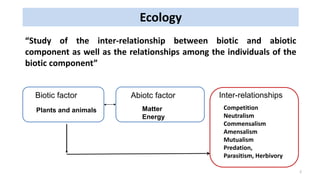
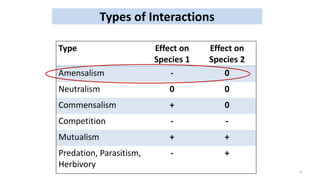
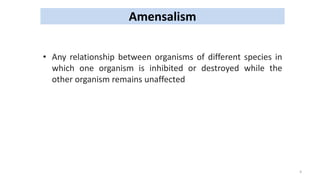
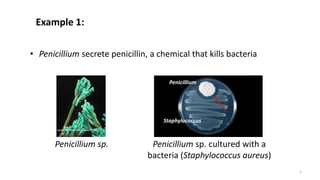
This document summarizes different types of inter-relationships between biotic and abiotic components in an ecosystem. It defines amensalism as a relationship where one species inhibits or destroys the other species with no effect on itself. Examples of amensalism provided include penicillium secreting penicillin that kills bacteria but is not affected, and allelopathy where some plant species release chemicals that inhibit the growth of other plants and microbes. The document also gives examples of black walnut trees and eucalyptus releasing chemicals through their leaves and roots that suppress the growth of surrounding vegetation.