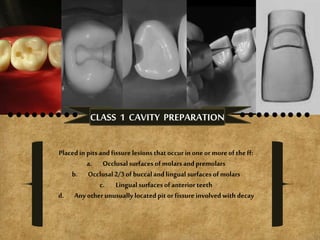
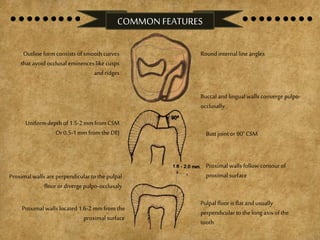
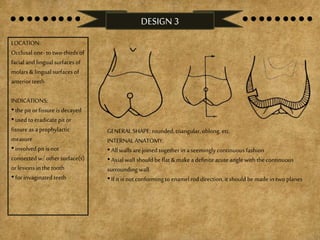
The document details various cavity preparation designs for molars and premolars, outlining specific locations, indications, and internal anatomy associated with each design. It describes eight different designs based on factors such as the extent of caries and the relationship with surrounding structures. Each design has unique characteristics tailored to specific dental scenarios and decay patterns.