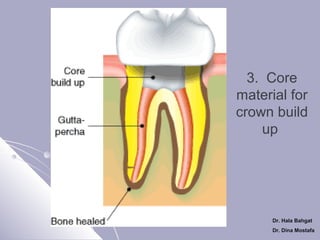
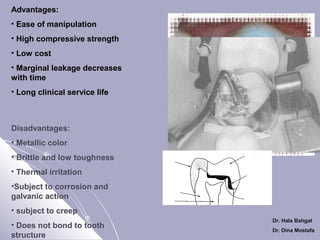
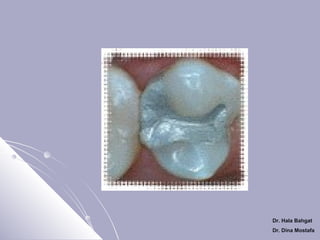
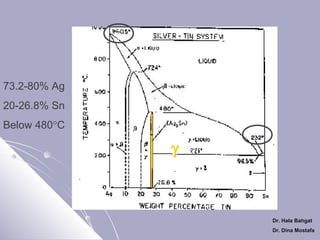
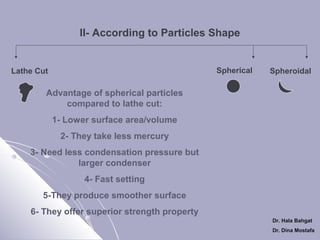
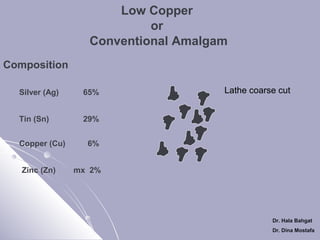
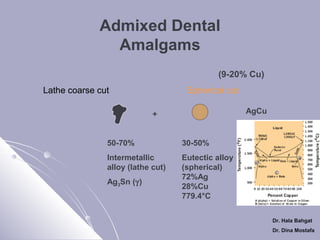
The document discusses dental amalgam, including its composition, setting reactions, classifications, and properties. Dental amalgam is an alloy made of silver, tin, copper, and sometimes zinc, combined with liquid mercury. It sets via a chemical reaction where the mercury dissolves the alloy powder to form intermetallic compounds. Amalgams are classified based on zinc content, particle shape/size, and copper percentage. Higher copper amalgams eliminate the gamma 2 phase during setting and have improved properties compared to conventional low copper amalgams.










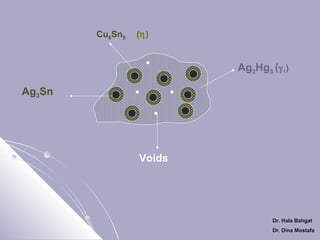
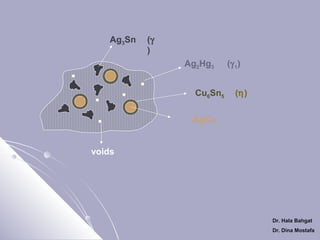
![Setting Reactions of Admixed Amalgam
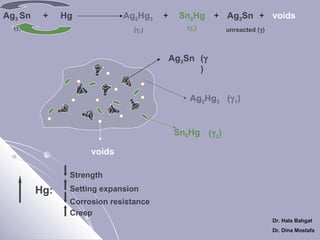
1- Dissolution of mercury in the alloy powder
[Ag3Sn+ Ag - Cu] + Hg → Ag2Hg3
γ
(eutectic)
(γ )
+ Sn8Hg + [Ag3Sn+ Ag - Cu] + voids
(γ 2)
1
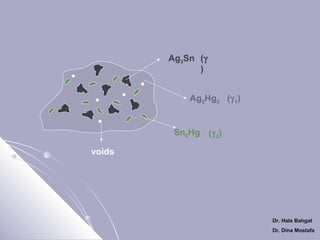
Ag3Sn
Cu6Sn5
(γ
)
Ag2Hg3
(γ 1)
AgCu
Sn8Hg (γ 2)
voids
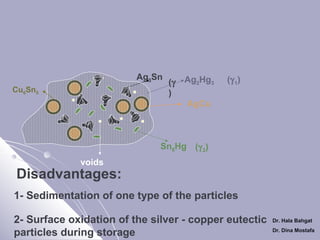
2- Elimination of γ 2 (Solid State Reaction)
Ag – Cu +
Sn8Hg
(γ 2)
Cu6Sn5 + Ag2Hg3 + Ag-cu unreacted + voids
η
(γ 1)
(eutectic)
Dr. Hala Bahgat
Dr. Dina Mostafa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amalgum-part1-140212221534-phpapp02/85/Amalgum-I-23-320.jpg)

![Setting Reaction
[Ag3Sn + Cu3Sn] +
ε
γ
Hg → Ag2Hg3 + Cu6Sn5+ Unreacted Ag Sn + voids
3
Cu6Sn5 γ 1
η
γ
Cu3Sn
Ag2Hg3 (γ 1)
Ag3Sn
Strength
Voids
Corrosion resistance
Creep
Dr. Hala Bahgat
Dr. Dina Mostafa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amalgum-part1-140212221534-phpapp02/85/Amalgum-I-27-320.jpg)