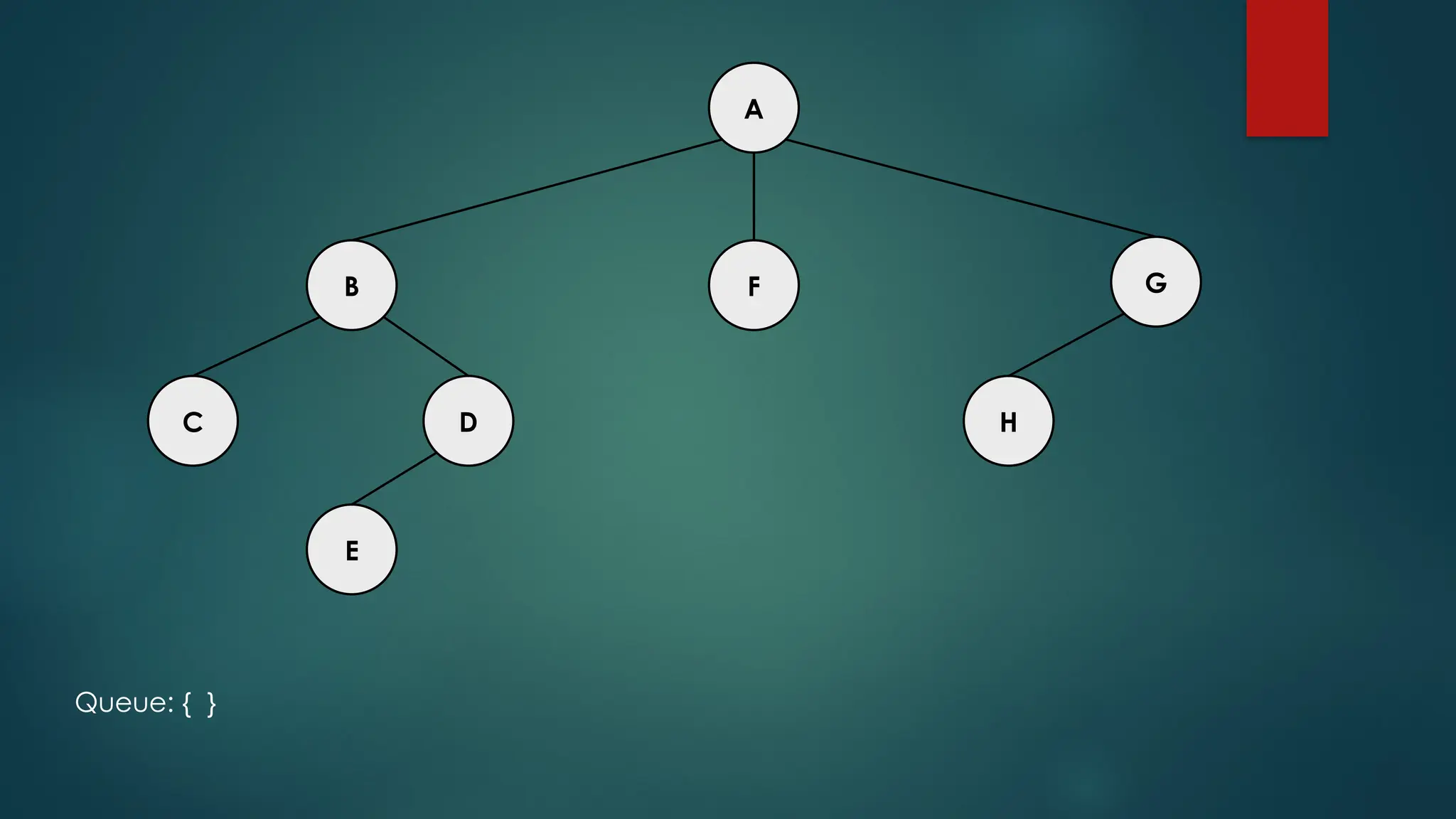
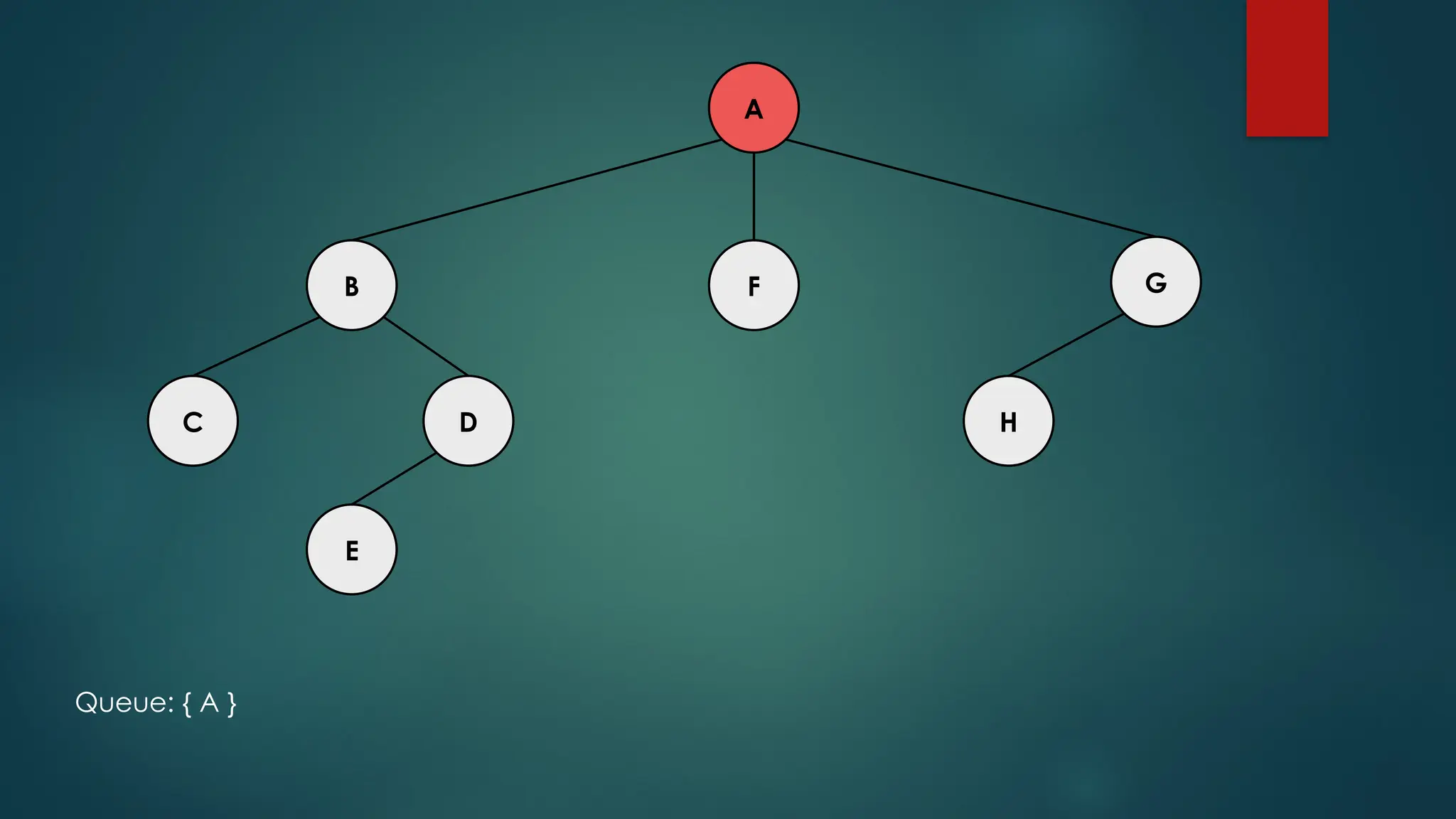
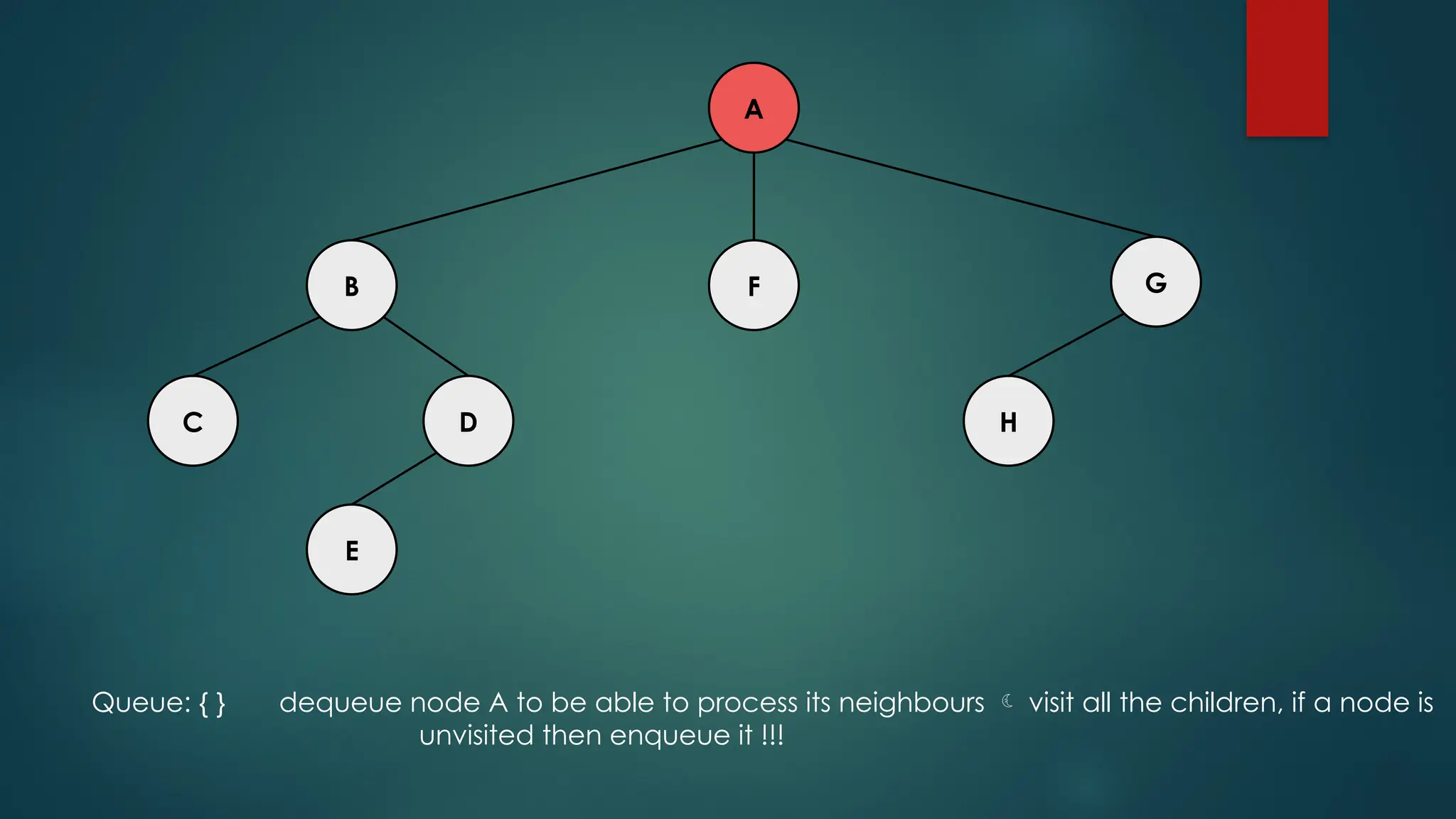
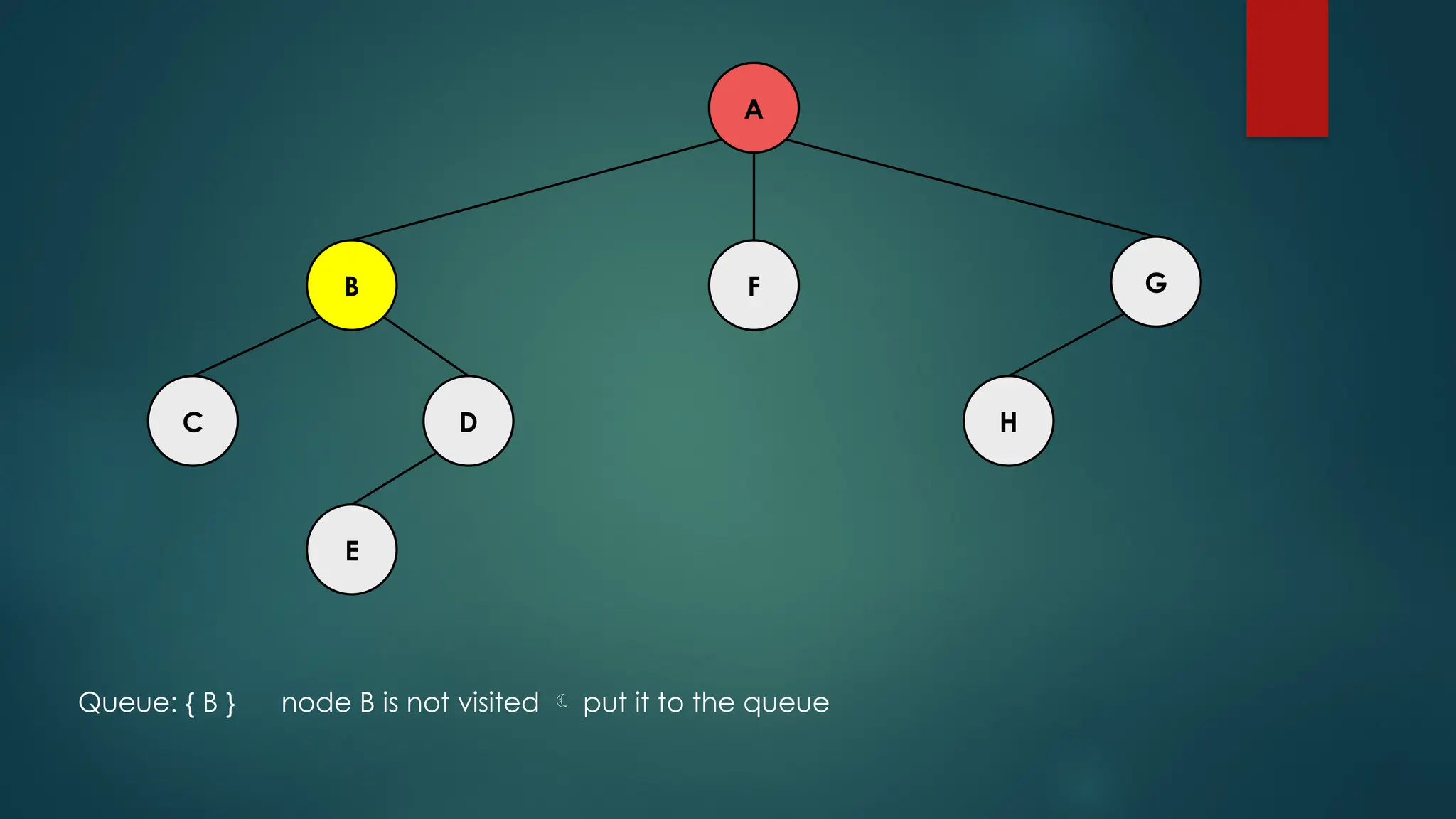
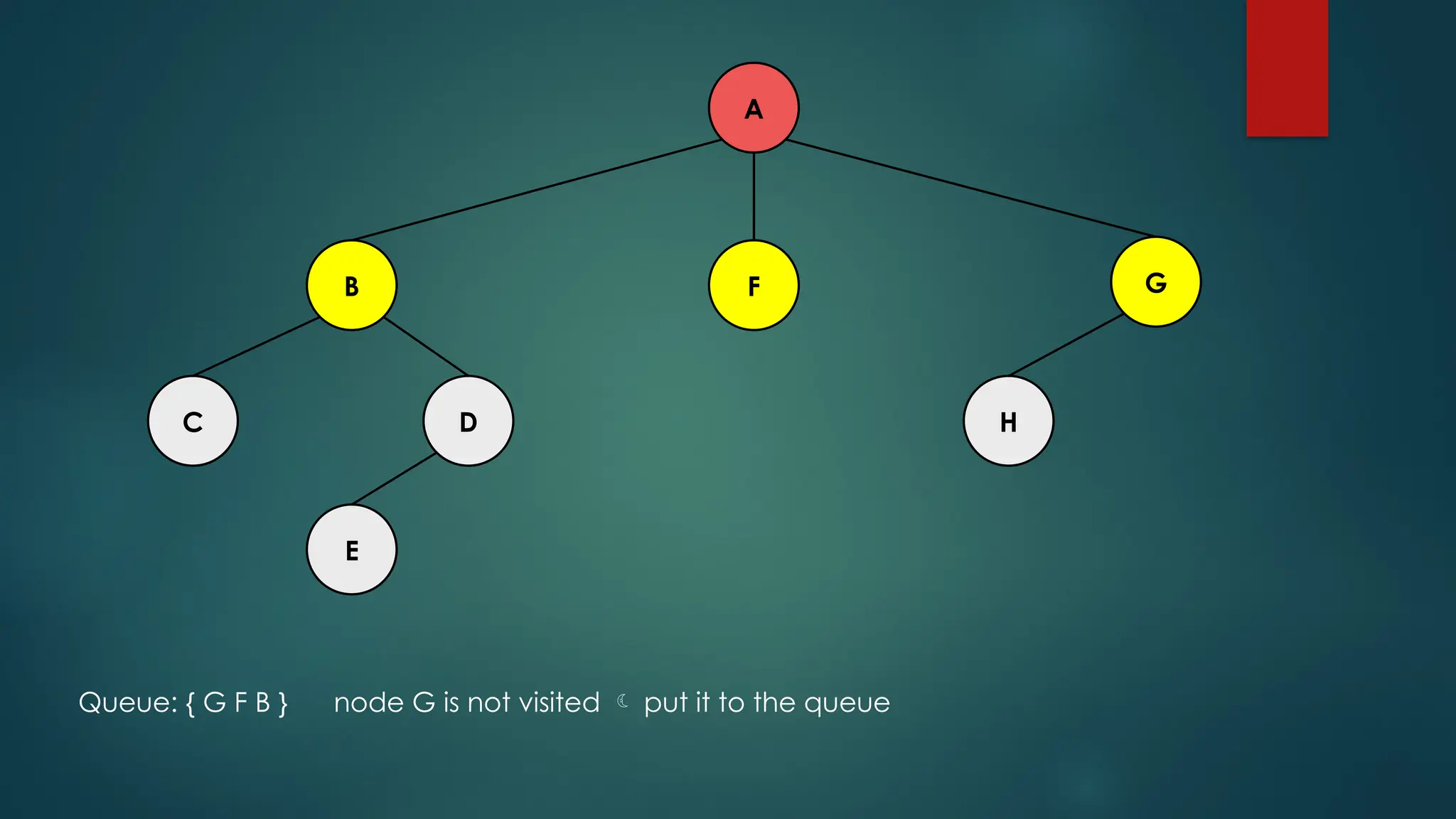
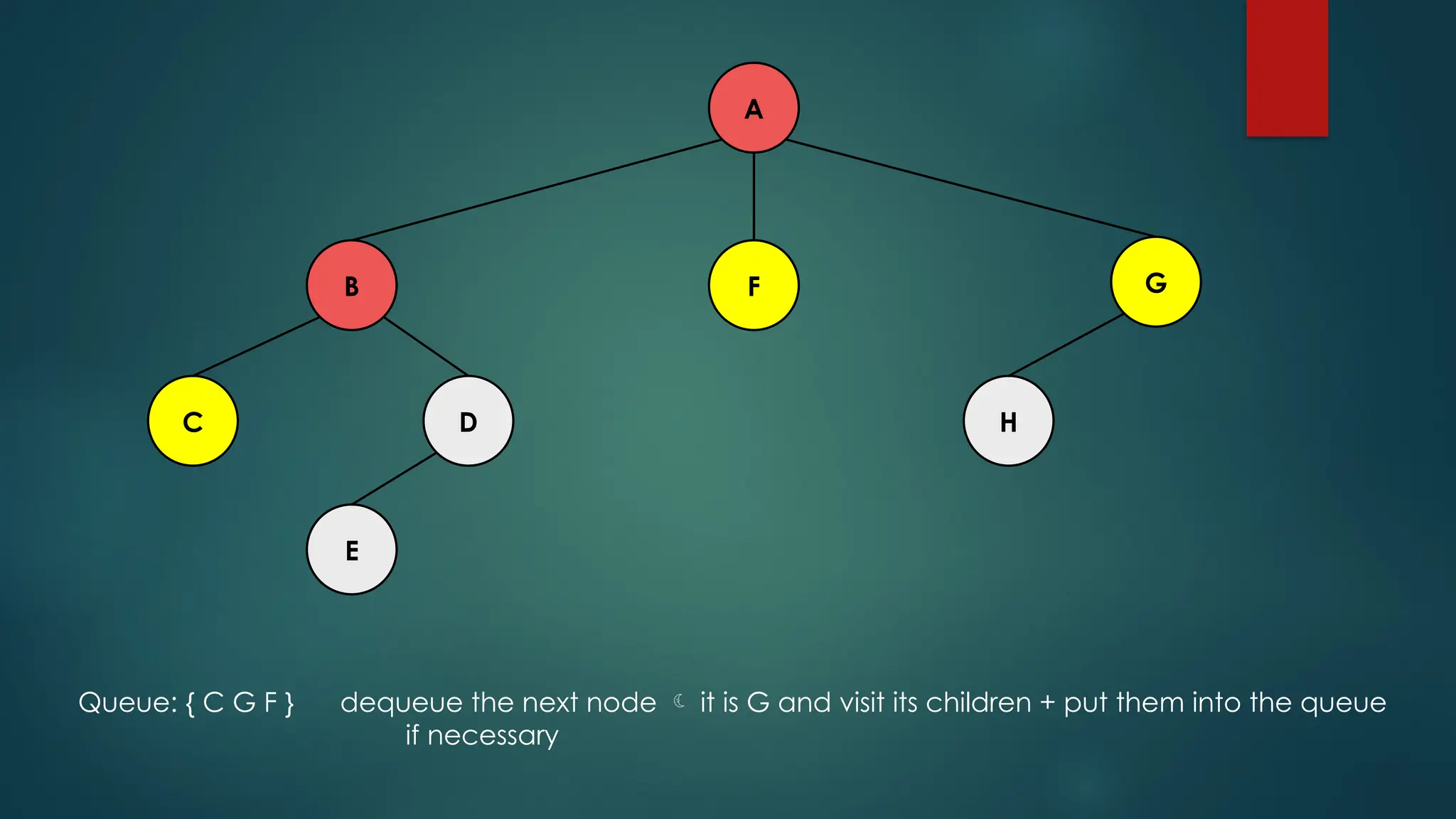
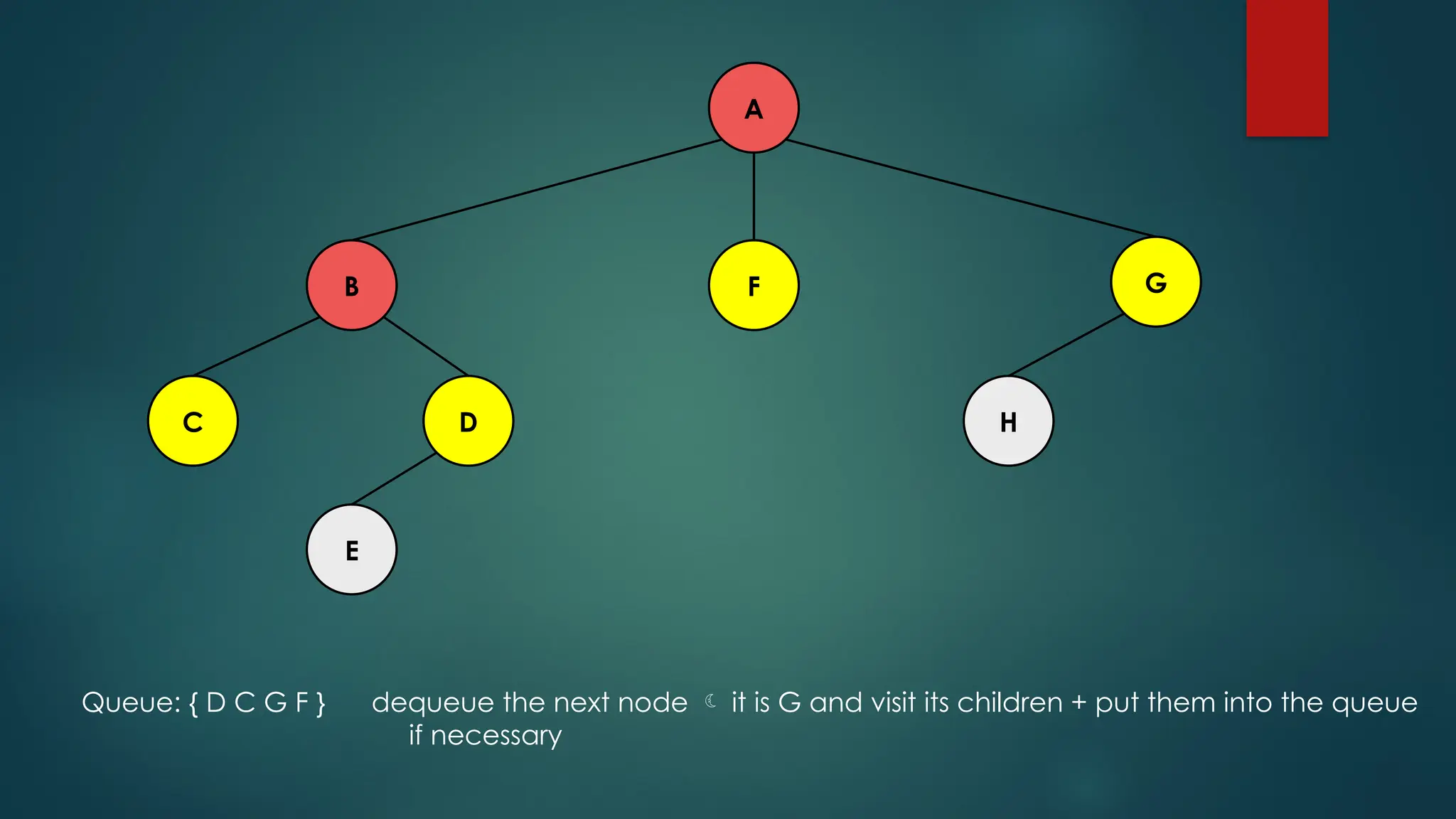
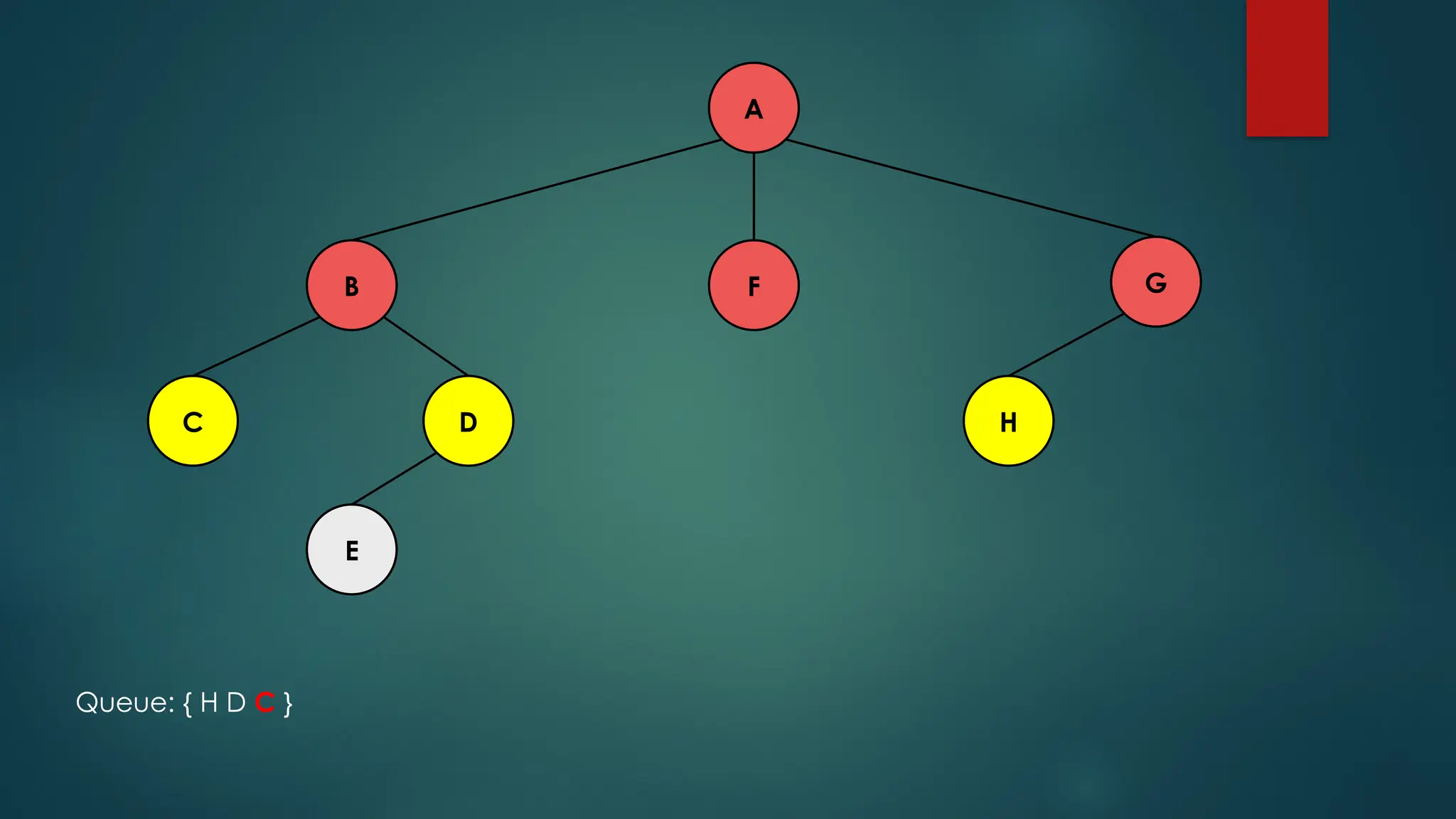
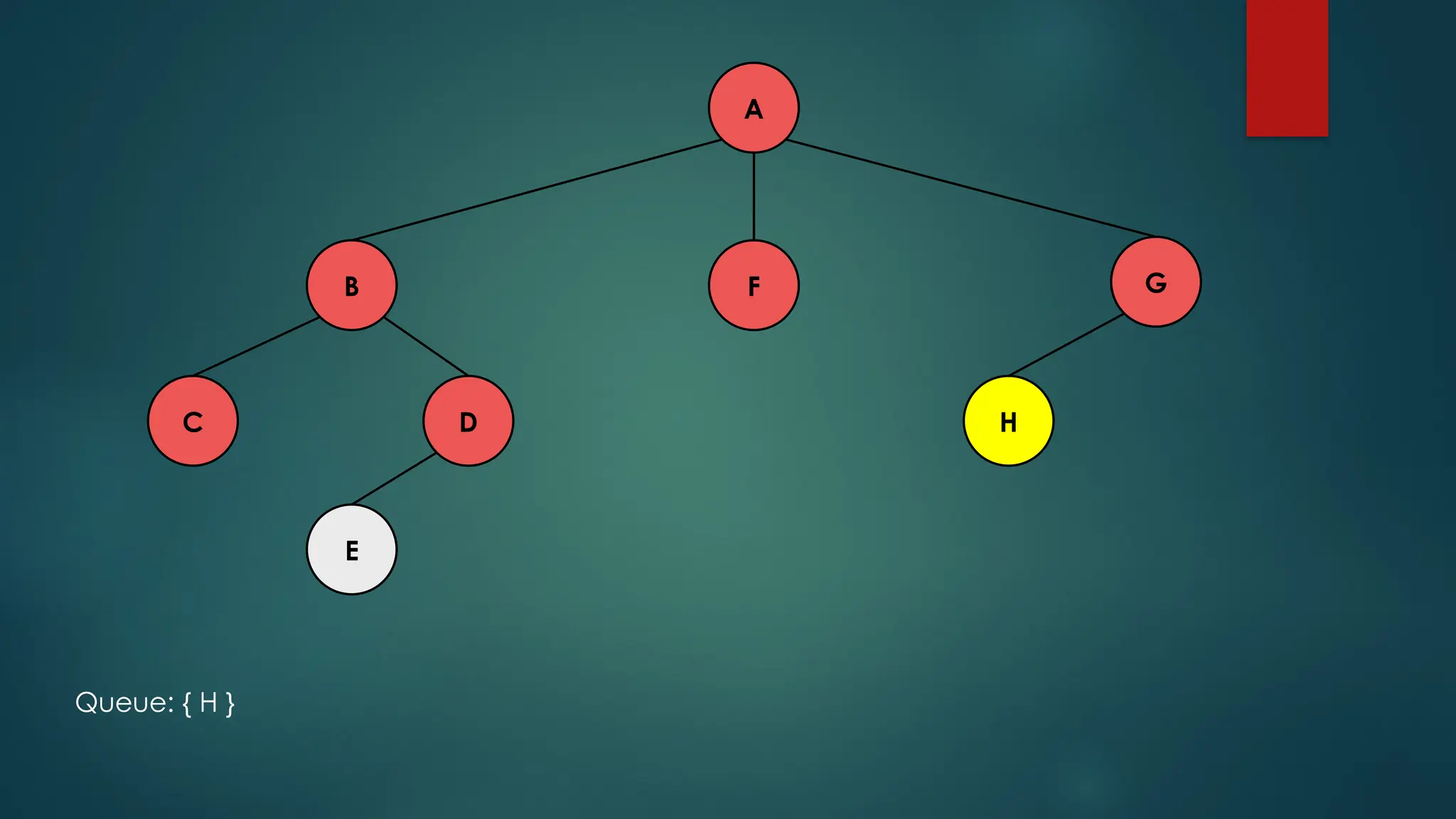
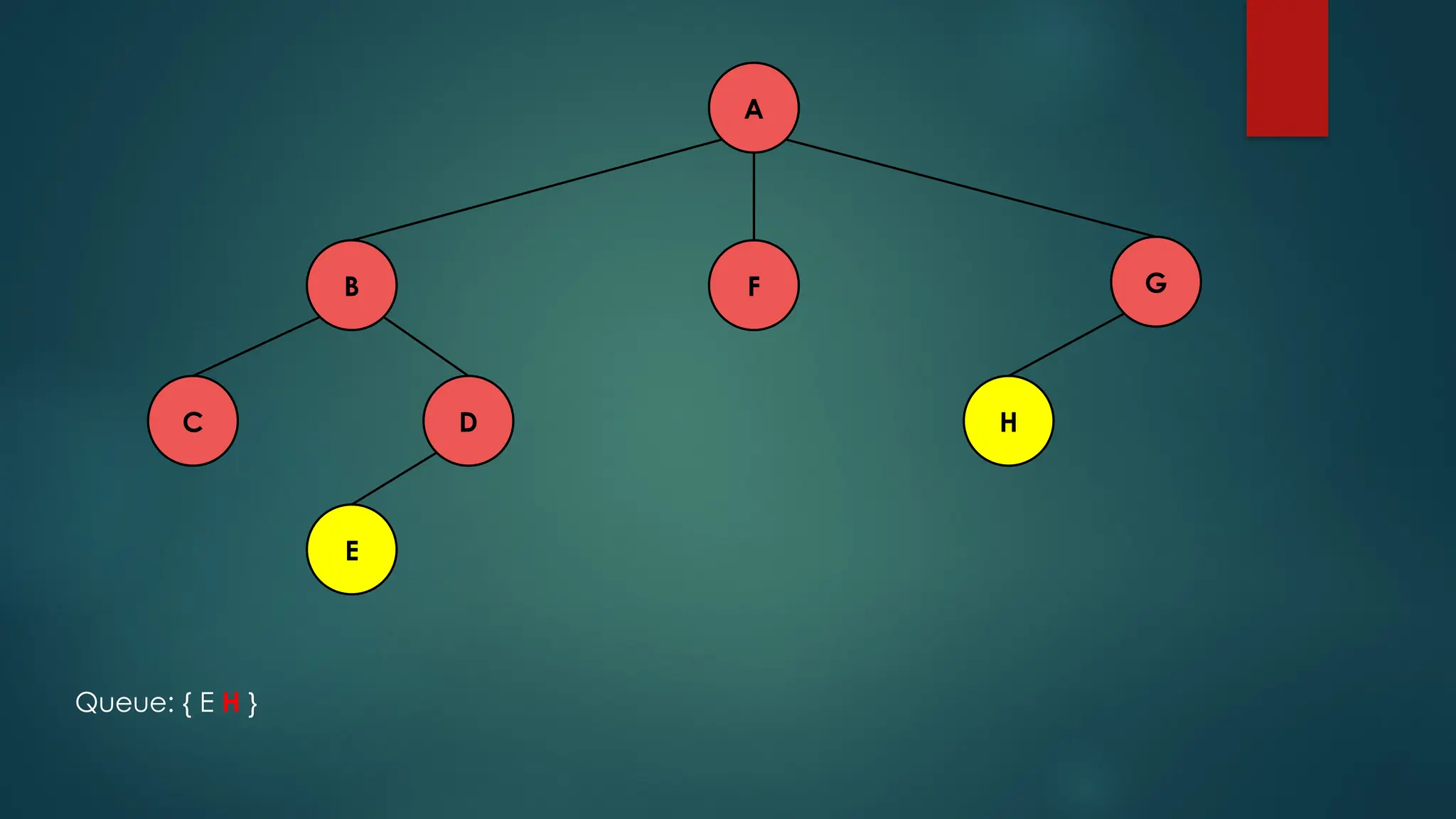
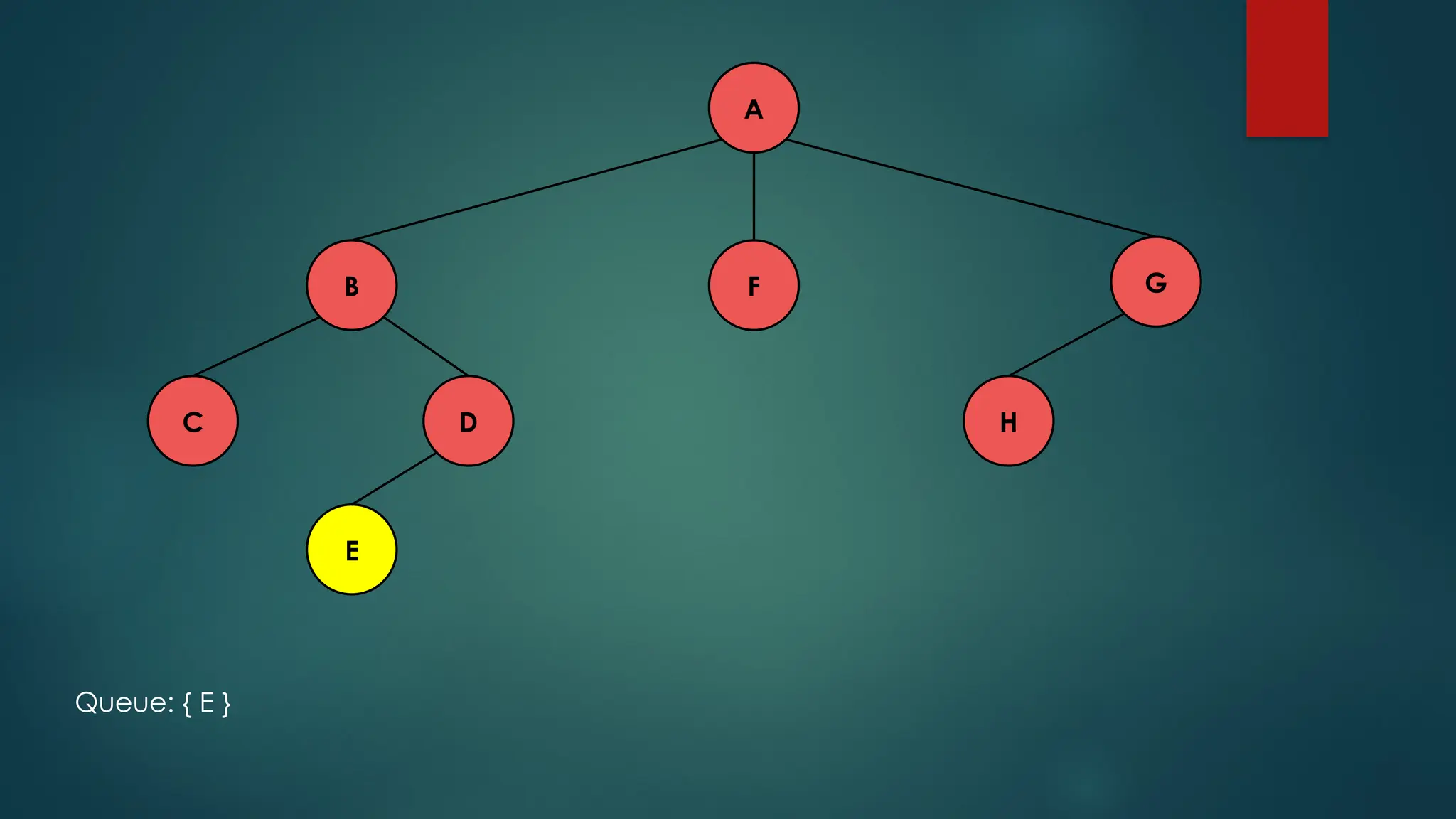
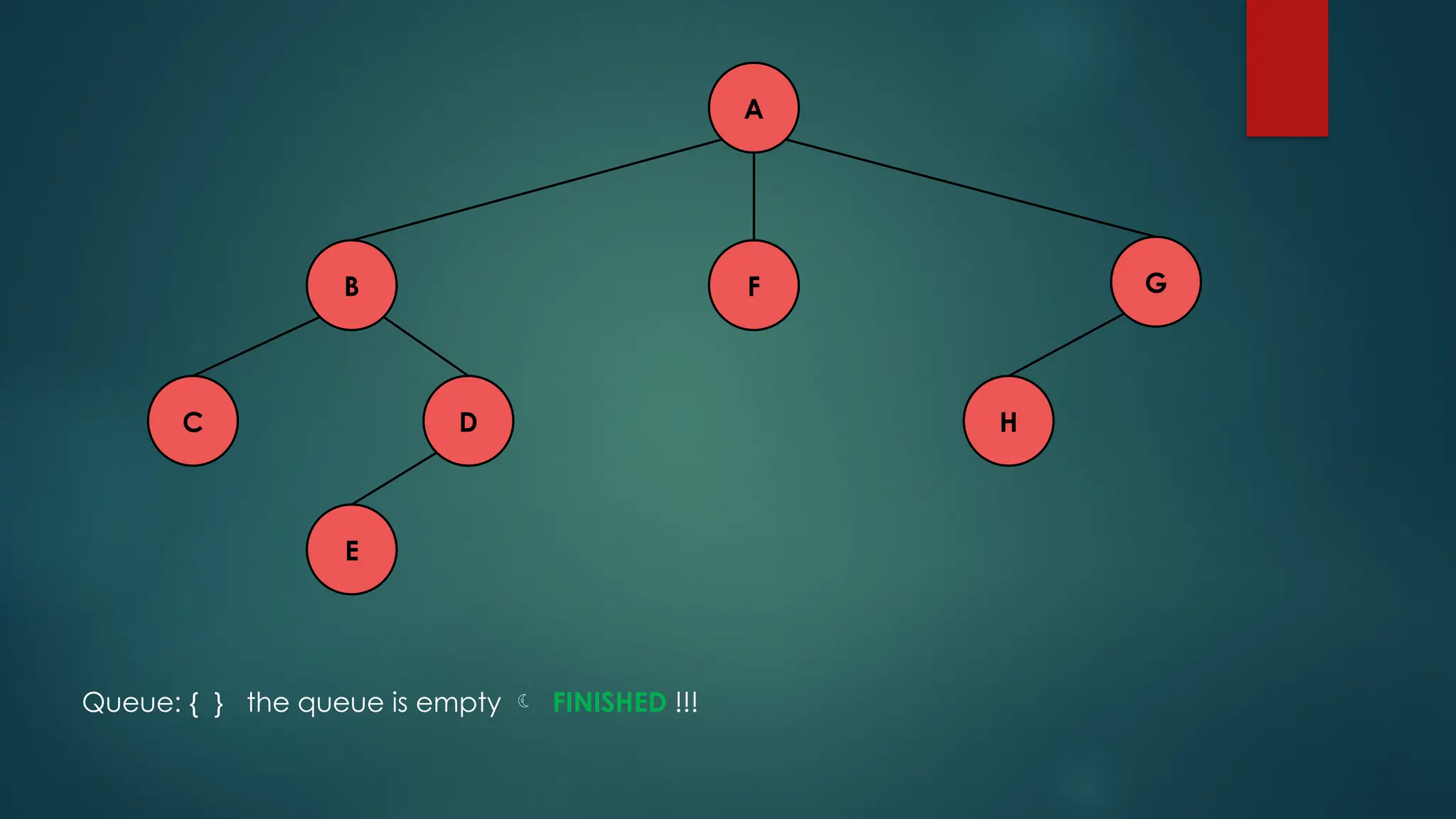
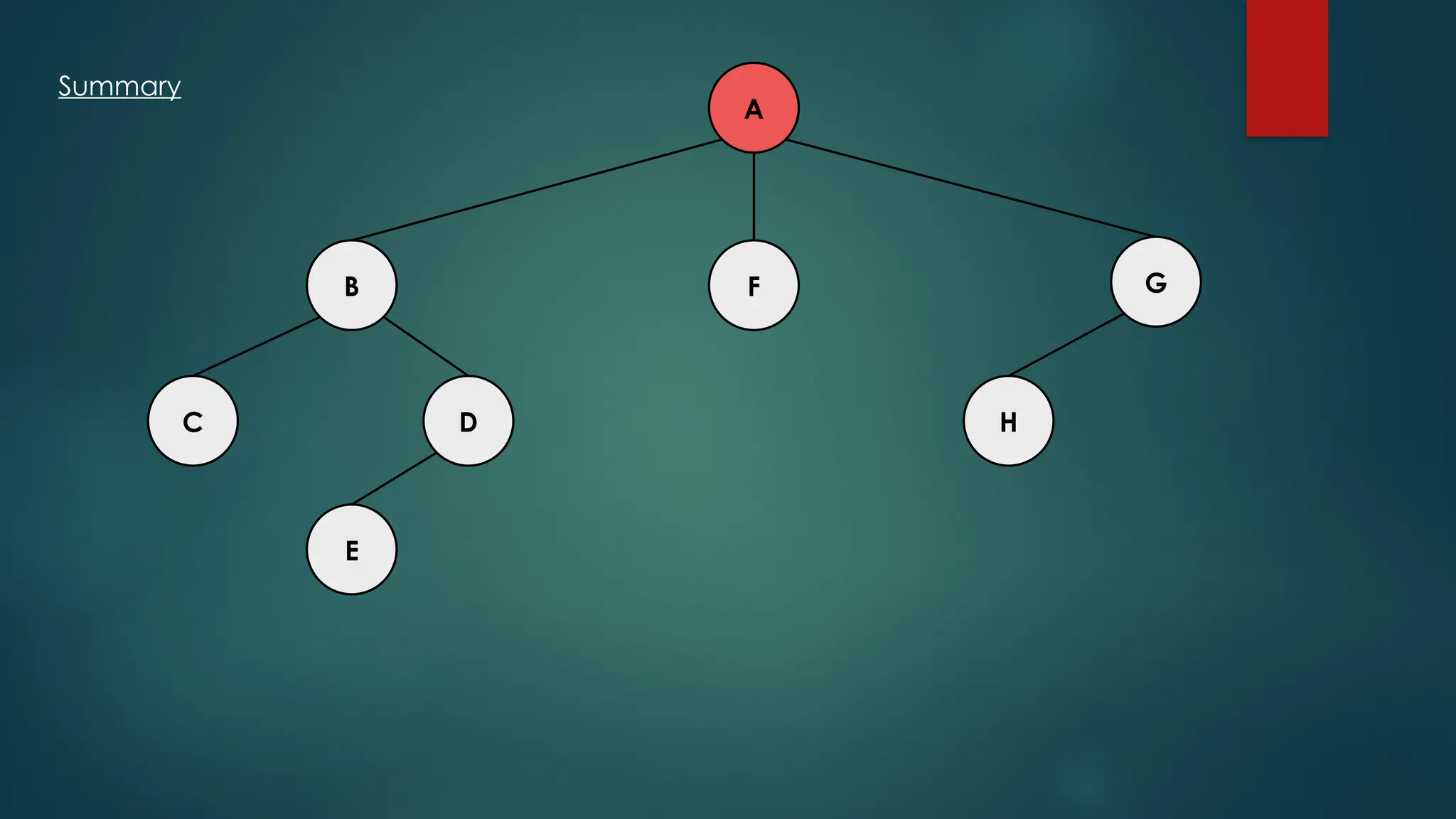
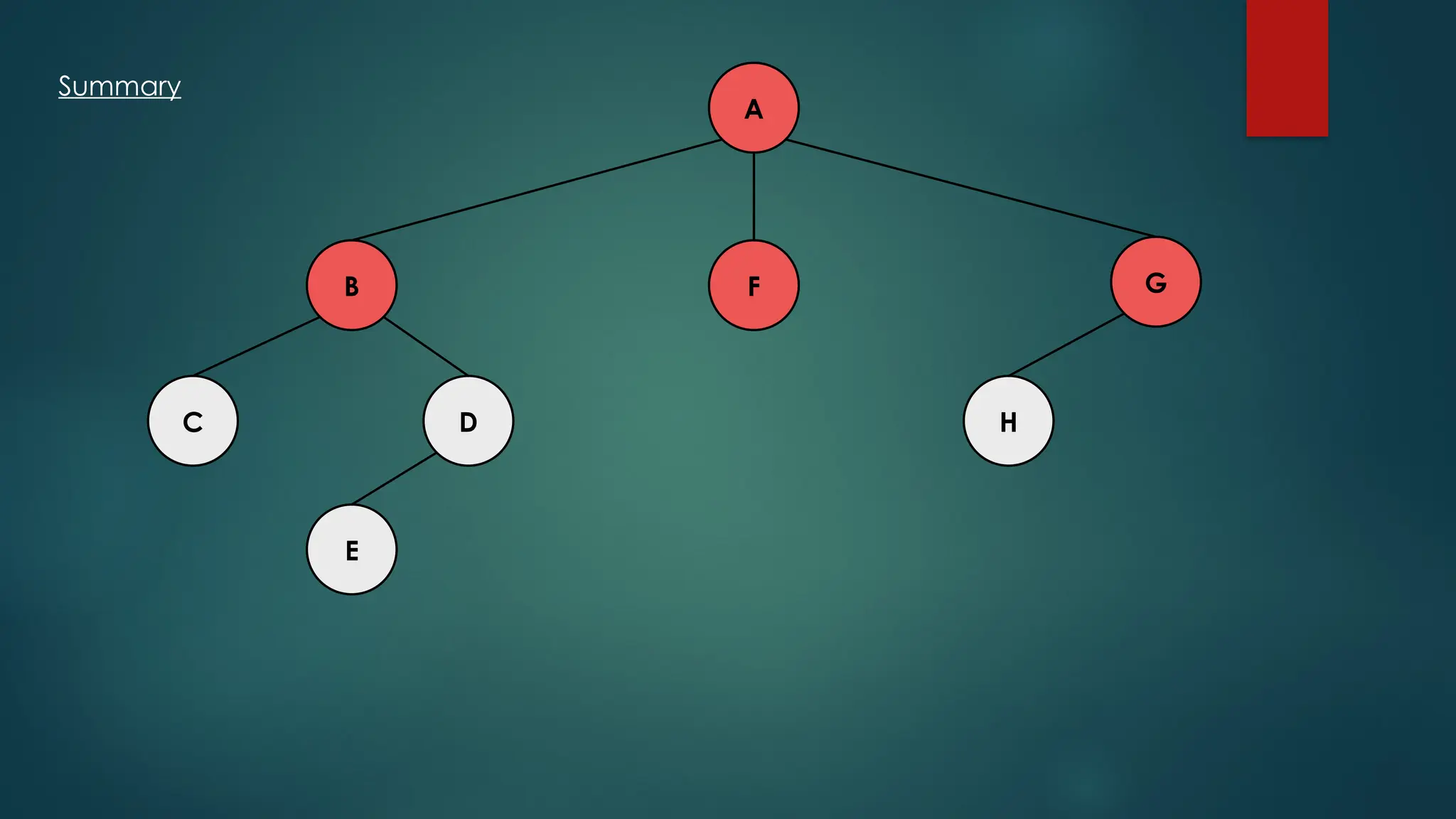
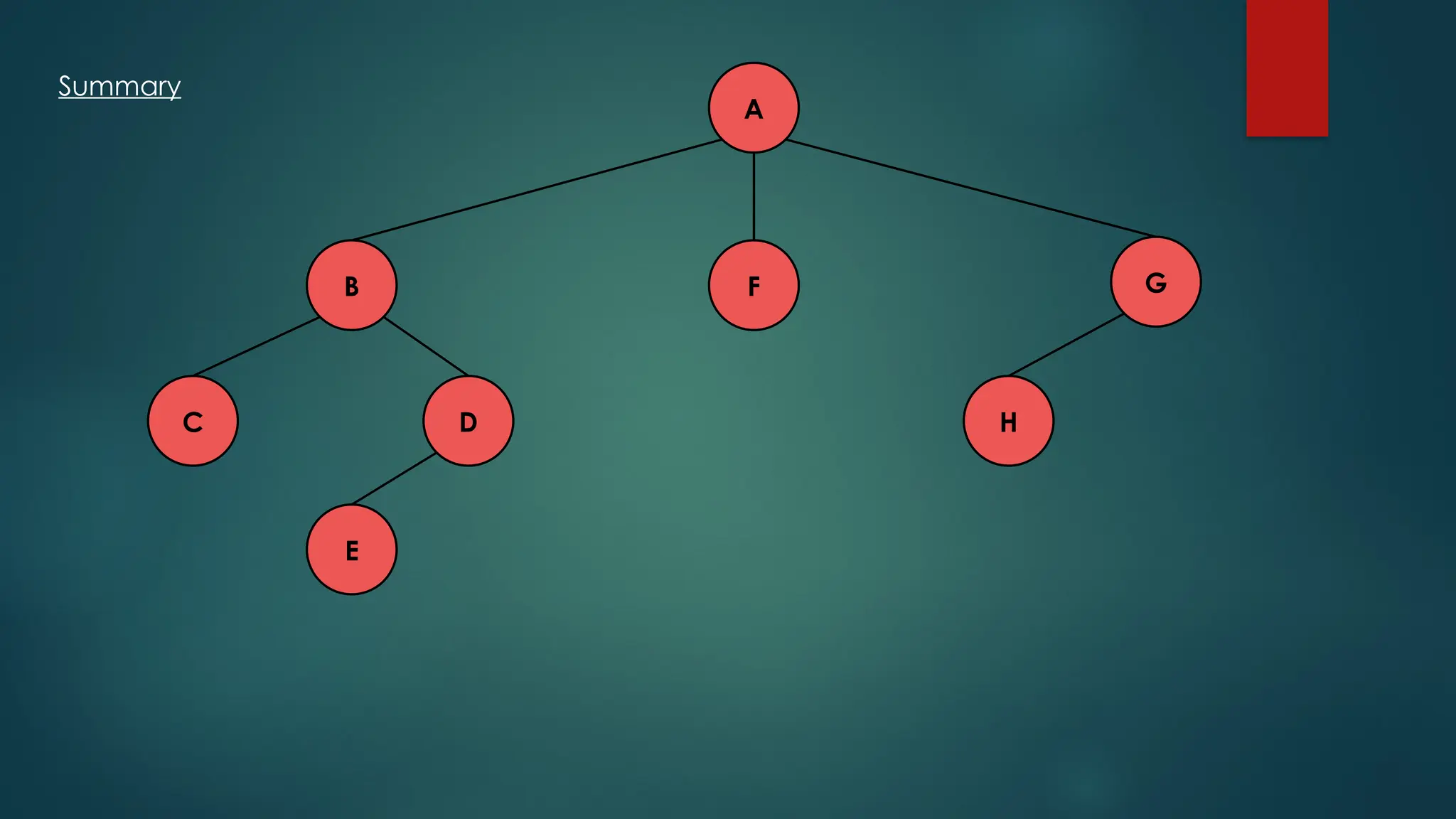
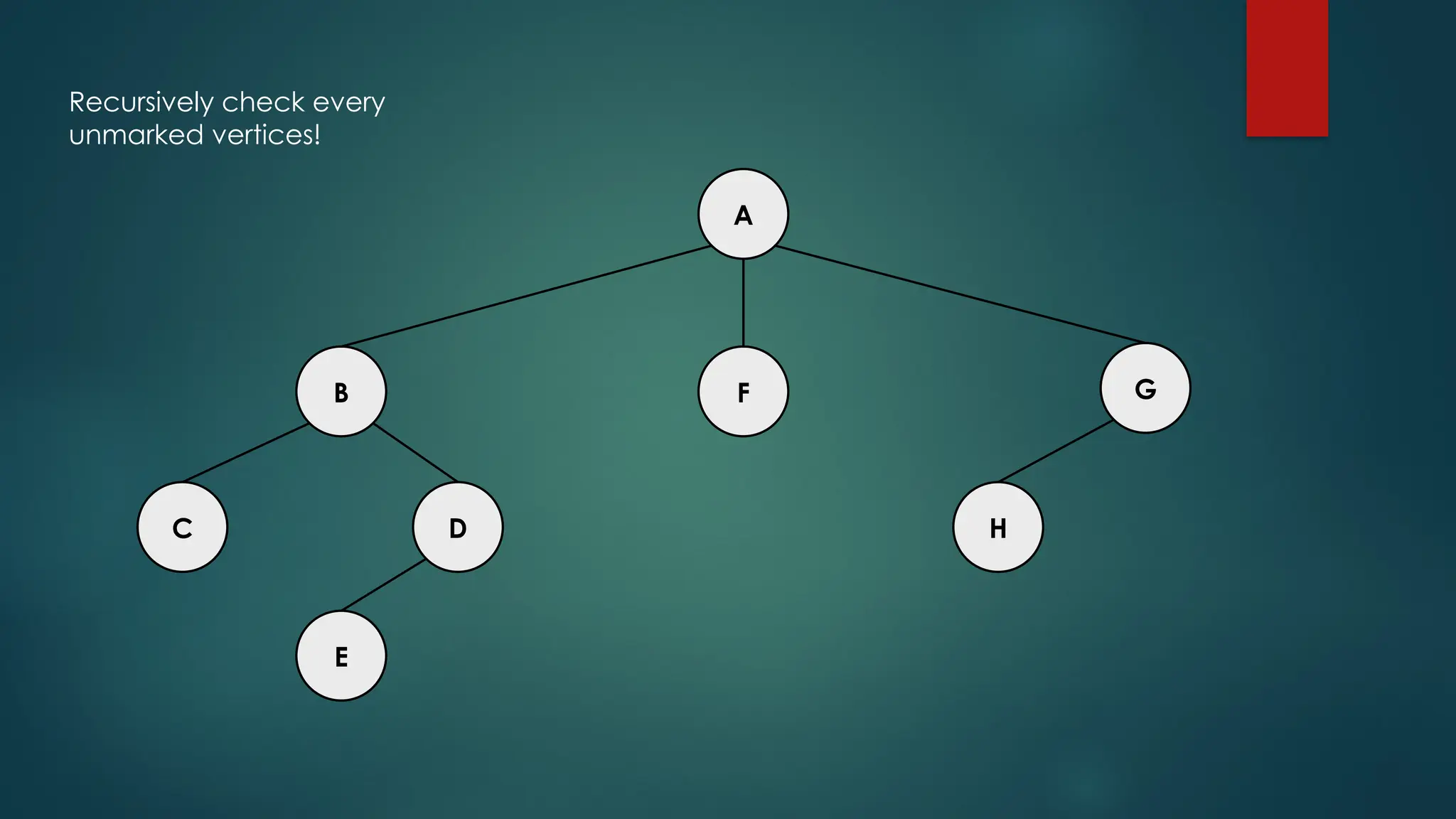
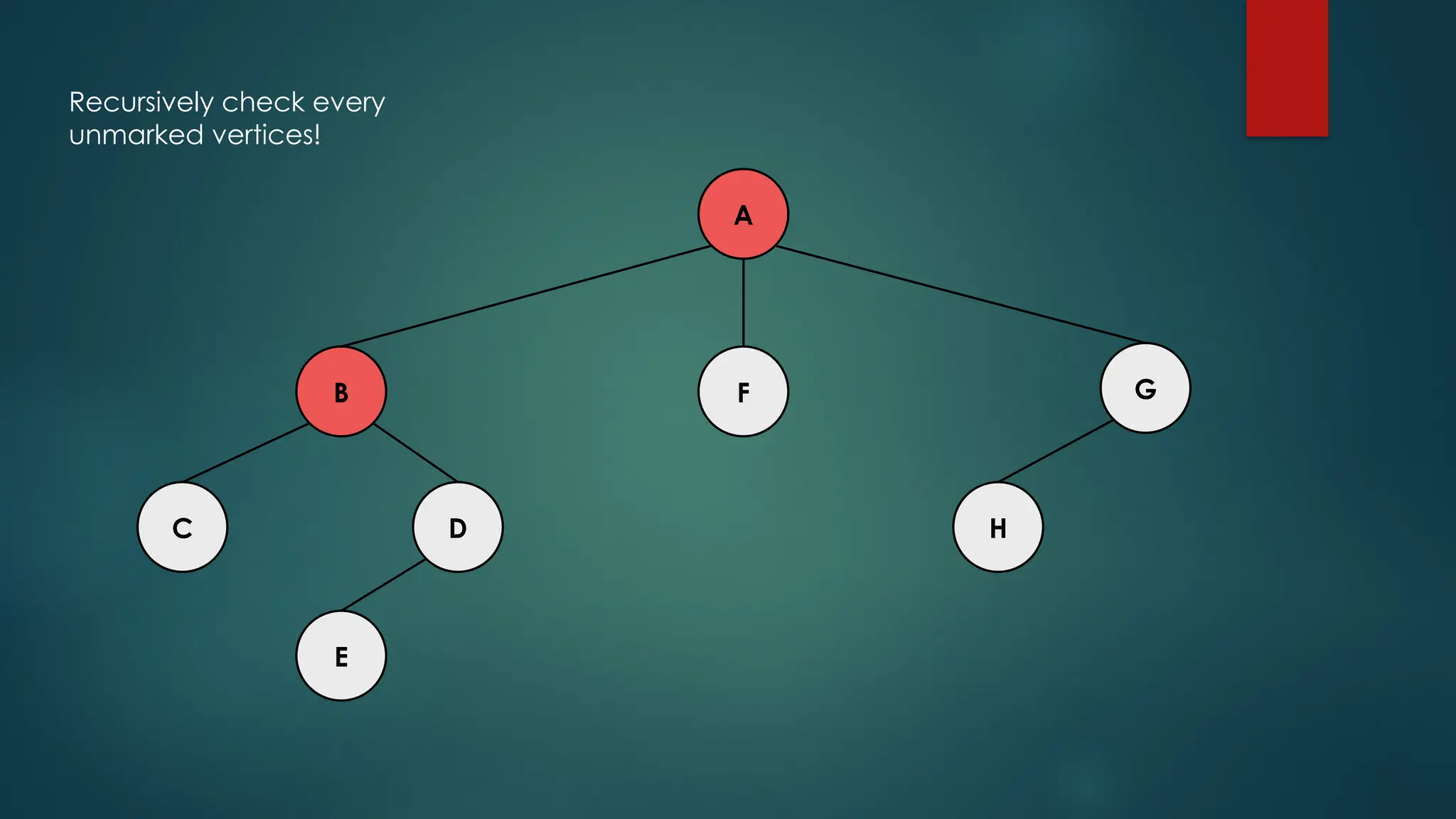
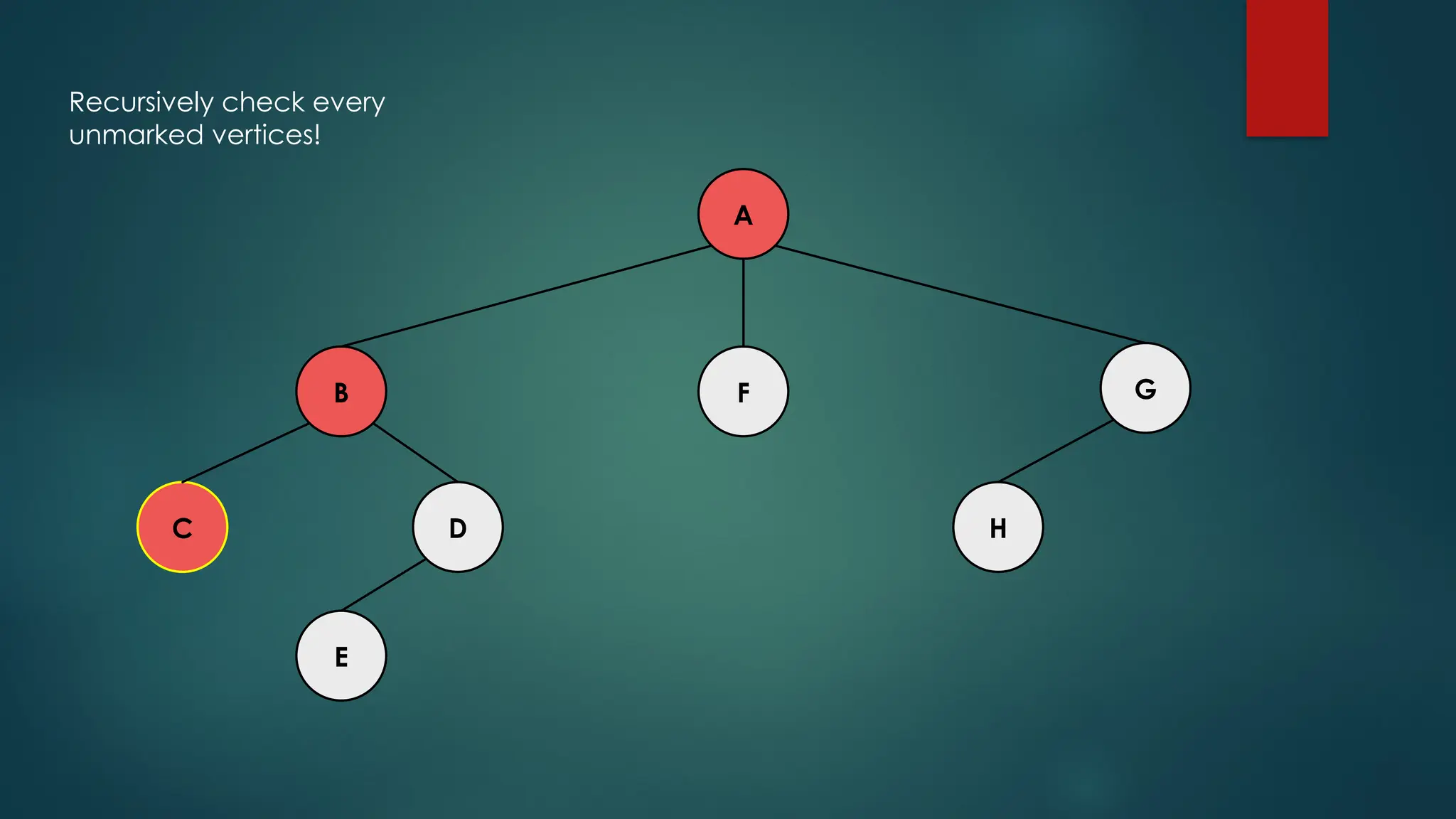
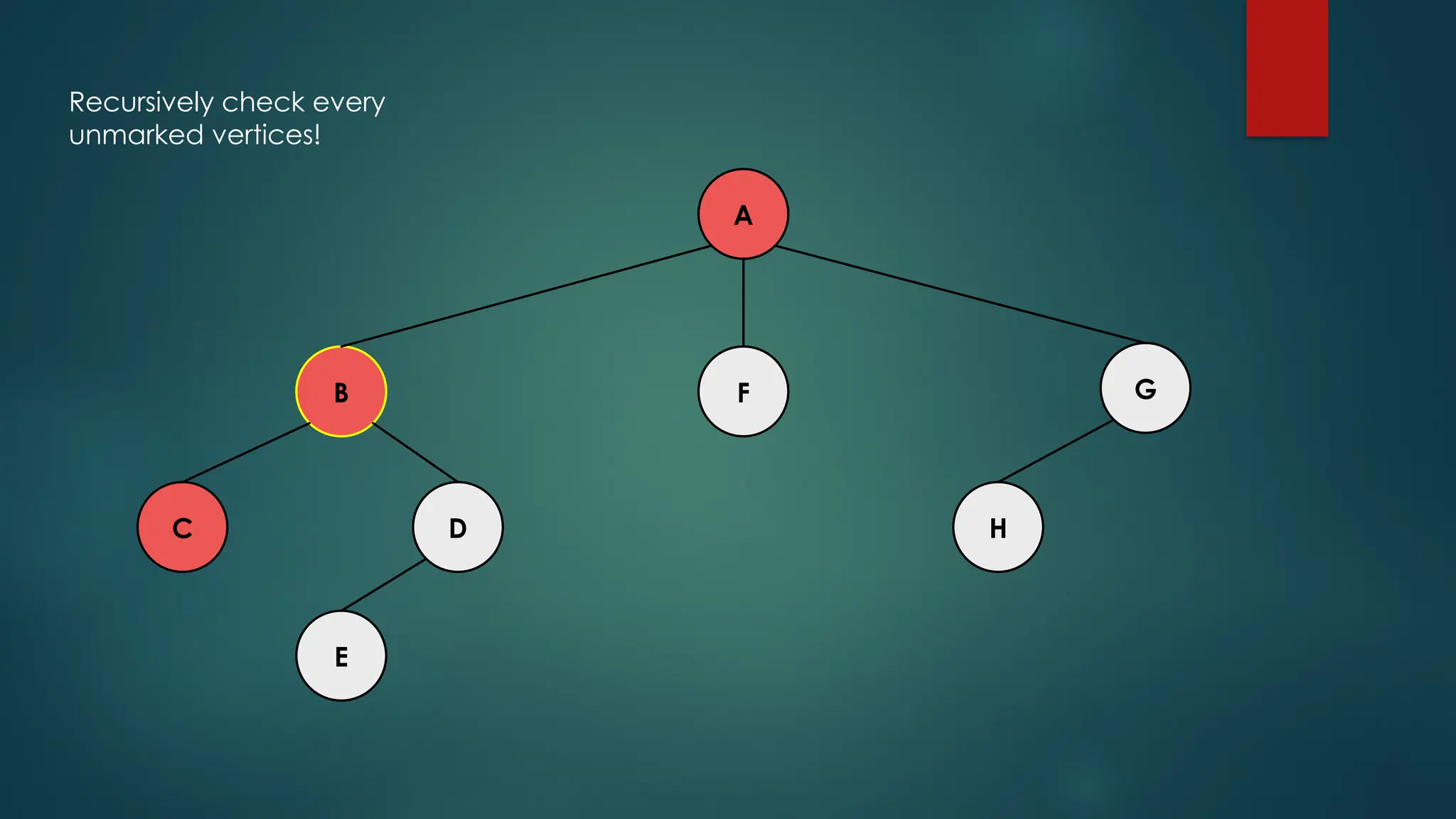
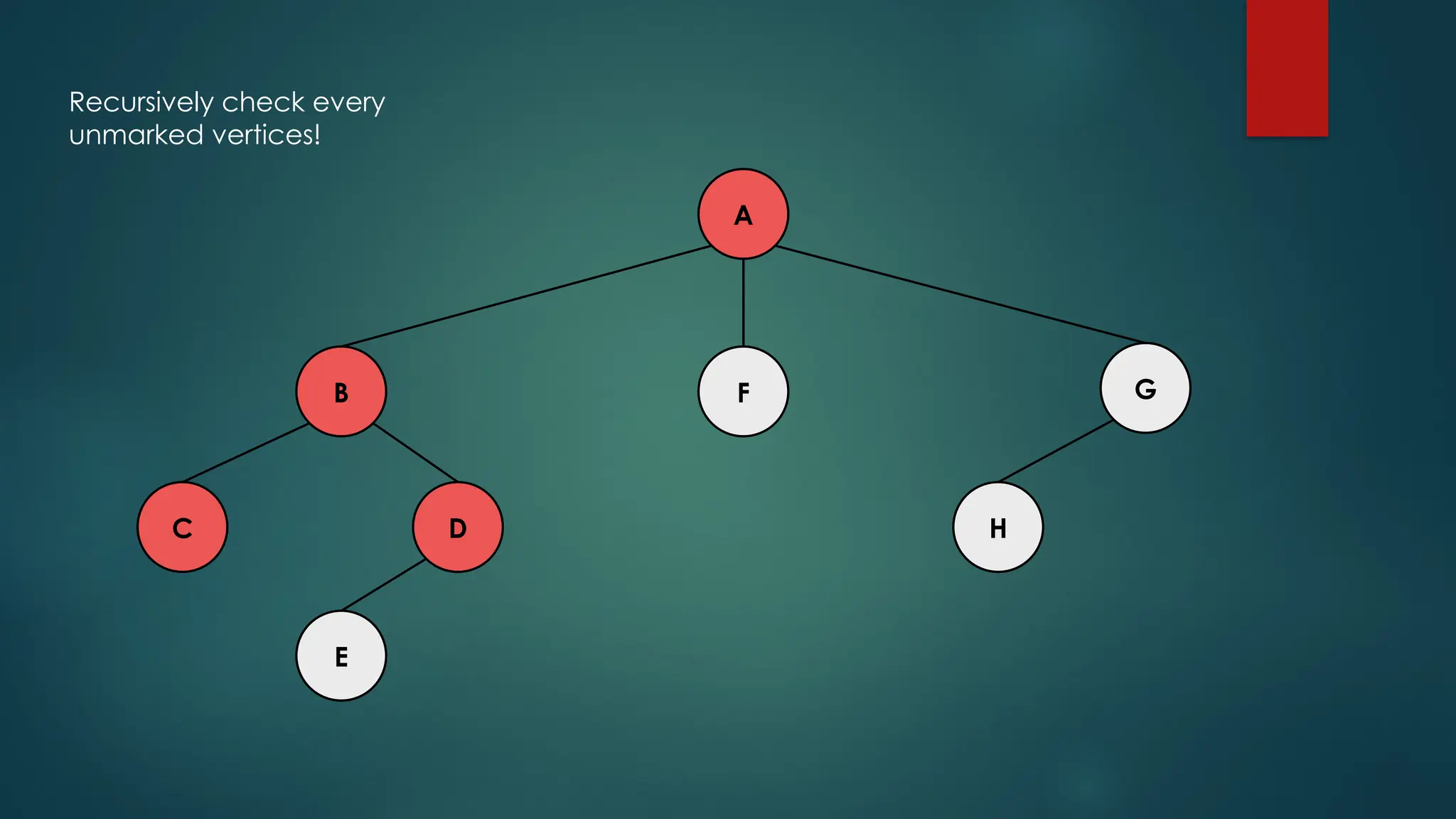
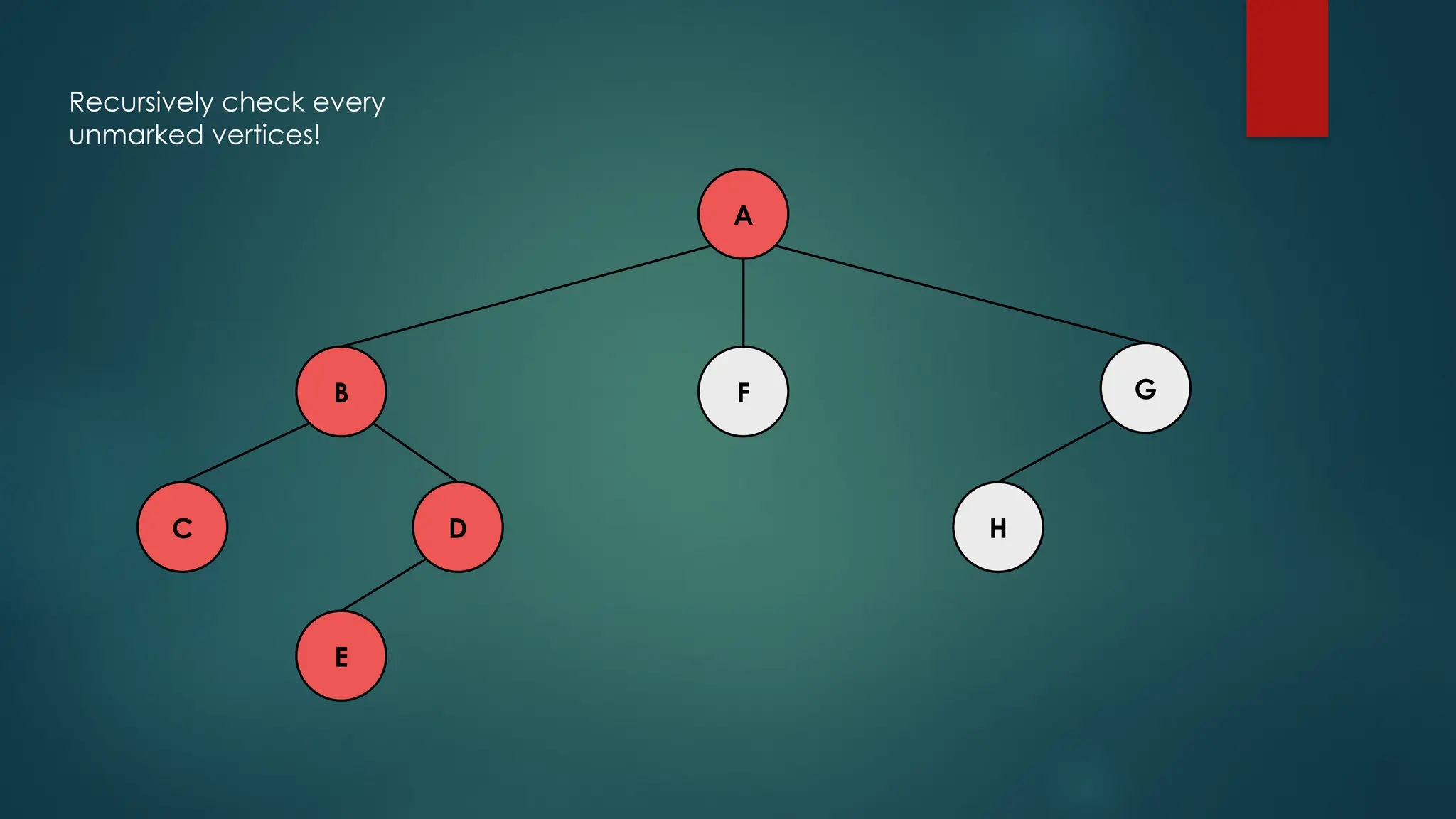
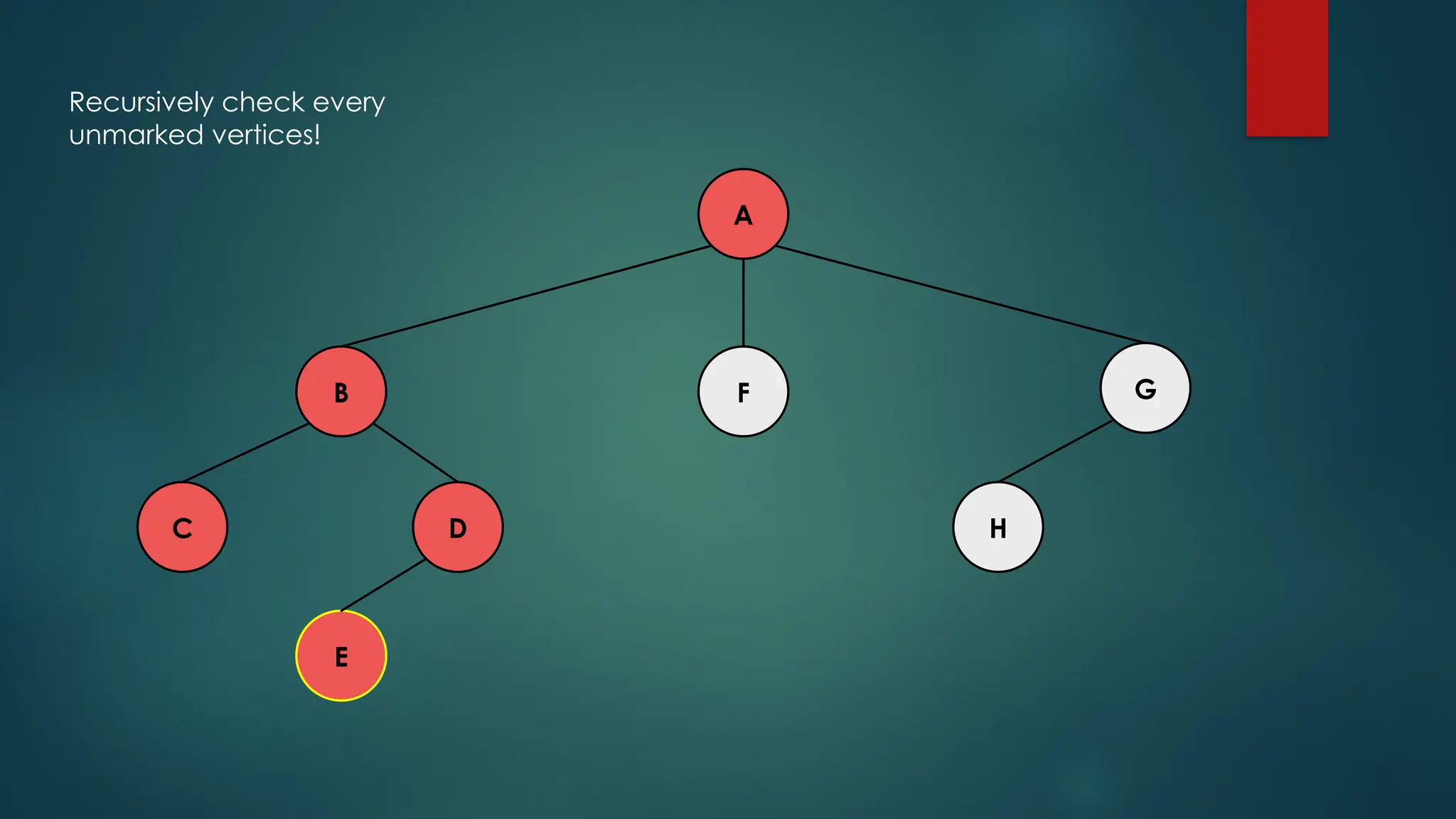
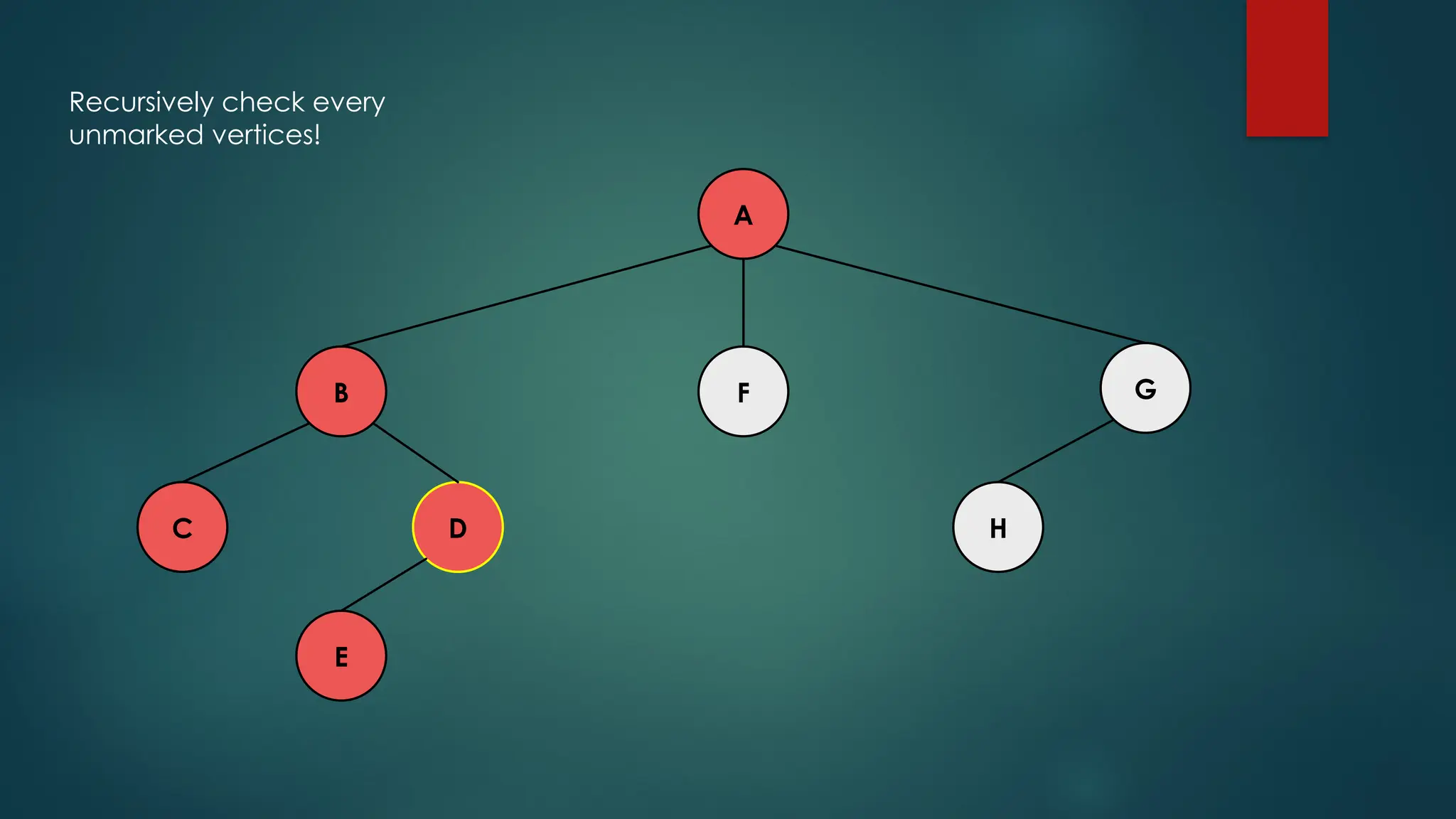
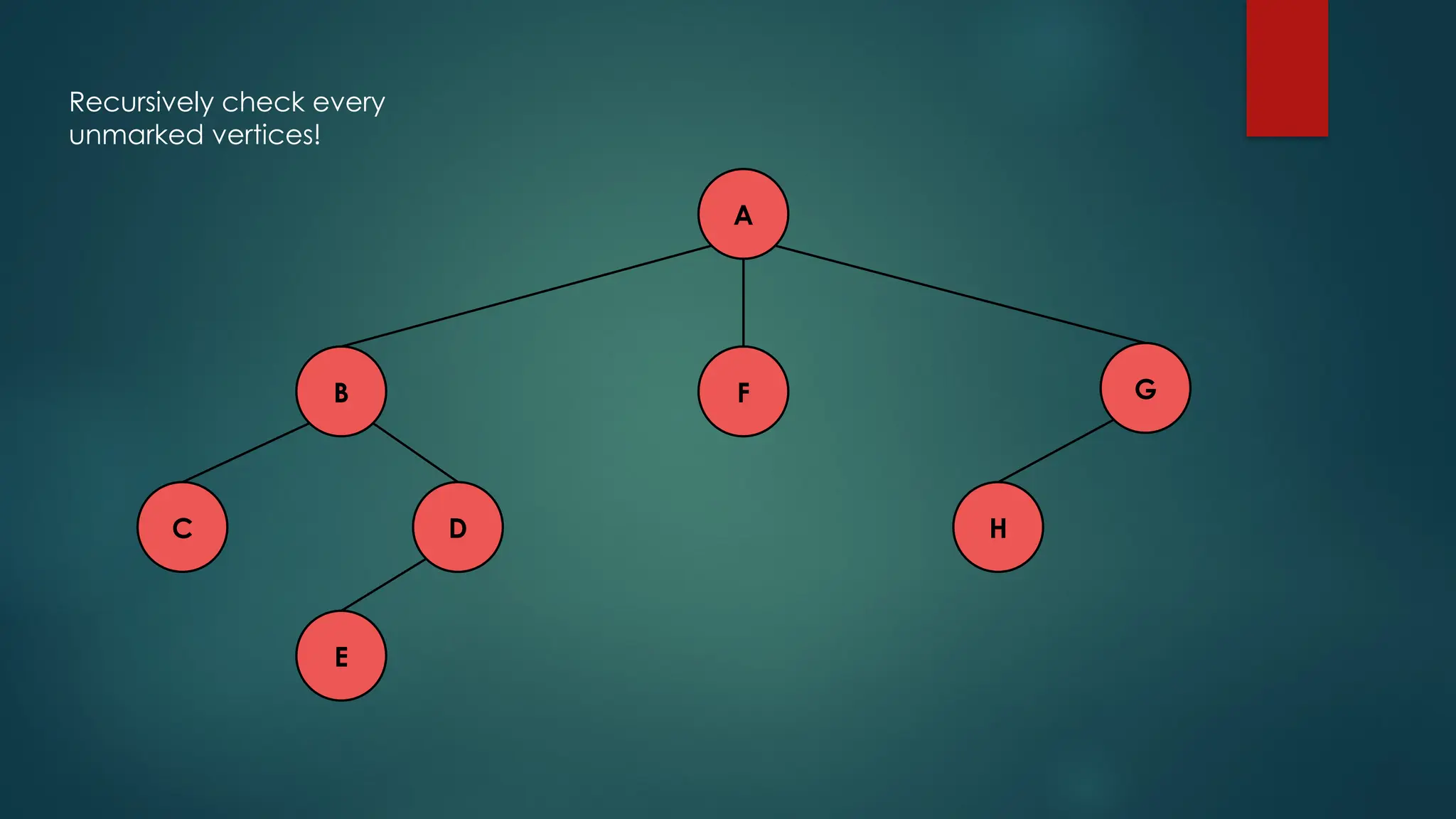
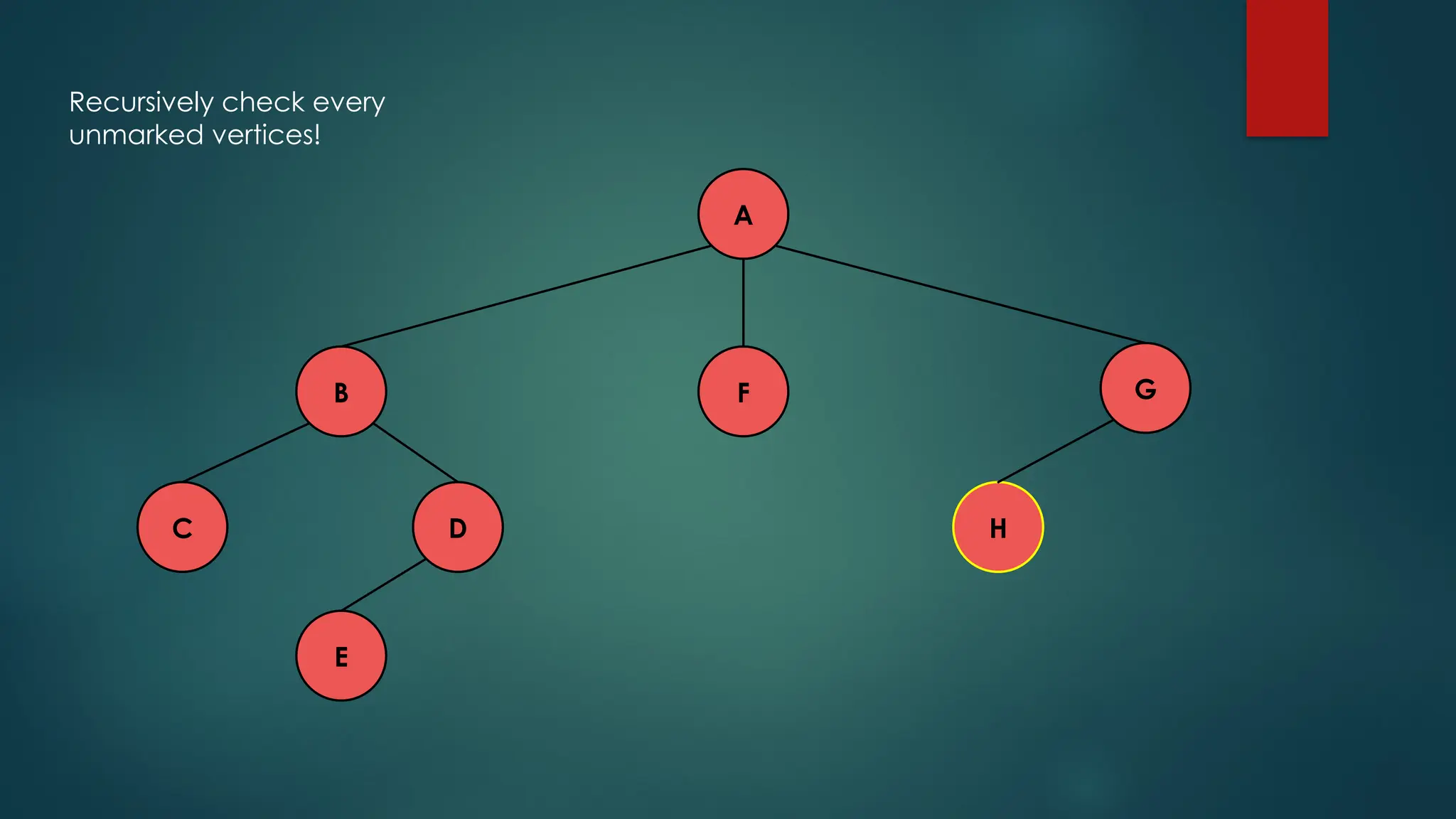
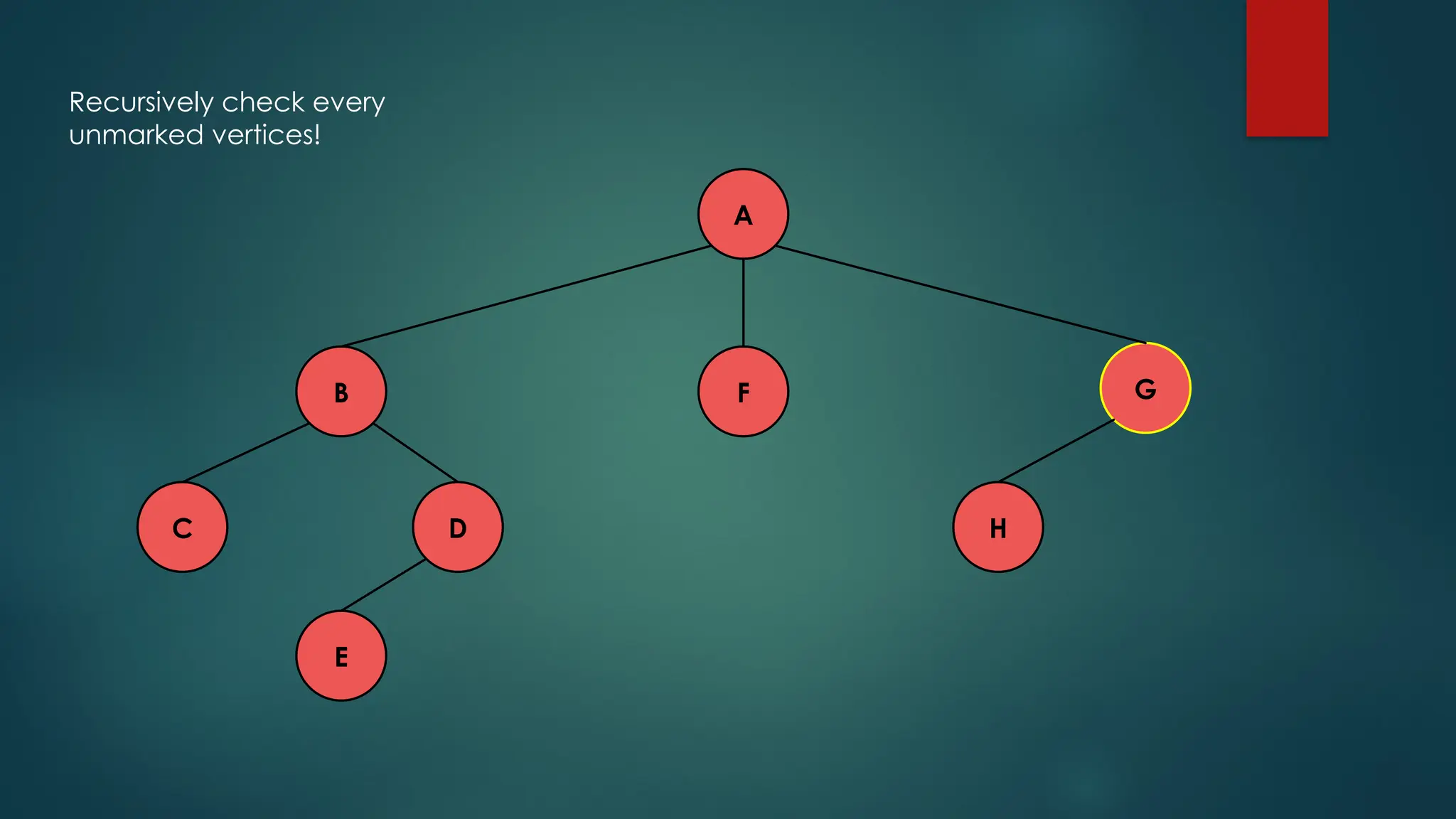
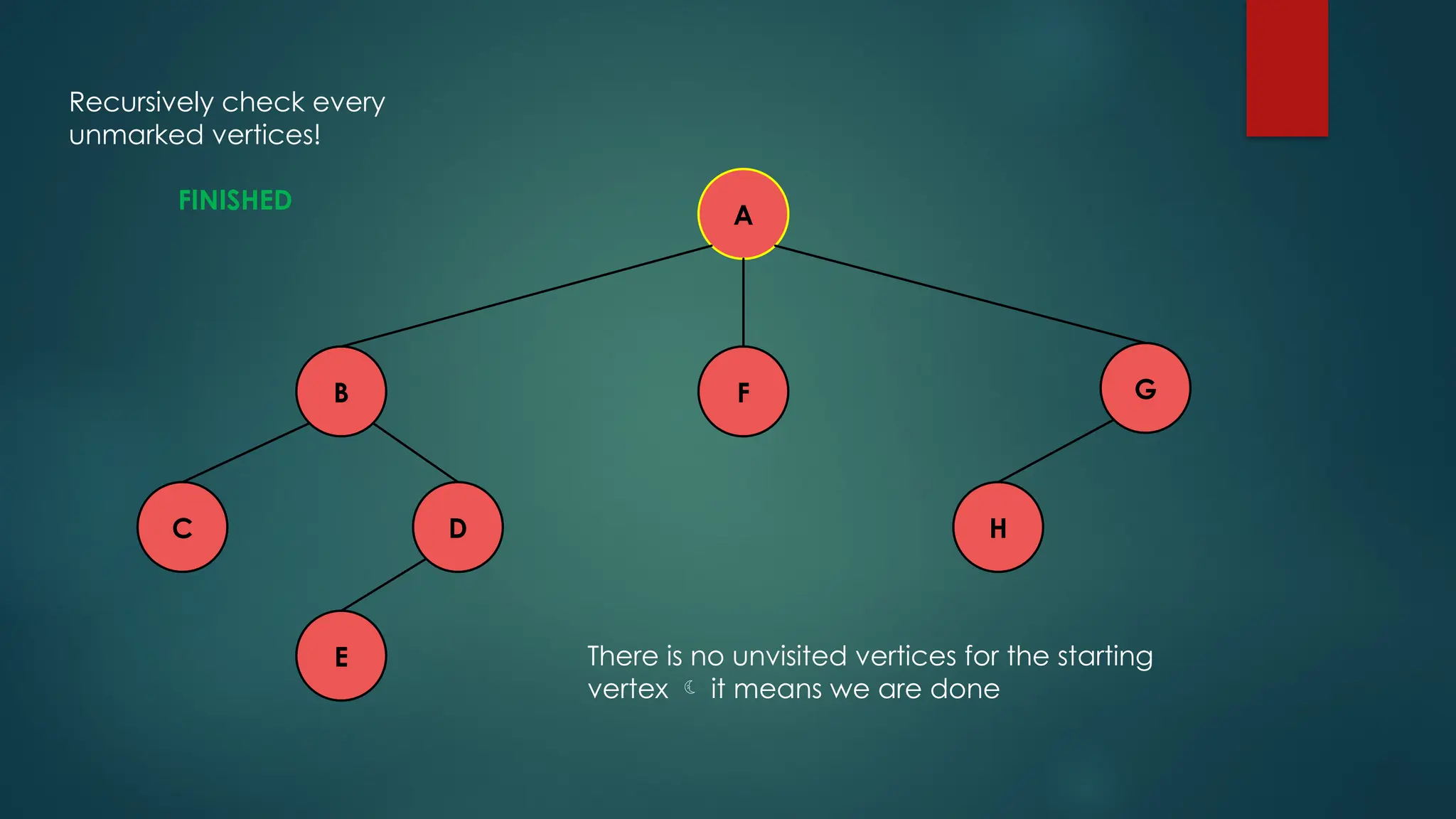
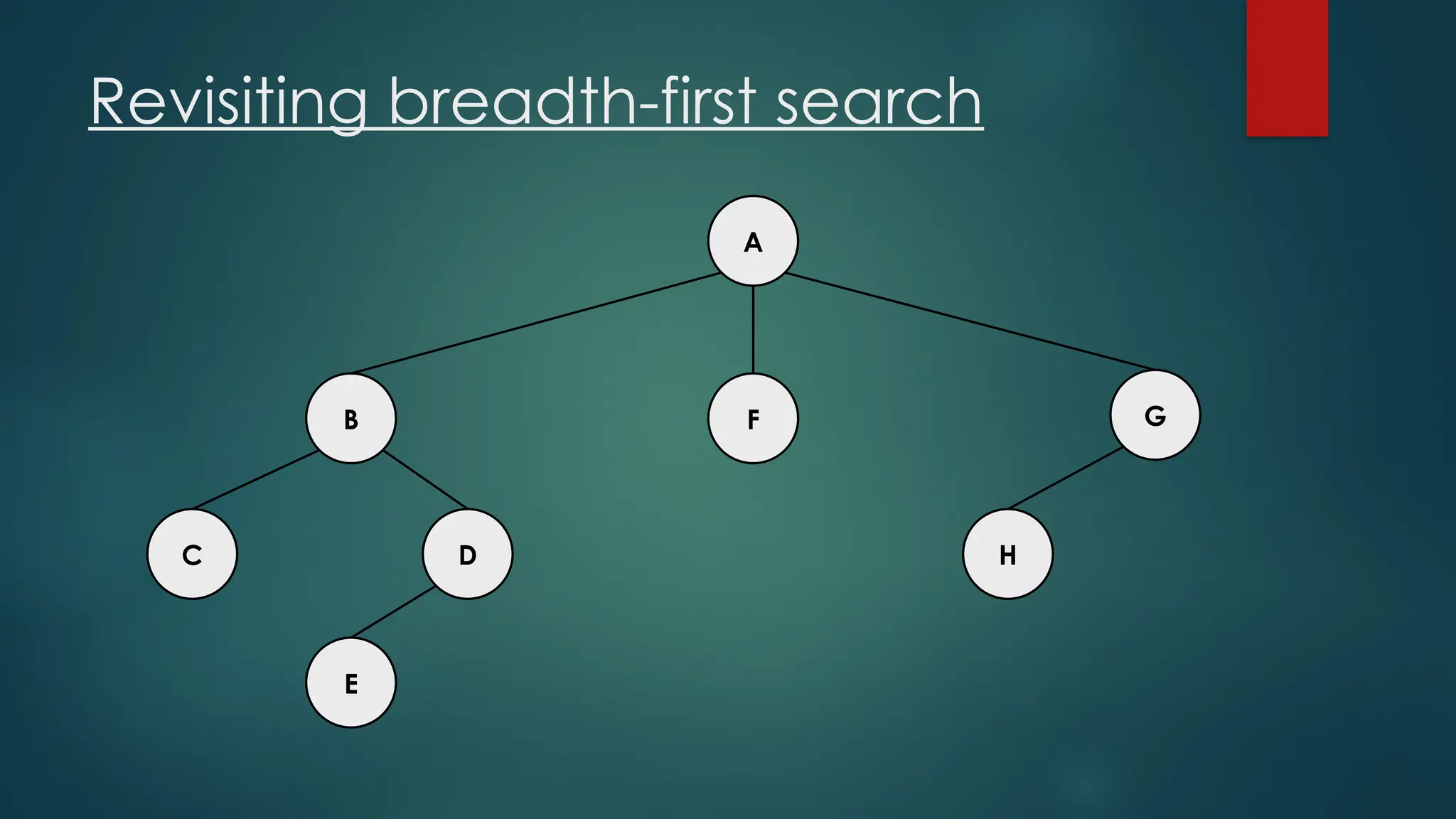
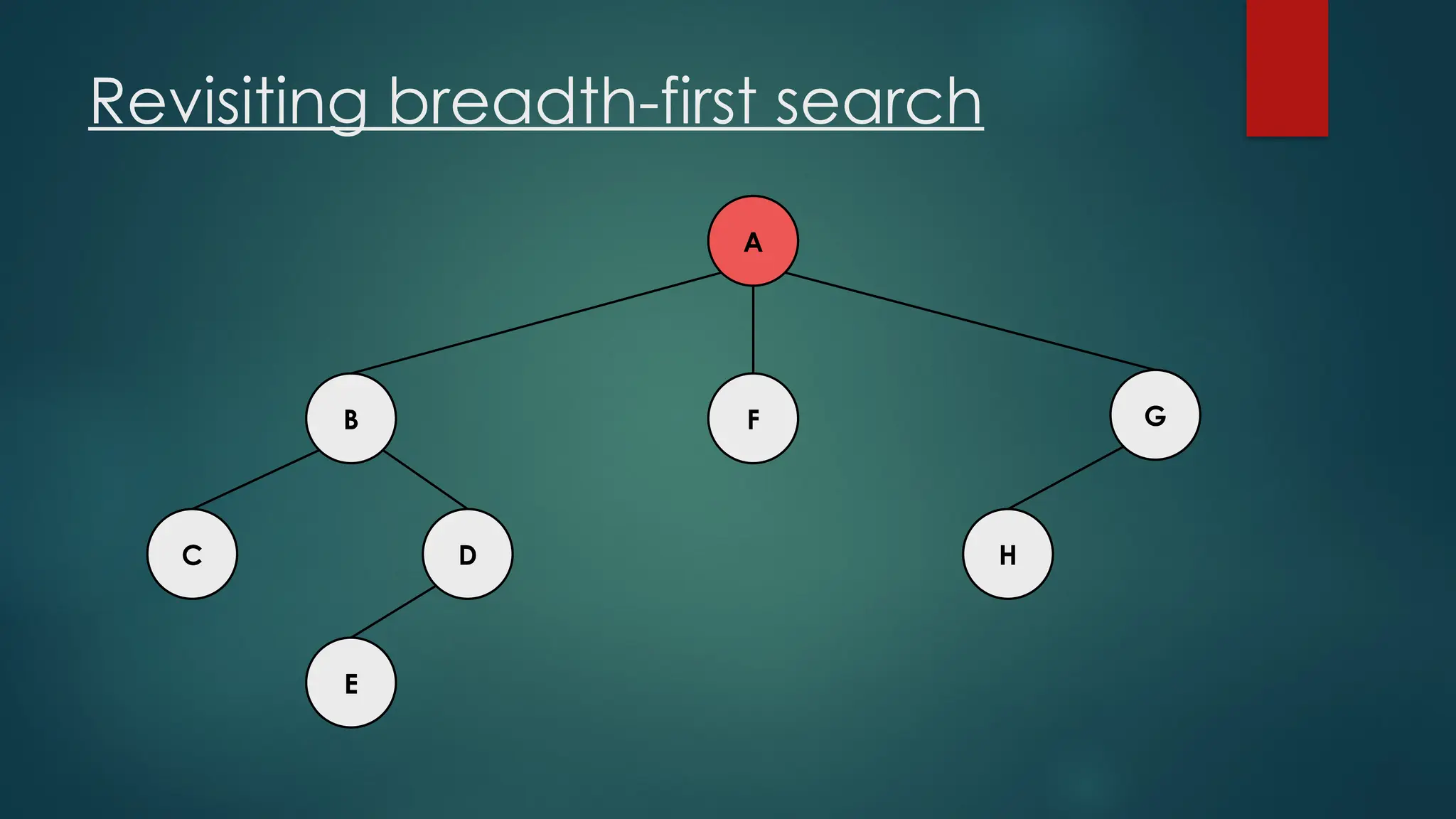
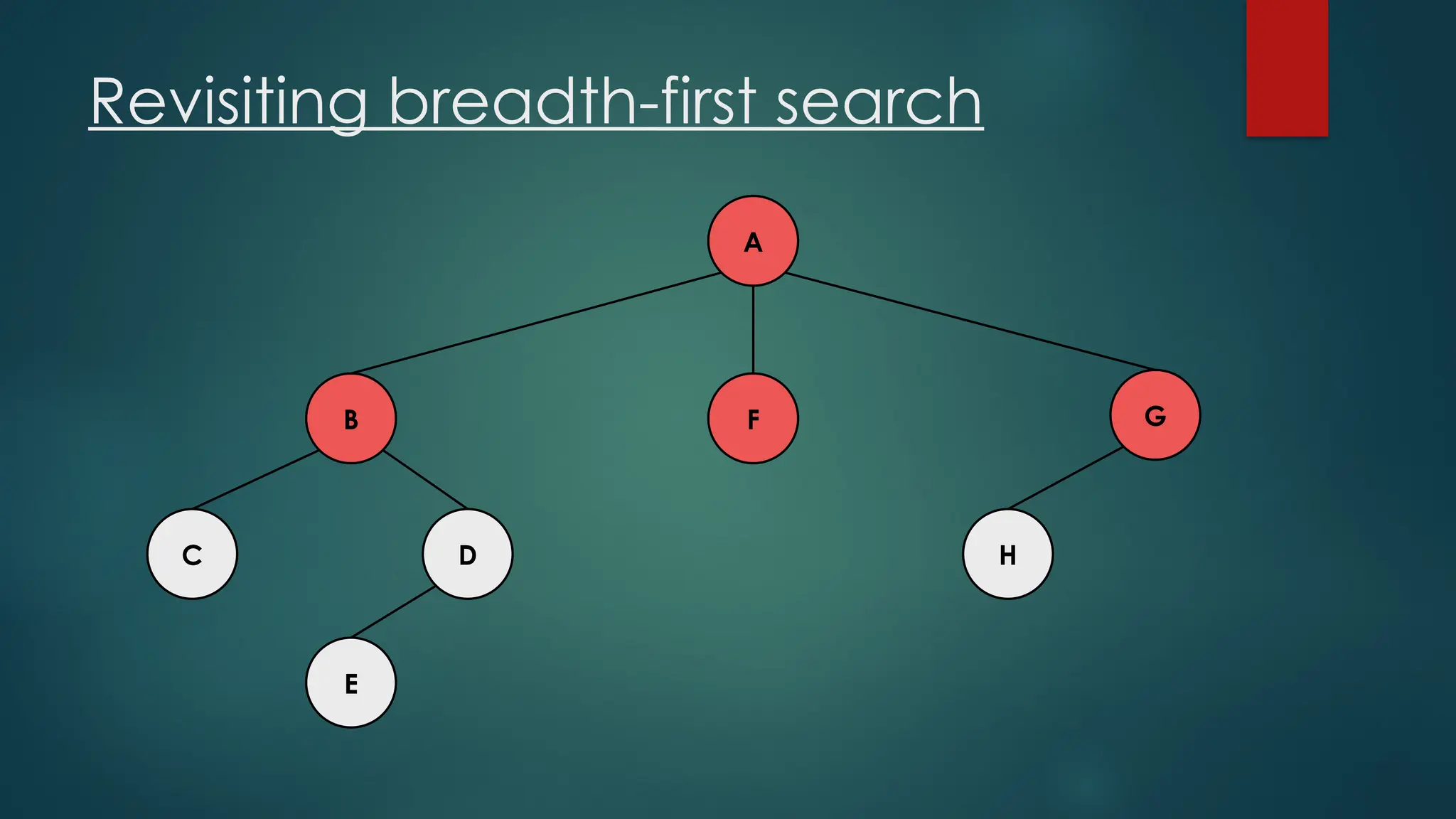
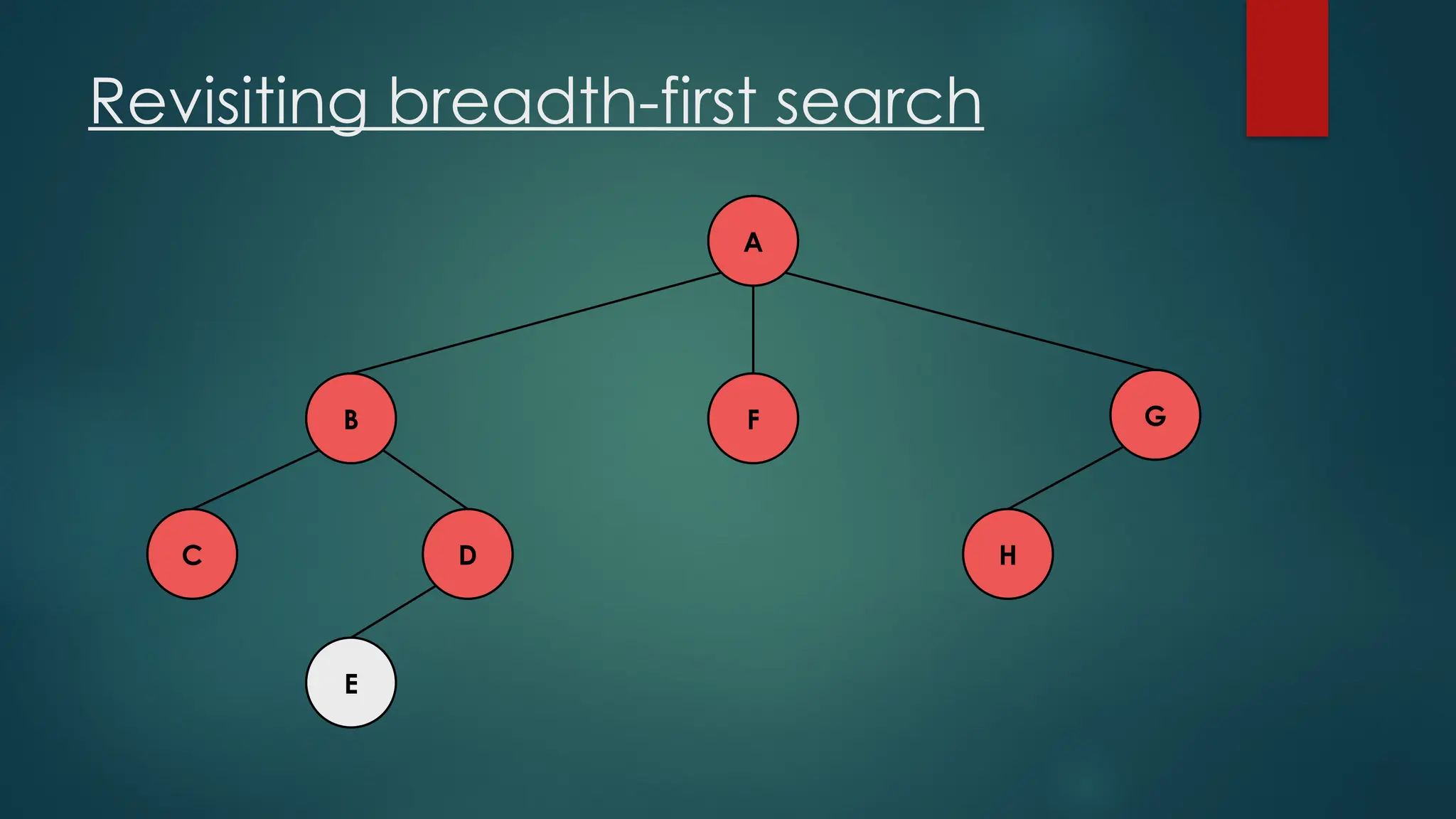
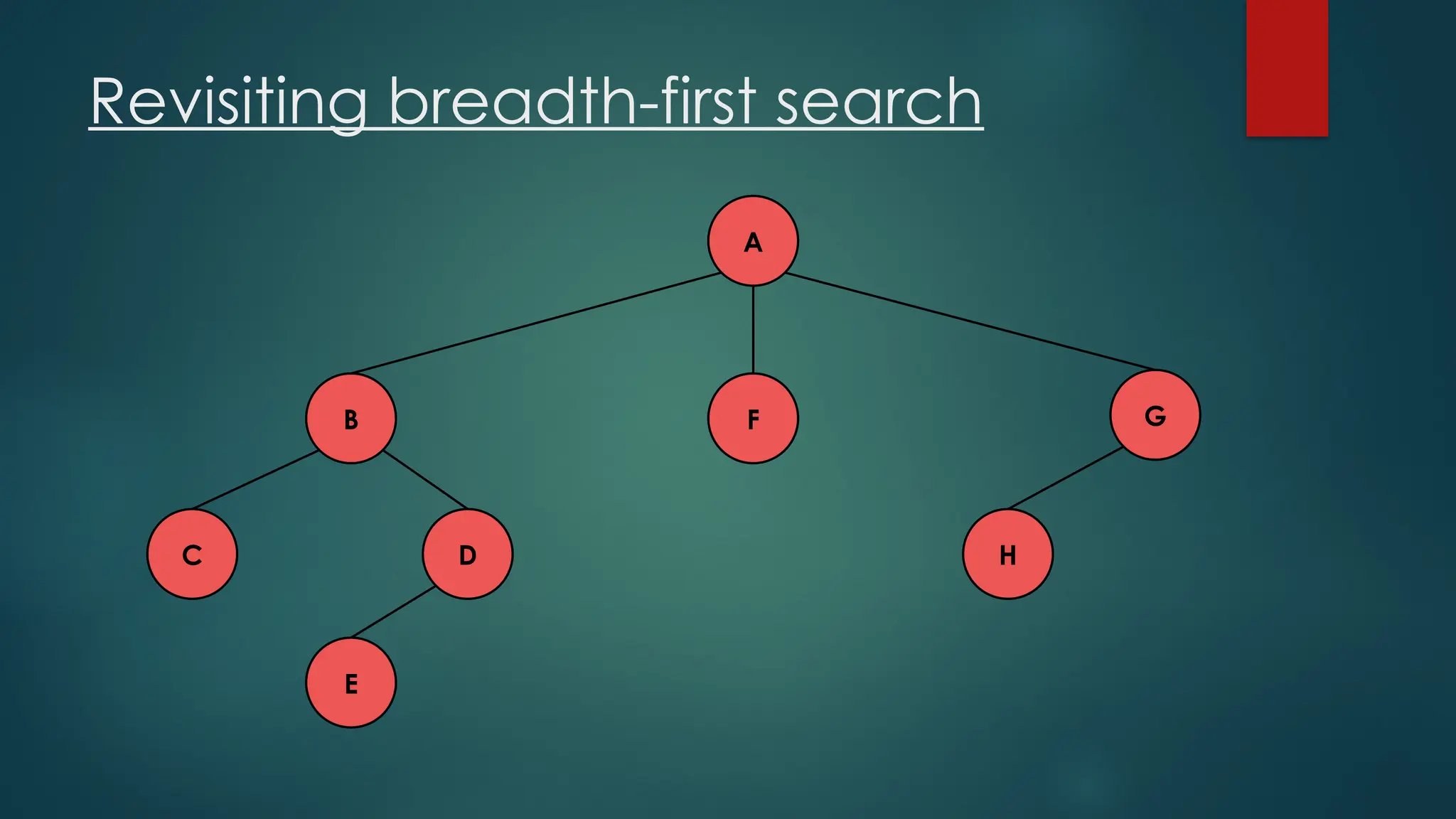
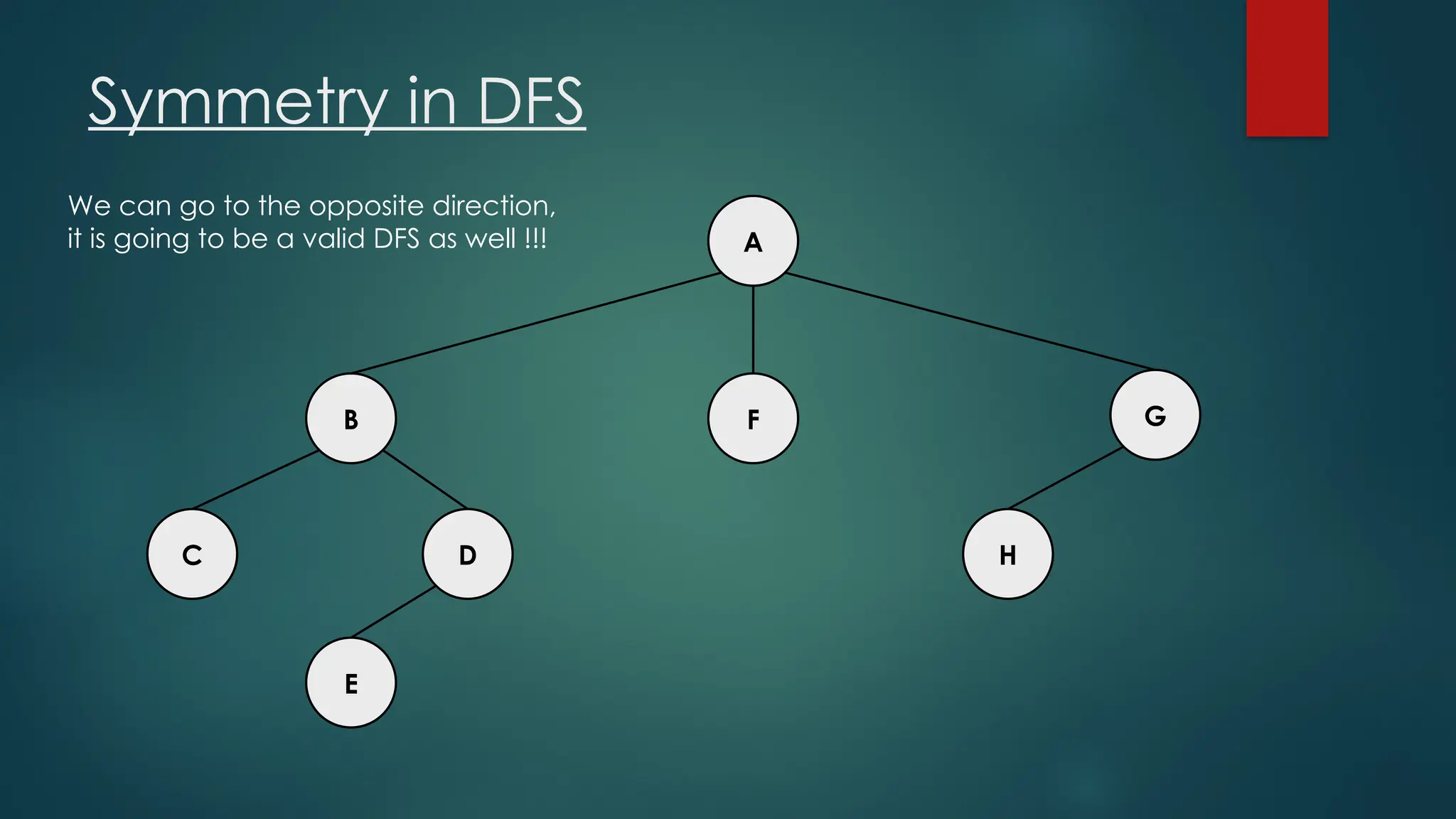
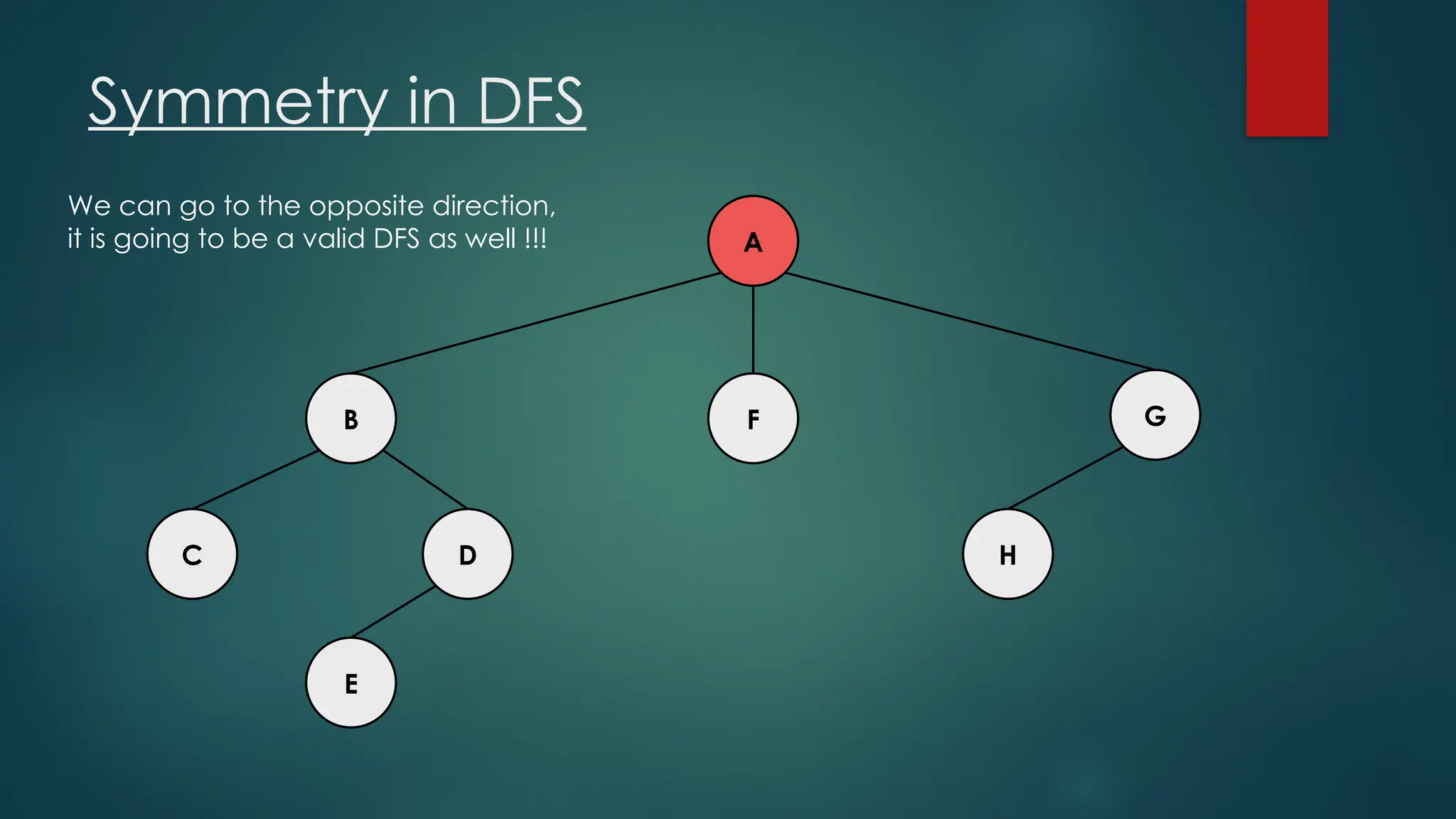
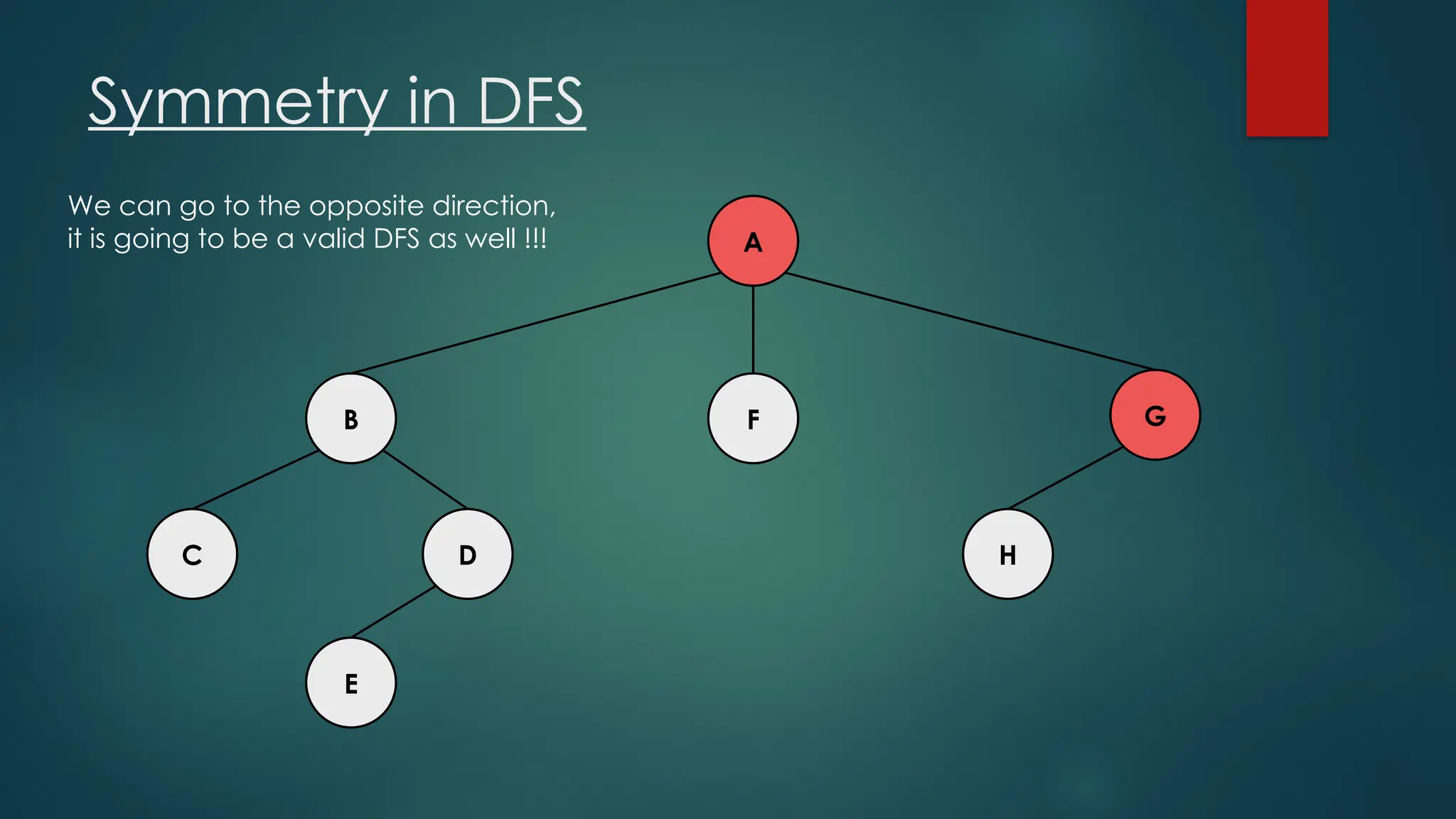
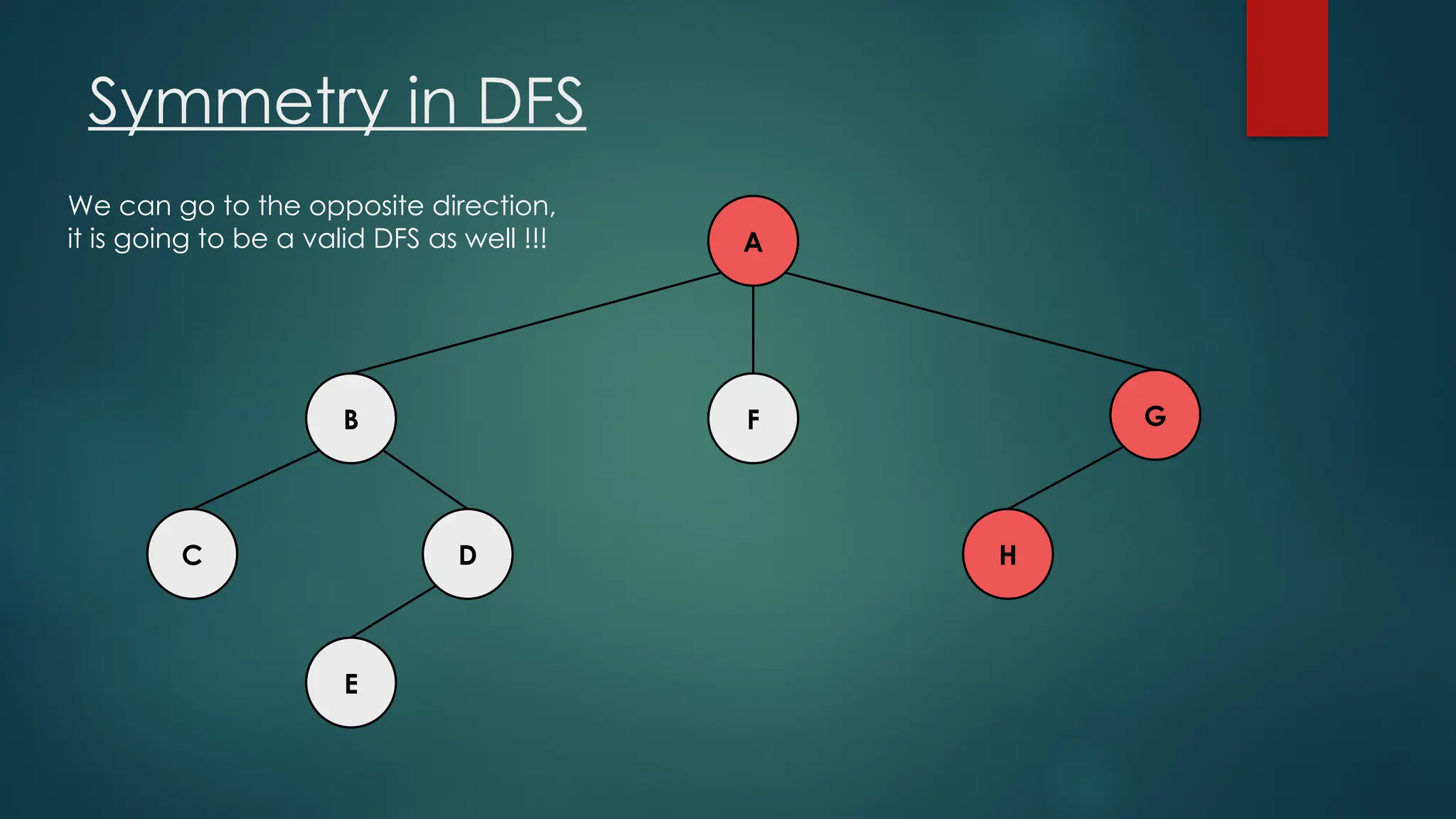
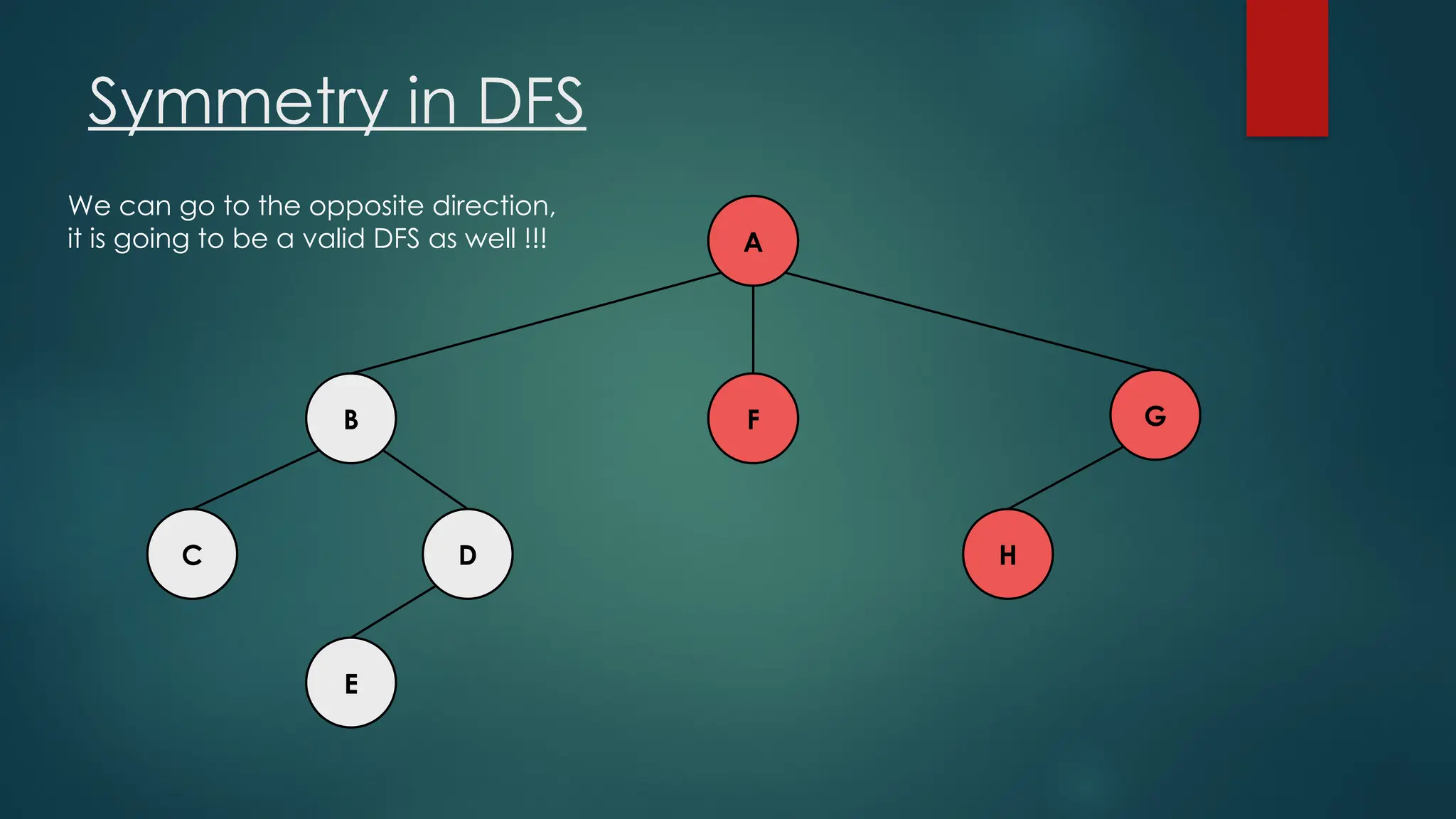
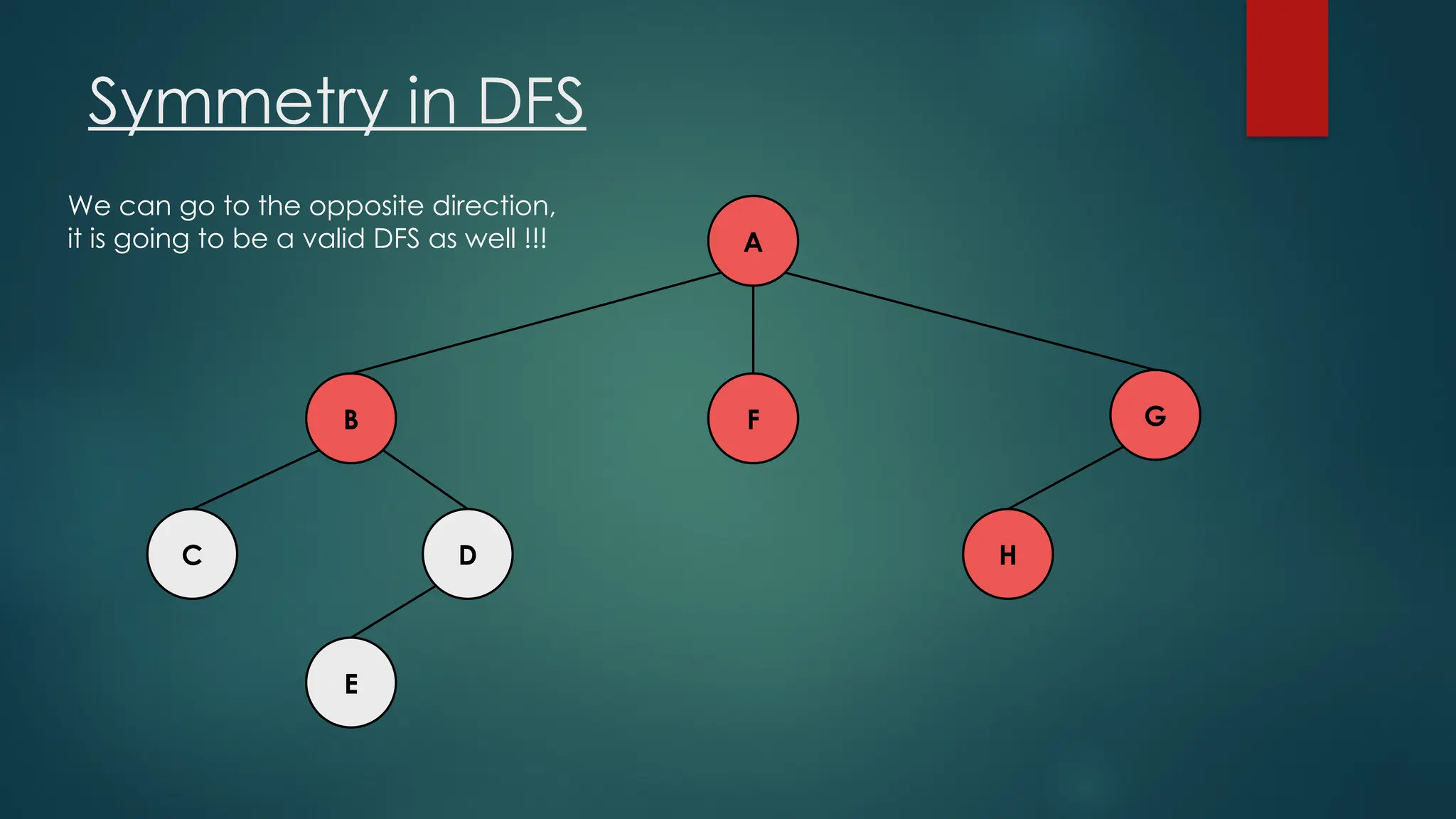
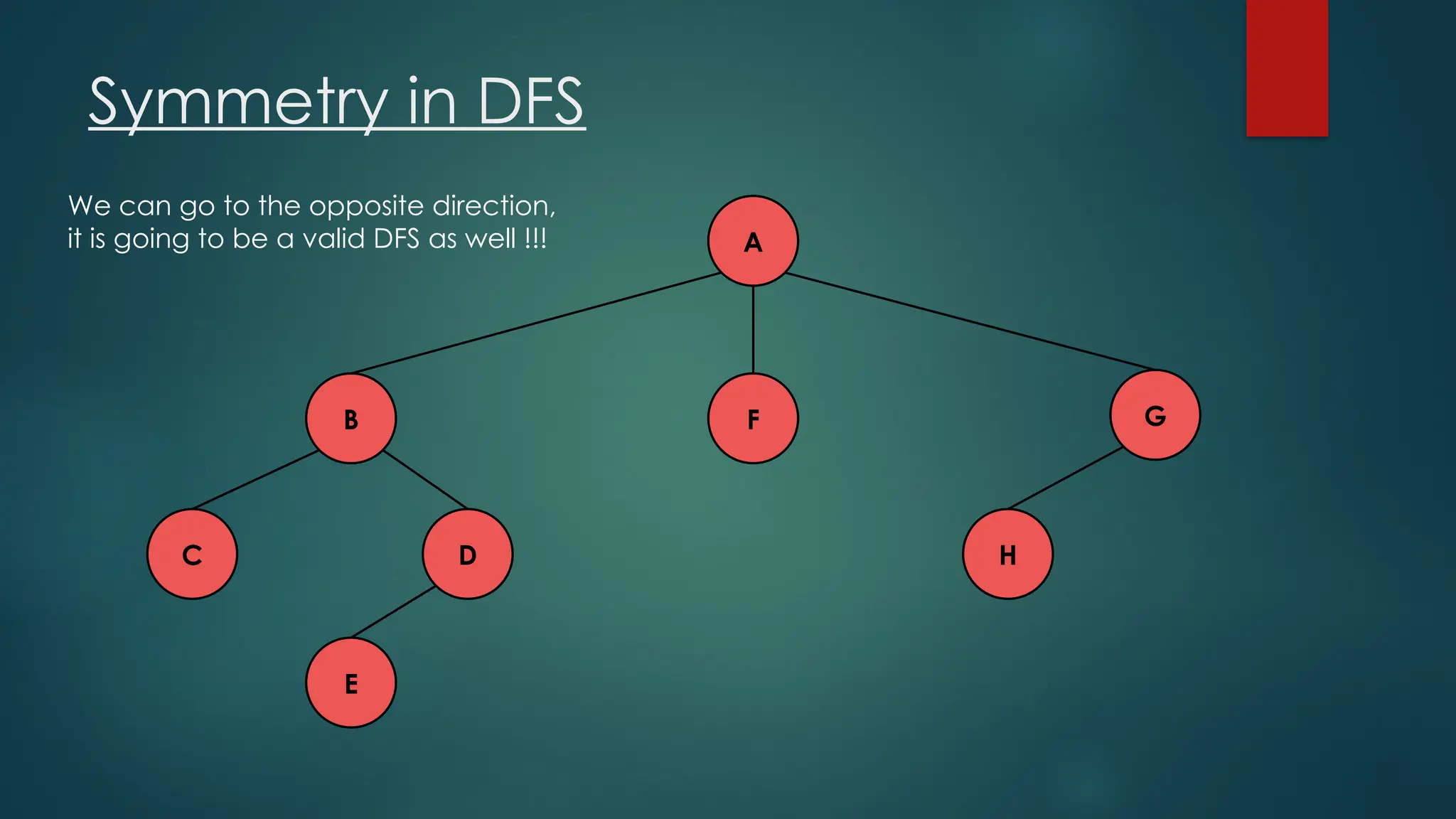
The document discusses breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS) algorithms for graph traversal, detailing their advantages, applications, and implementations. BFS visits every vertex once and has a time complexity of O(V + E) but uses more memory, while DFS explores branches as far as possible with slightly better memory efficiency. Applications include artificial intelligence, garbage collection, topological ordering, and cycle detection.