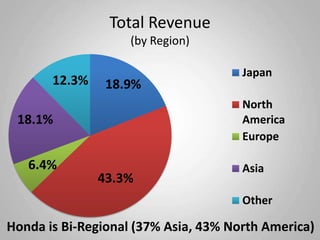
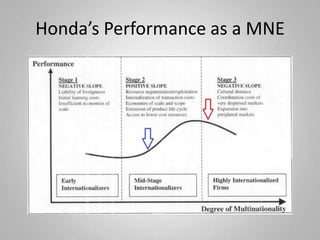
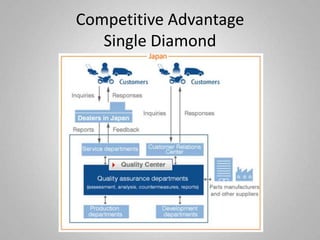
Honda Motor Company, founded in 1948, is a Japanese multinational corporation known for manufacturing automobiles and motorcycles, with a strong presence in North America and Asia. The company leverages its extensive resources, including factories and R&D facilities worldwide, to produce innovative and fuel-efficient vehicles, aiming for leadership in environmental technologies. Challenges include navigating regulatory environments and resource recombination in its international operations.