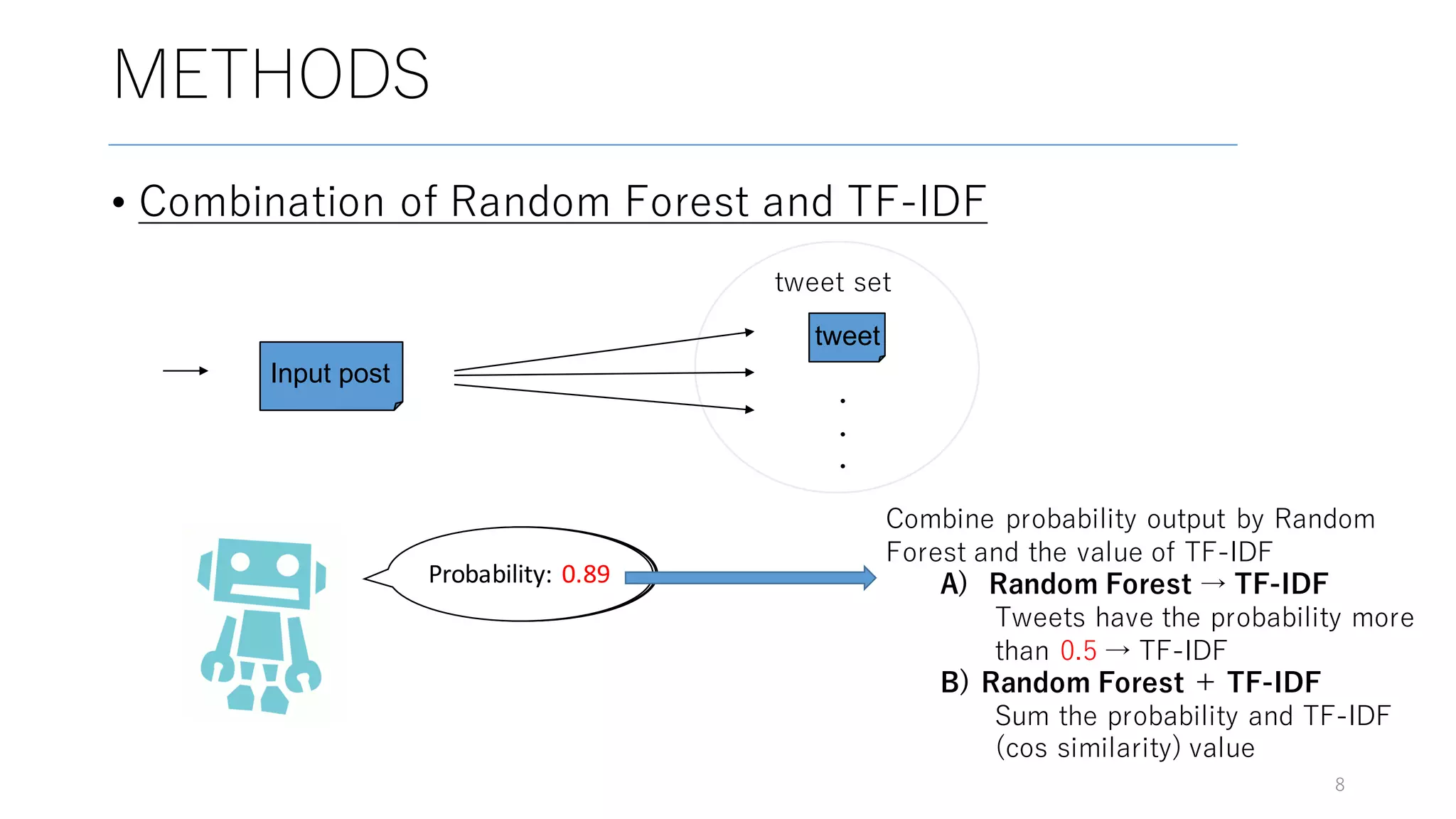
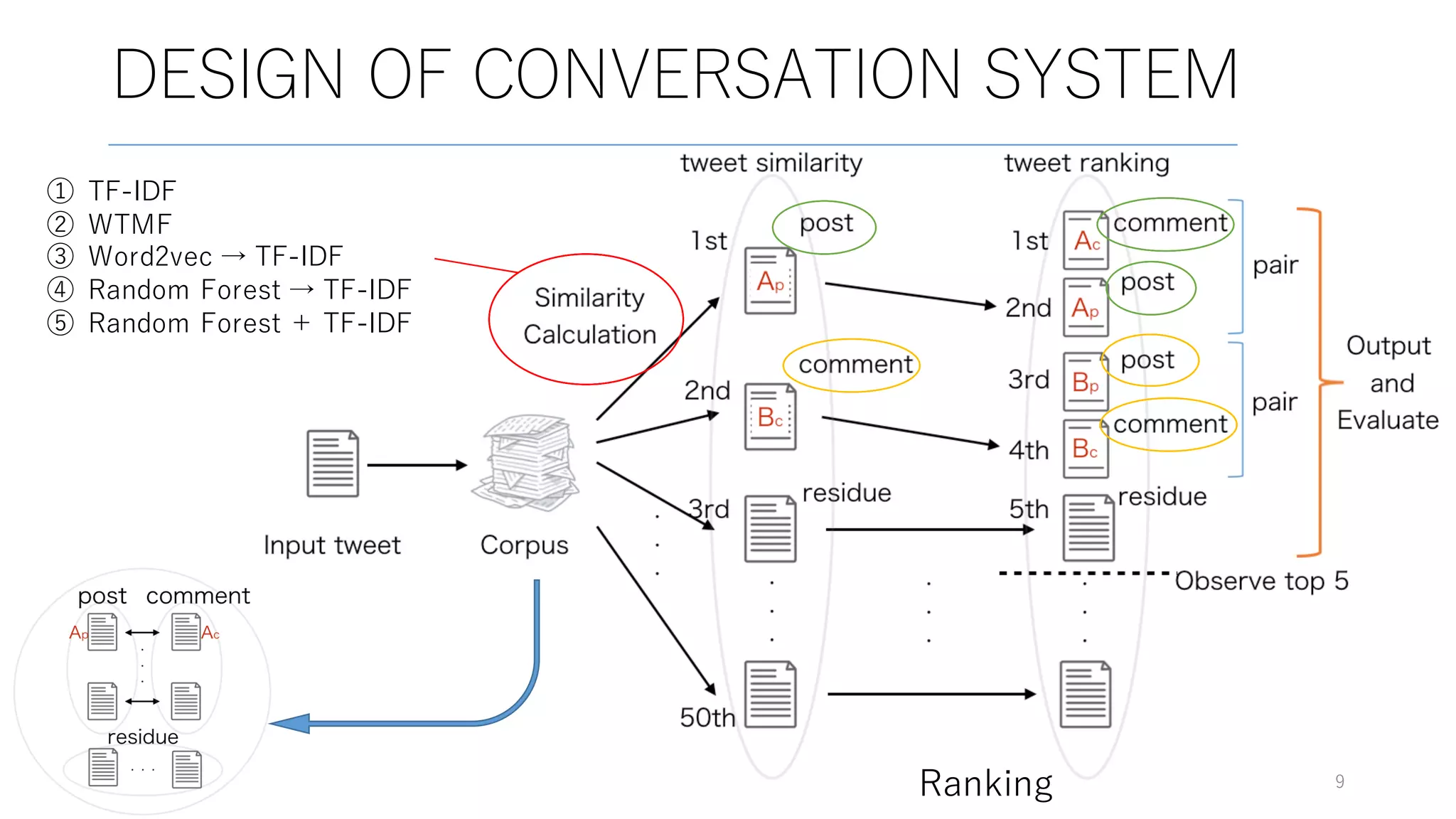
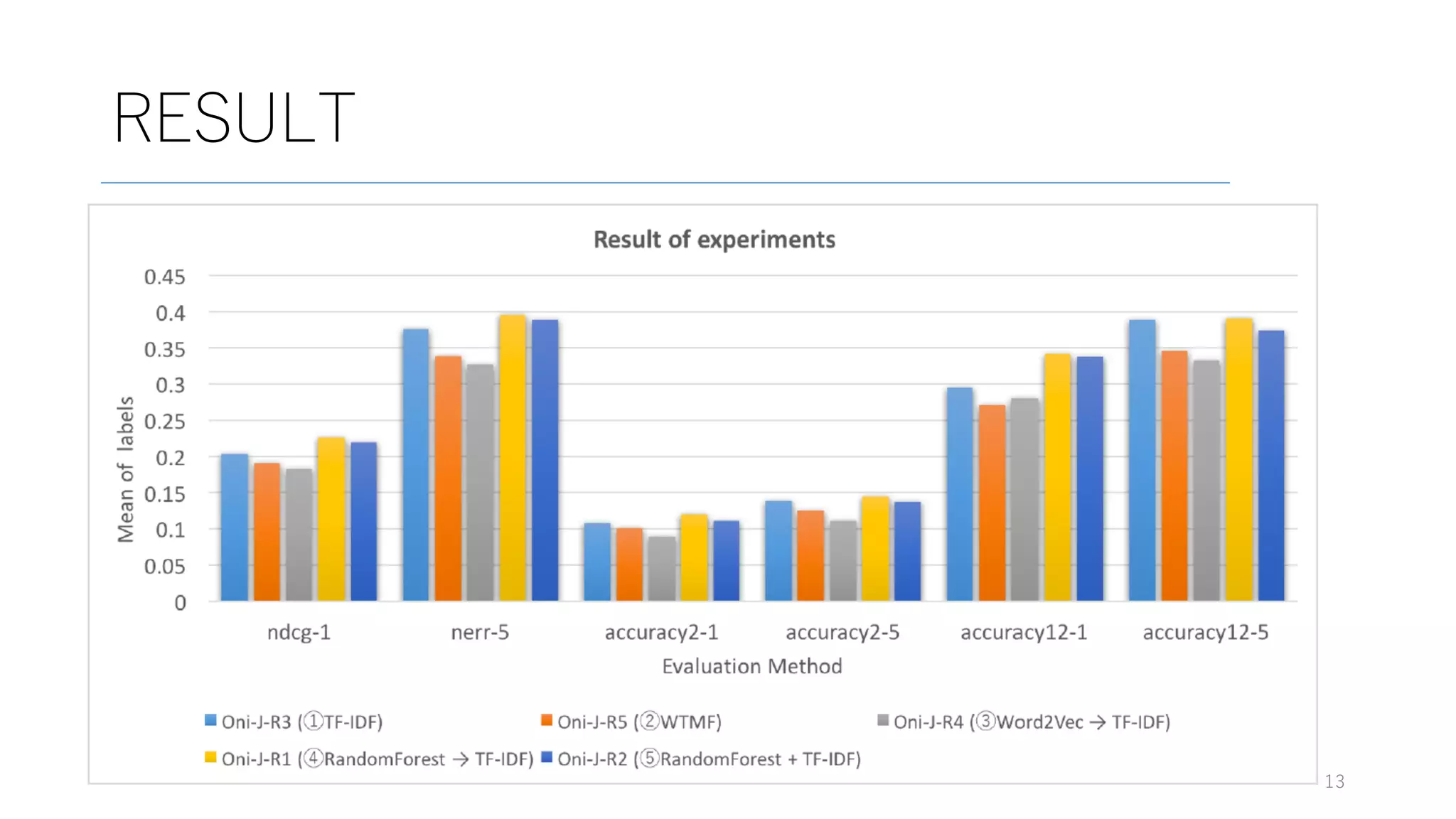
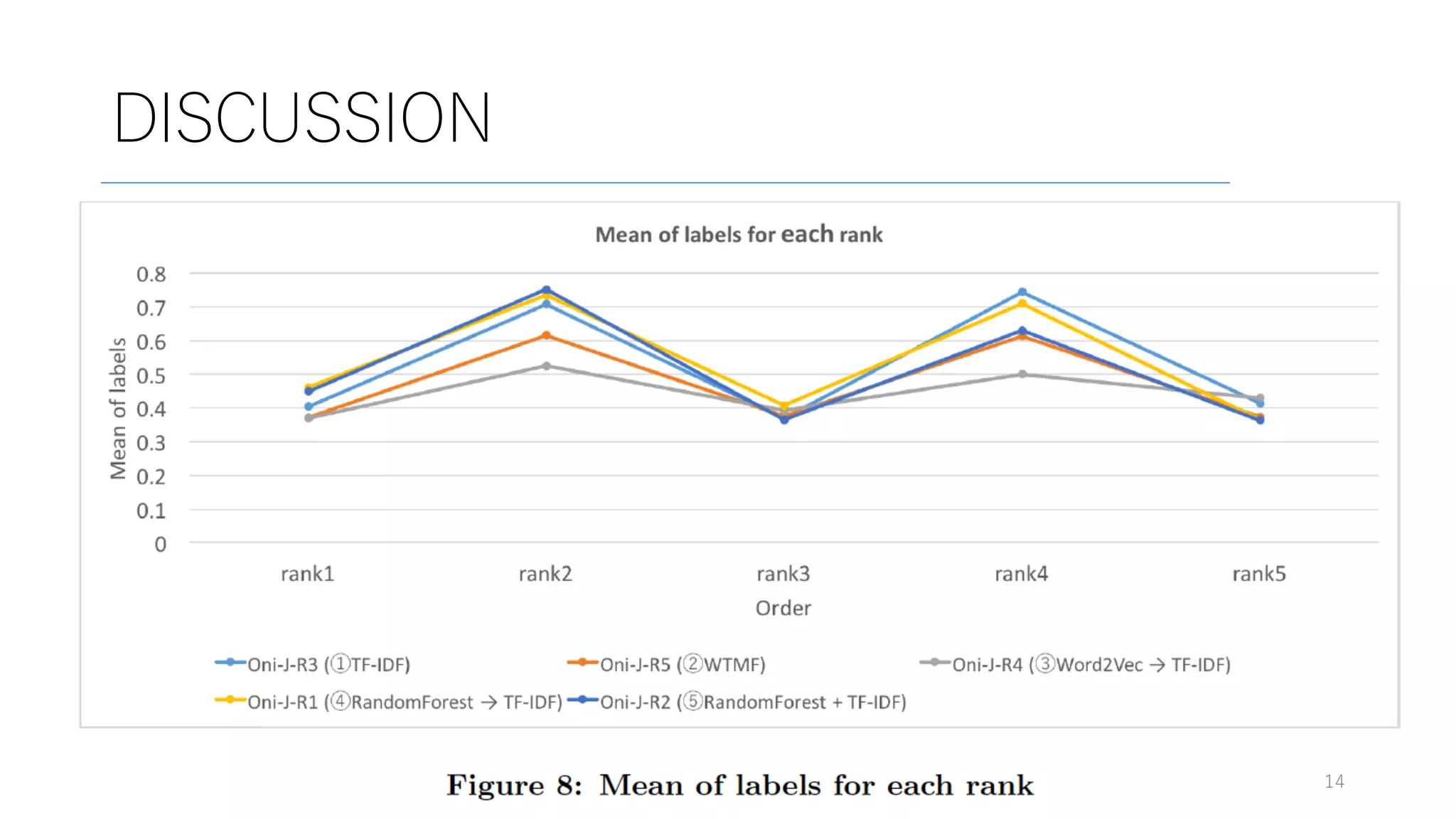
Here are some potential replies to your input tweet:
1. Summer is the best season in Hokkaido.
2. It does get pretty hot in Hokkaido in the summer.
3. I love Hokkaido in the summer too, so many outdoor activities!
4. What are your plans for the summer in Hokkaido?
5. The scenery is beautiful everywhere in Hokkaido.