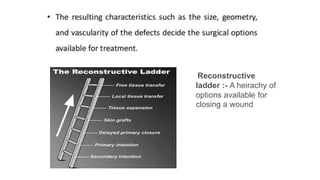
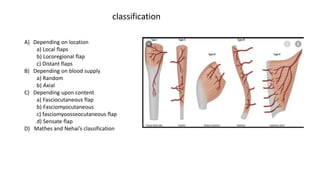
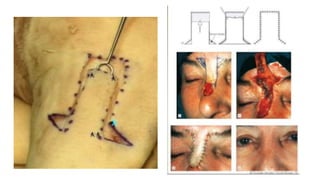
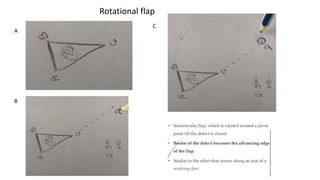
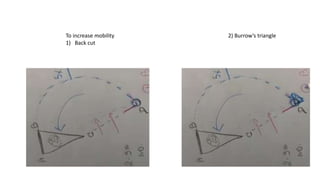
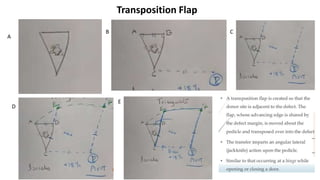
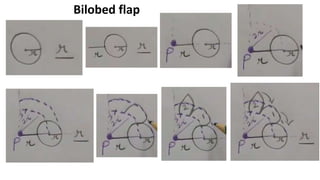
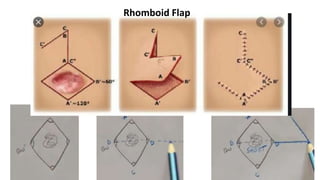
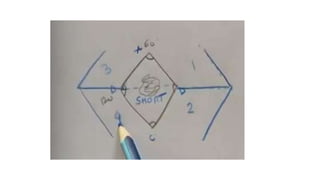
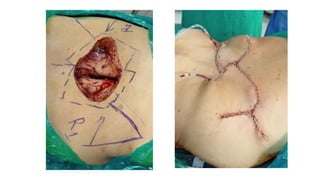
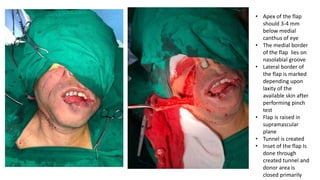
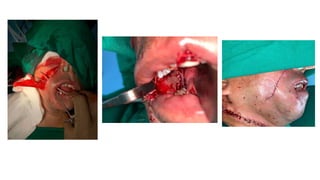
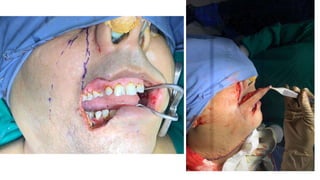
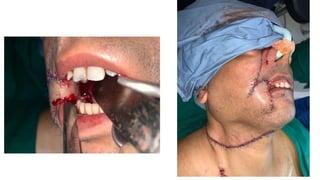
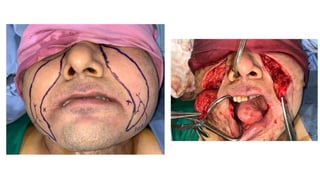
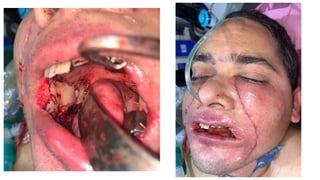
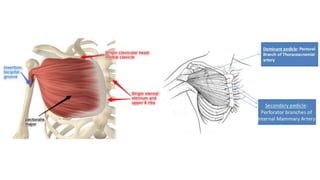
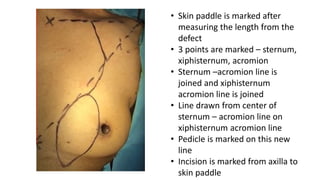
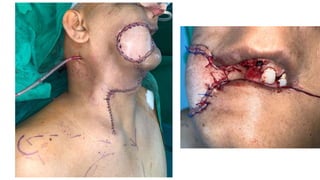
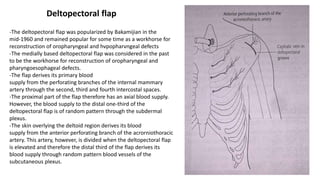
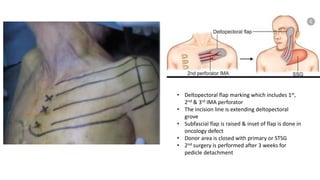
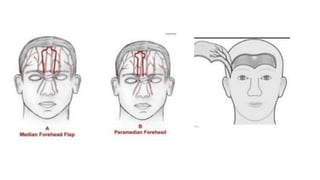
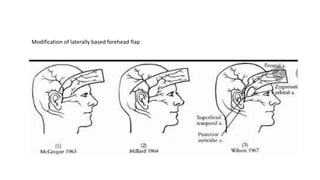
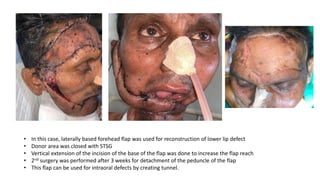
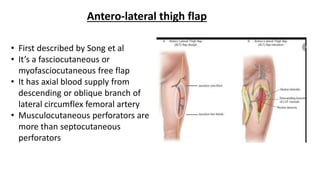
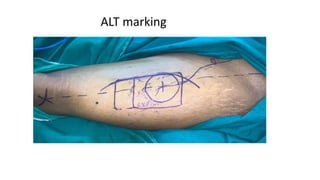
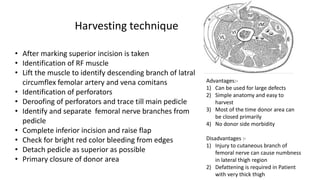
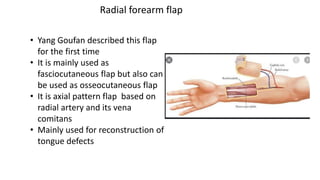
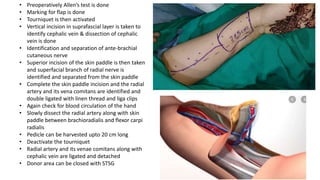
The document outlines various soft tissue flaps used in reconstructive surgery, detailing types based on location, blood supply, and content, along with examples of commonly used flaps like the pectoralis major myocutaneous flap, deltopectoral flap, and radial forearm flap. It describes specific techniques for harvesting these flaps, their advantages and disadvantages, and their applications in different surgical contexts, particularly within head and neck reconstruction. Additionally, classifications such as Mathes and Nahai’s are mentioned to aid in the selection of appropriate flaps for specific wound types.