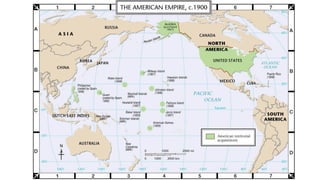
By 1900, European nations and former European colonies controlled 85% of the Earth's land. Major imperial powers included Britain, France, Germany, the United States, and Russia. New imperialism between 1870-1914 was driven by demands of industrial economies for resources and markets, nationalism and militarism, and beliefs in social Darwinism and the white man's burden. European powers colonized much of Africa and Asia, often exploiting local populations. The United States also joined in imperialism through acquiring Alaska, Hawaii, Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines following the Spanish-American War of 1898.