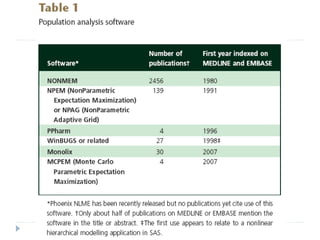
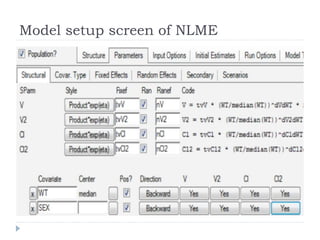
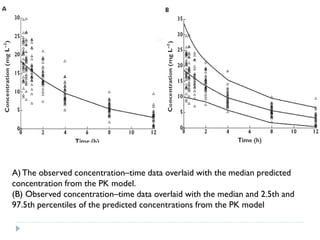
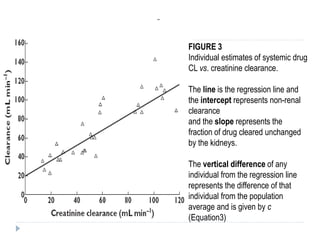
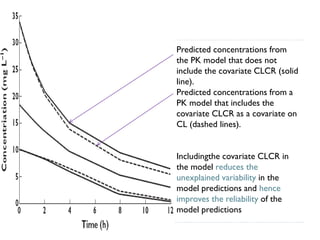
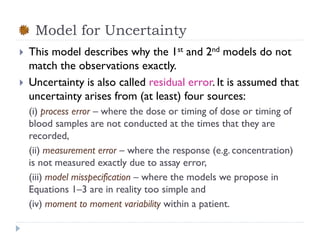
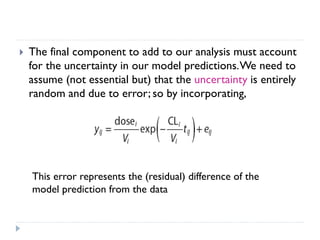
The document discusses population pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis. Population PK seeks to identify factors that cause variability in drug concentrations among patients and quantify their effects to help determine appropriate dosages. It describes common PK parameters, software used for PK analysis like NONMEM, and approaches for analyzing population PK data, including nonlinear mixed-effects modeling. An example population PK analysis is provided using simulated gentamicin concentration-time data from 30 patients to illustrate modeling the typical response, heterogeneity between individuals, and uncertainty in the model.