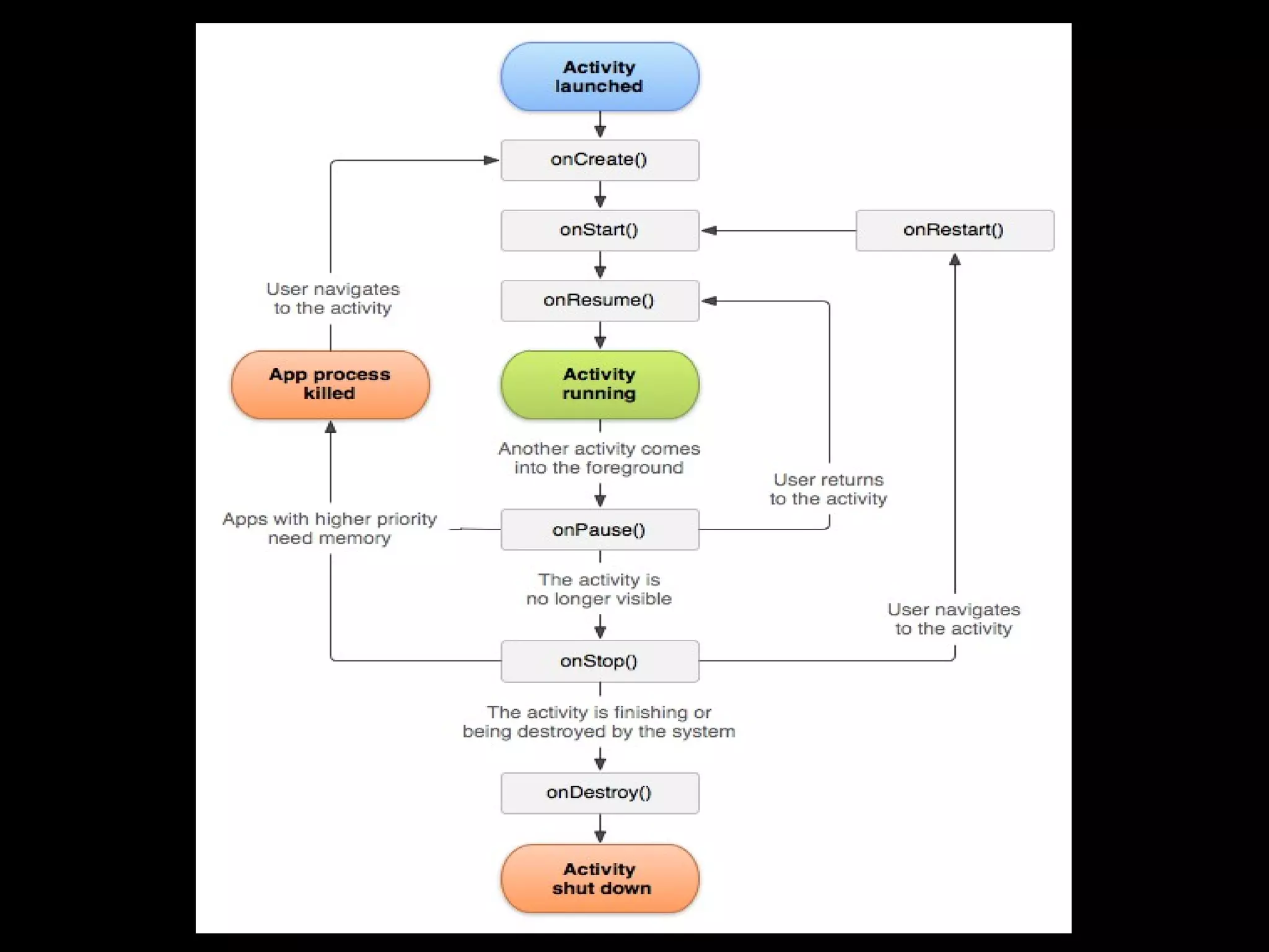
This document provides an overview of the basics of Android development. It discusses the Android platform, ecosystem, SDK and tools. It describes the key building blocks like activities, services, content providers and broadcast receivers. It also covers the app lifecycle, intents, user interface components and common widgets like lists, dialogs and toasts.