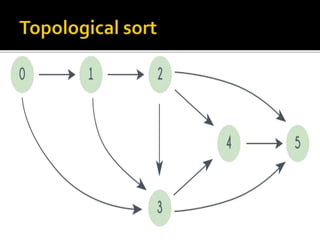
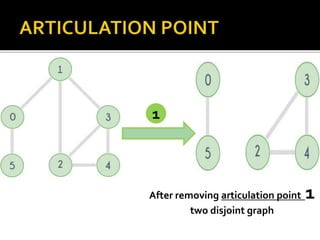
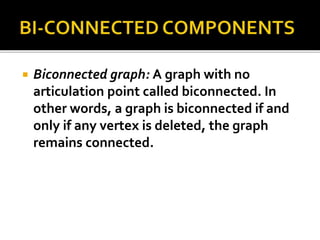
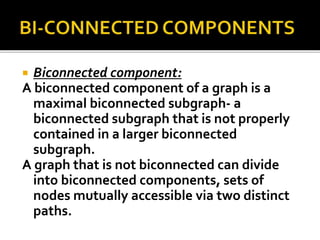
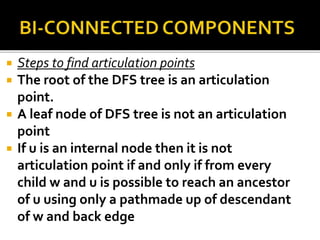
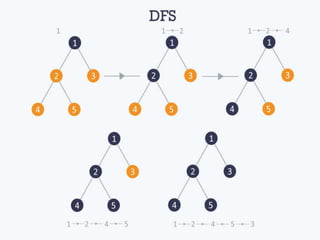
The document discusses various graph search algorithms including breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS). It provides pseudocode for BFS and DFS, and describes how they work. It also covers topological sorting of graphs, articulation points that disconnect graphs, and finding biconnected components.







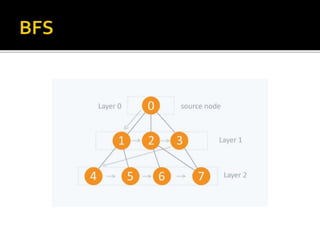
![node level[ node ] s(source node) 0 1 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 2 6 2 7 3node level[ node ] s(source node) 0 1 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 2 6 2 7 3node level[ node ] s(source node) 0 1 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 2 6 2 7 3node level[ node ] s(source node) 0 1 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 2 6 2 7 3
node Level
[ node ]
s(source node) 0
1 1
2 1
3 2
4 2
5 2
6 2
7 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analysisdesignofalgorithm-161004172103/85/Analysis-amp-design-of-algorithm-11-320.jpg)