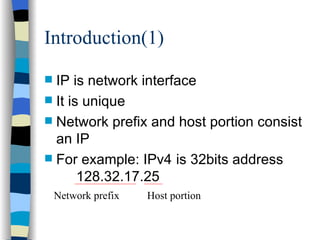
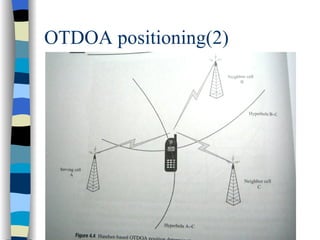
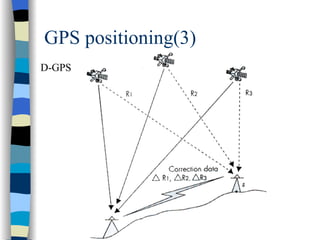
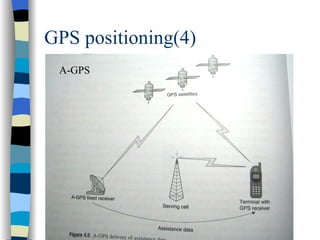
This document discusses user mobility and location management. It covers IP and mobility, including mobile IP packet routing and agent discovery. It also discusses location determination, including both handset-based and network-based position determination techniques like cell-ID, OTDOA, and GPS. Finally, it outlines different approaches for accessing and reporting location data, such as immediate services, reporting services, and accessing points of interest.