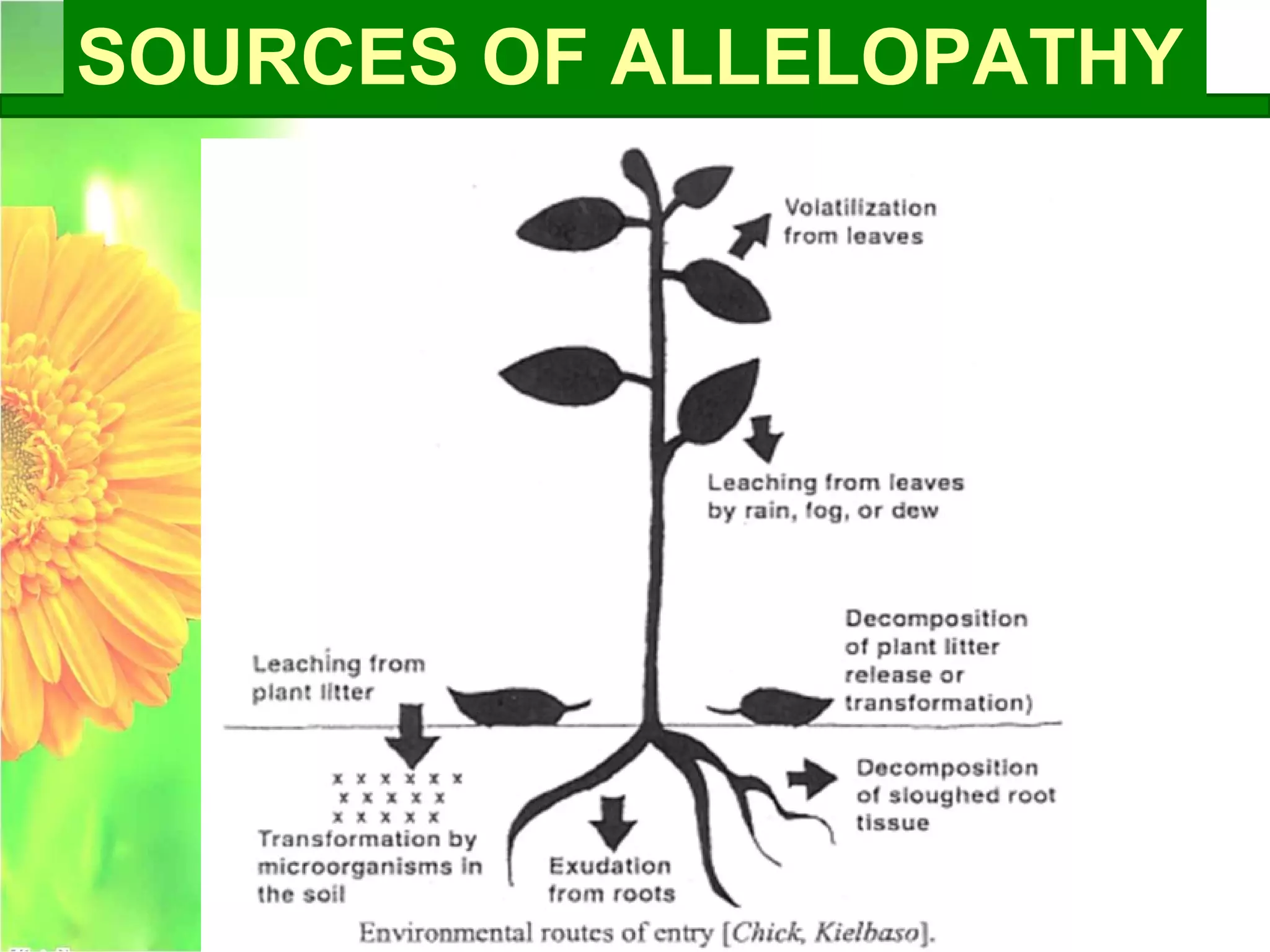
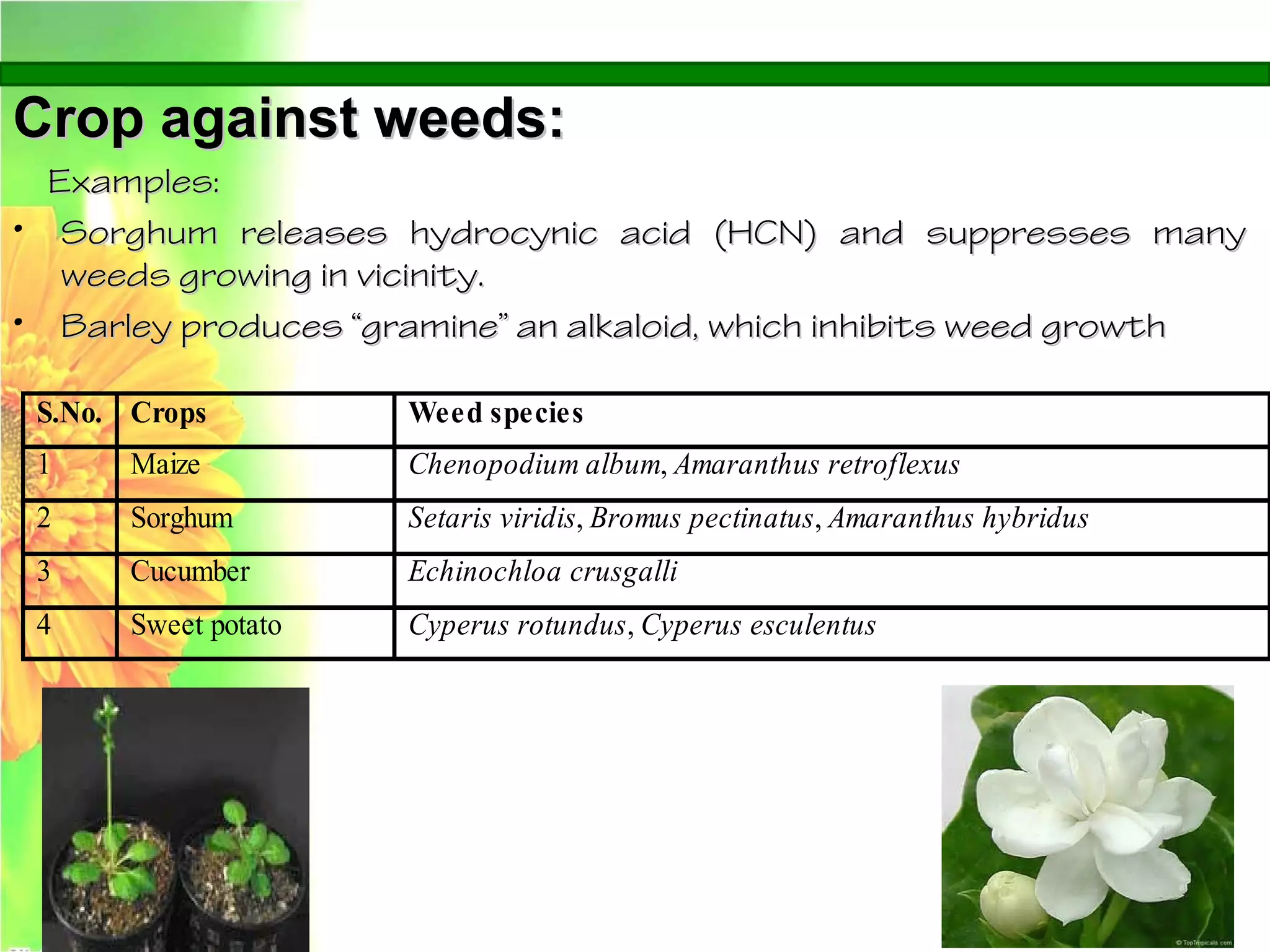
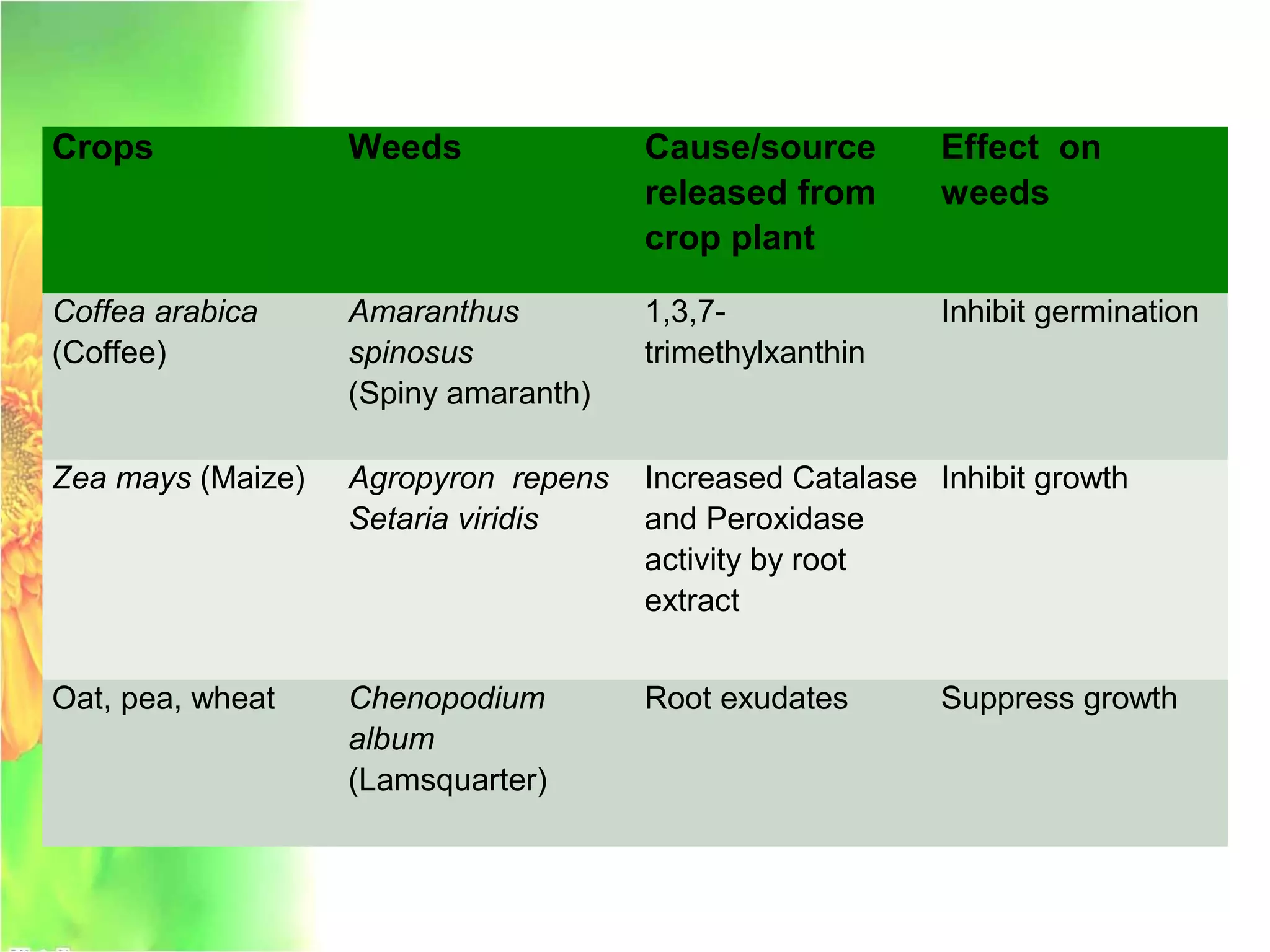
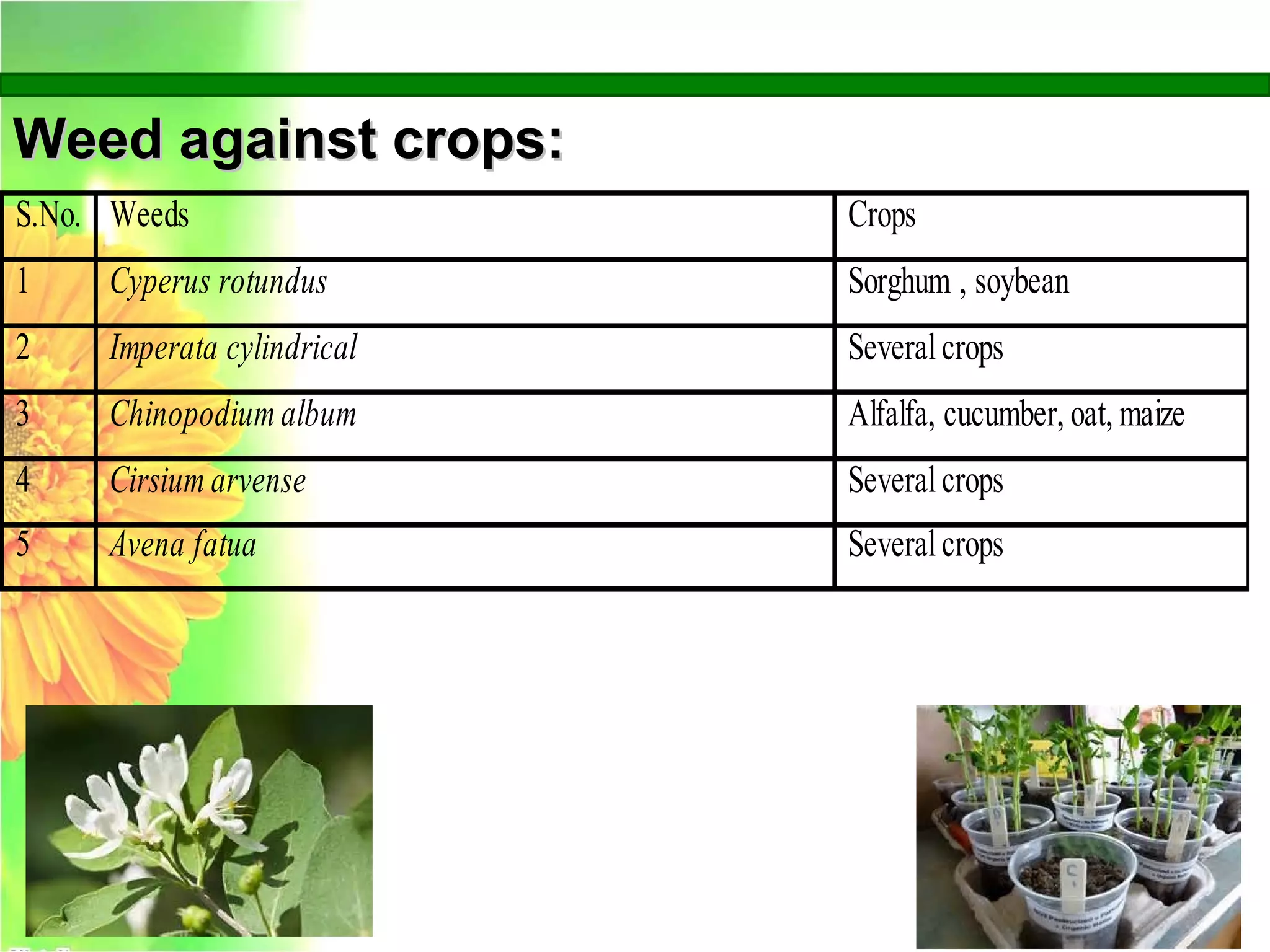
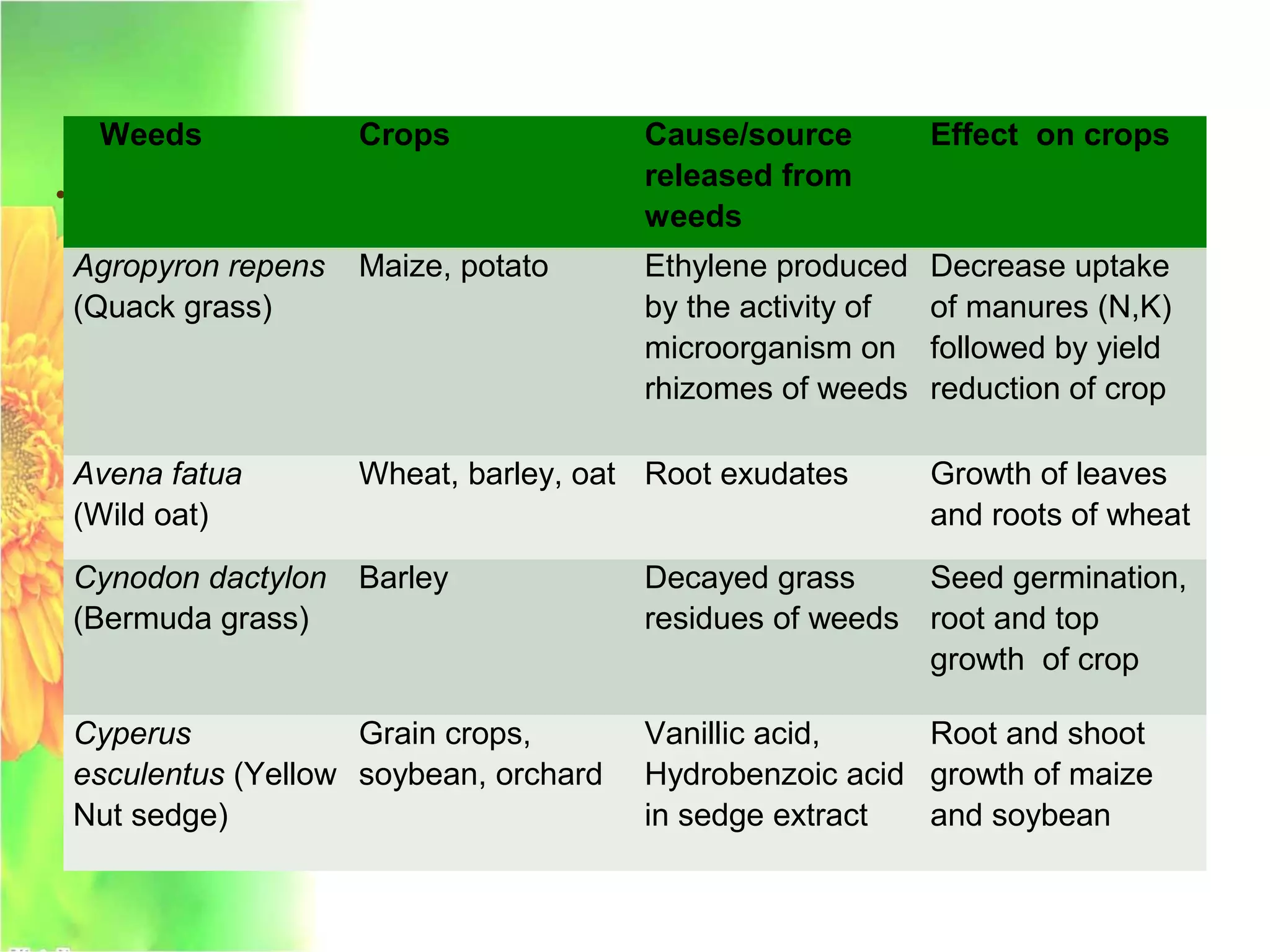
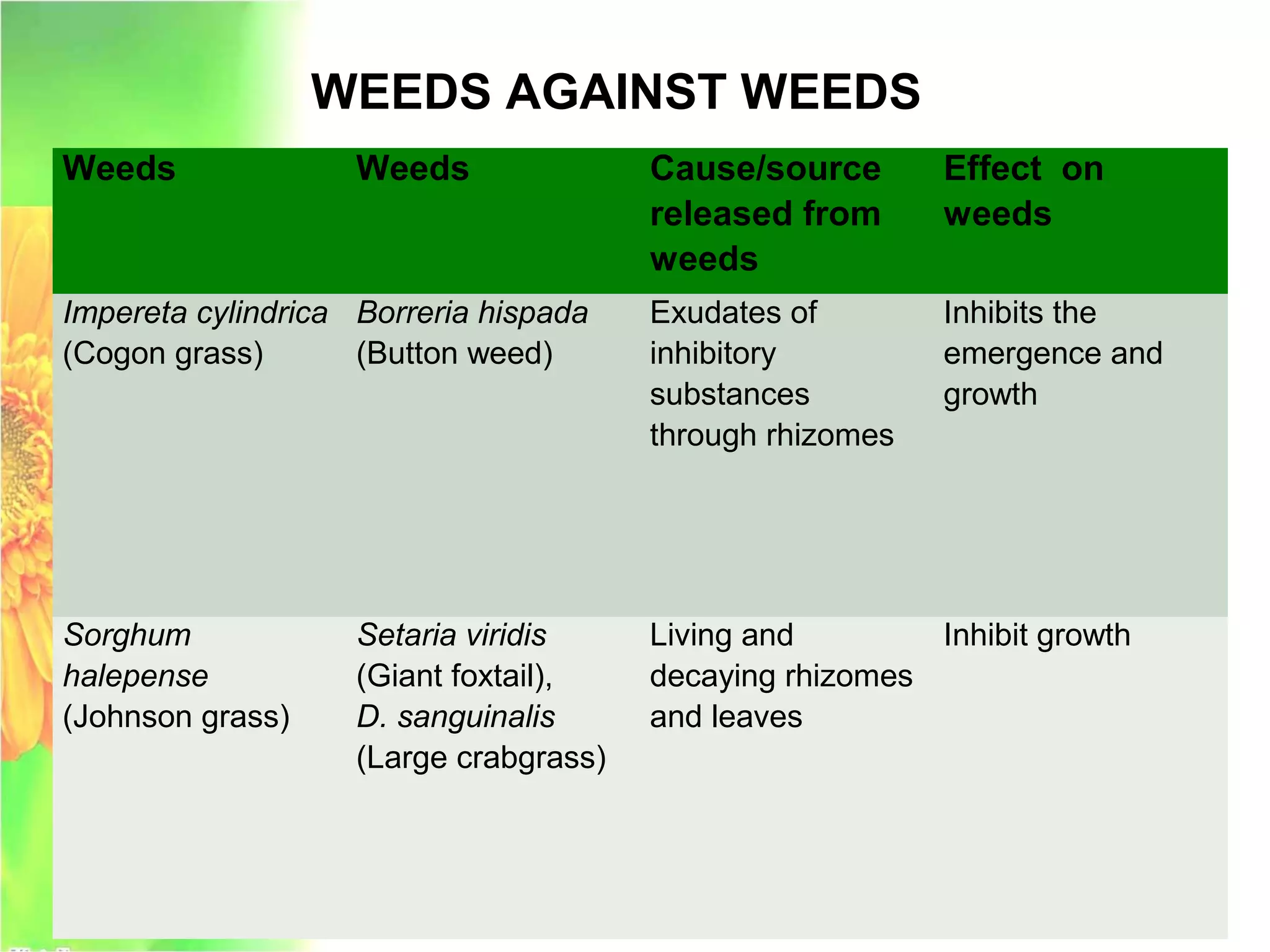
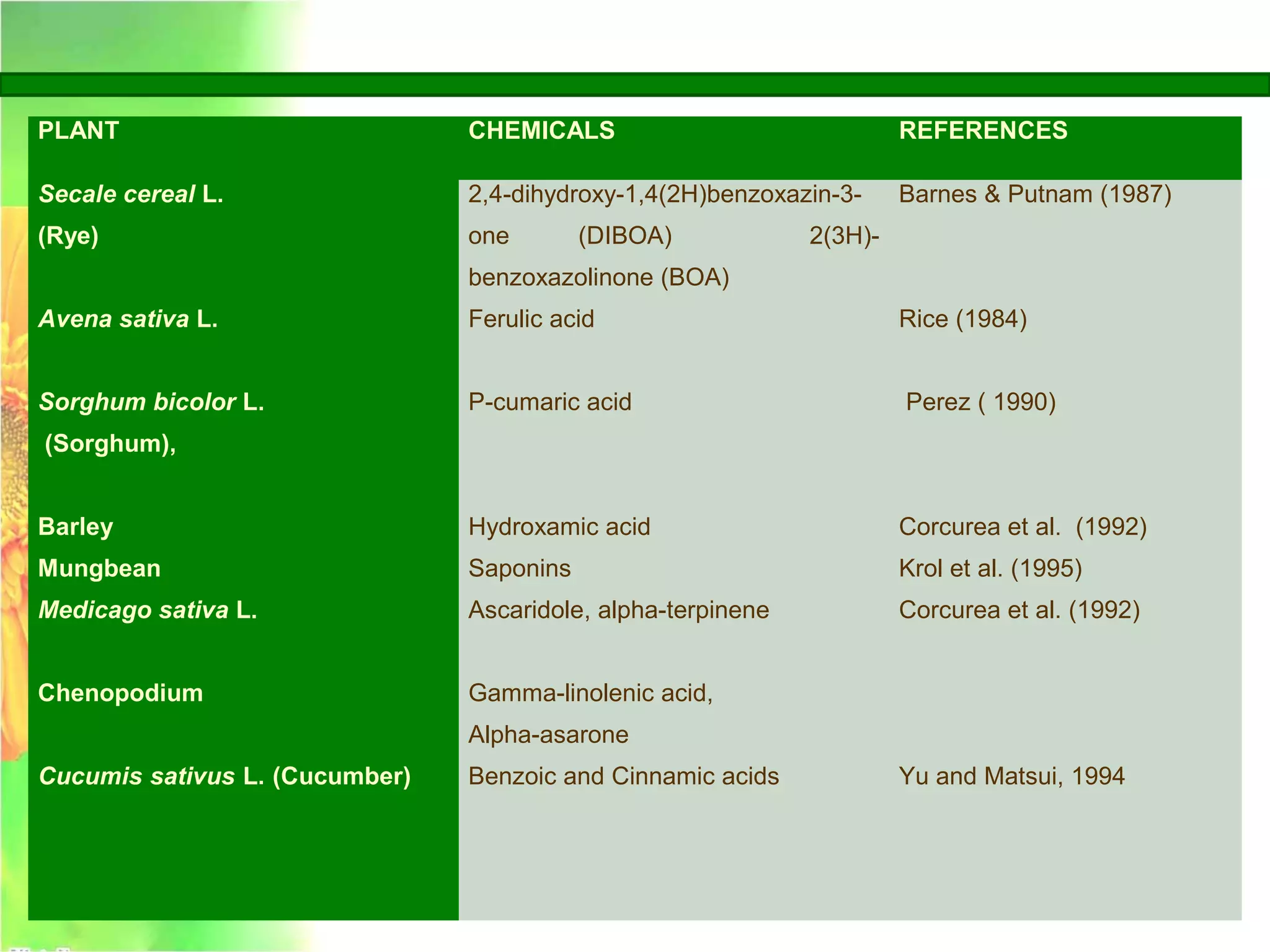
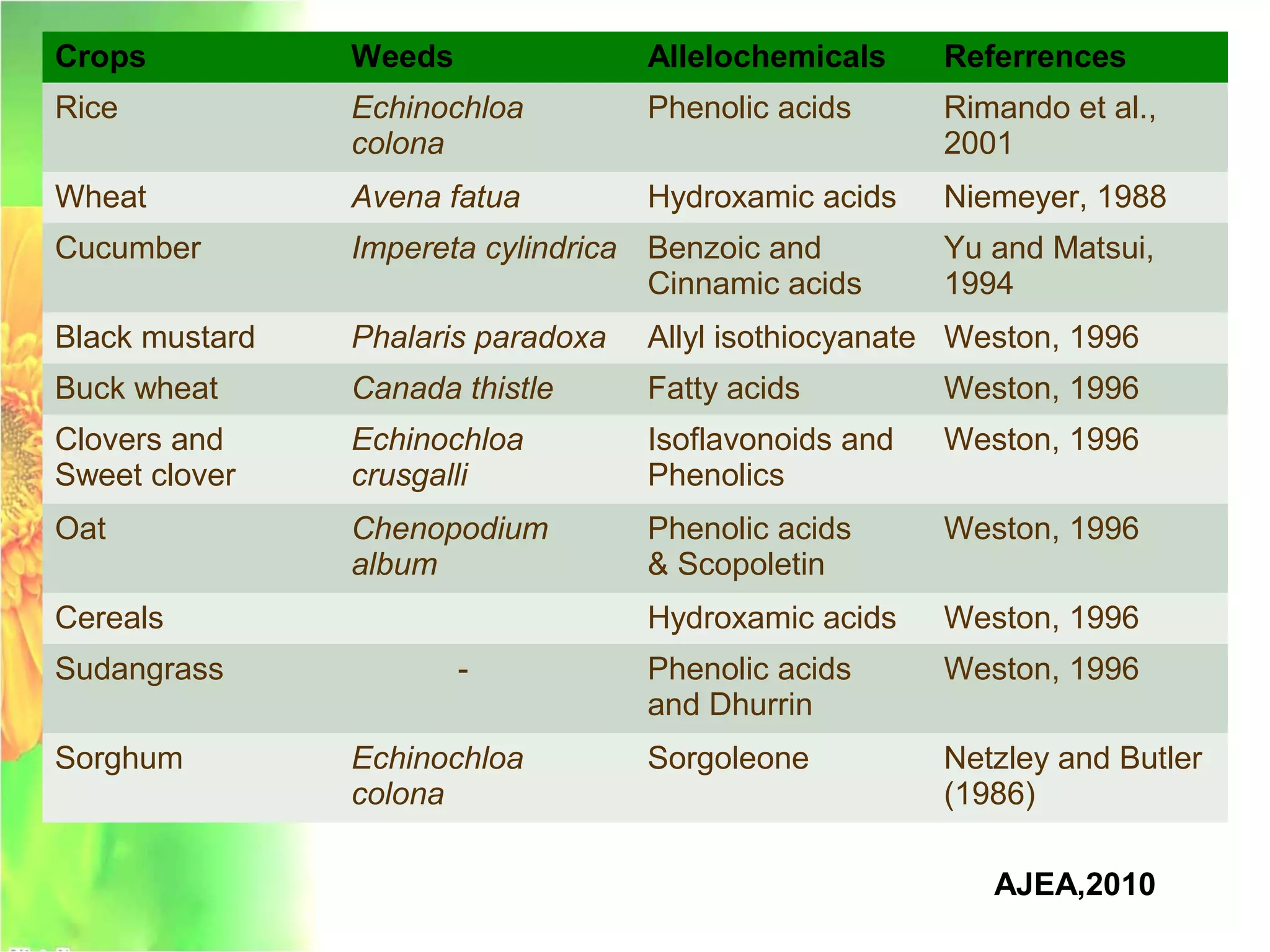
This document discusses allelopathy, which is the phenomenon where one plant produces chemicals that harm other plants. It provides examples of allelopathy between crops and weeds. Some common allelochemicals produced by plants are phenolic acids, coumarins, terpenoids, and flavonoids. These chemicals are released through leaching, exudation, volatilization, or decomposition. Allelopathy can affect weed suppression and crop yields. The strength of allelopathic effects depends on factors like crop variety, environmental conditions, and soil fertility. Further research on allelopathy could provide natural herbicides and support sustainable agriculture.