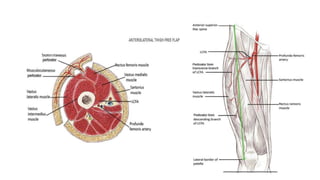
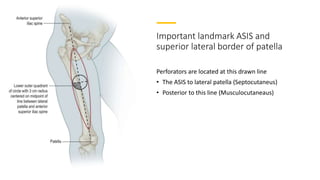
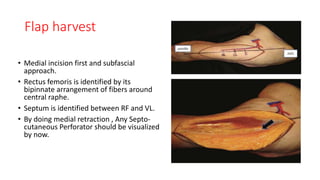
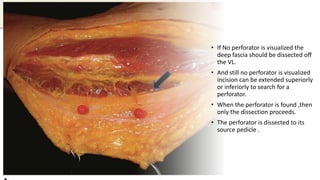
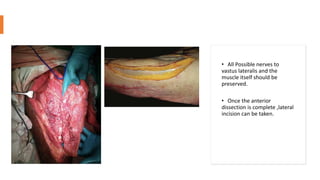
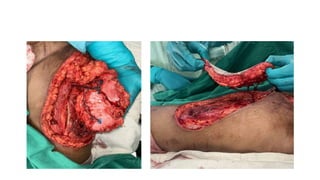
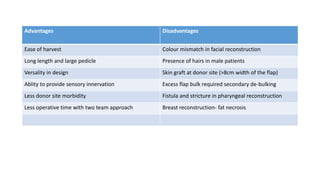
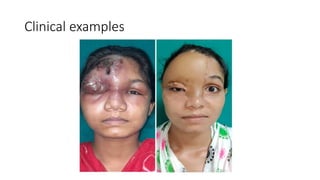
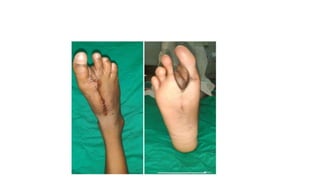
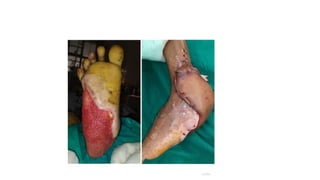
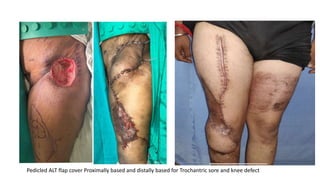
The anterolateral thigh (ALT) flap is a versatile soft tissue flap that can be used as a pedicled or free flap for reconstruction. It is supplied by septocutaneous or musculocutaneous perforators from the lateral circumflex femoral artery. The ALT flap is commonly used to reconstruct defects of the head and neck, extremities, breast, and perineum due to its long pedicle and ability to provide skin and soft tissue with or without muscle. While it has many advantages like long pedicle length and versatility, disadvantages include potential skin grafting at the donor site and contour abnormalities.