Embed presentation
Download to read offline



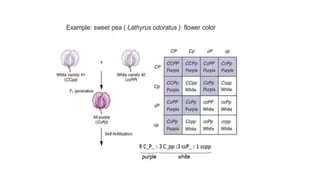

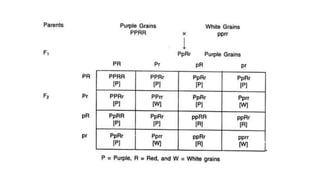

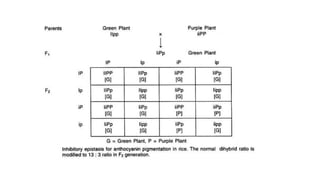
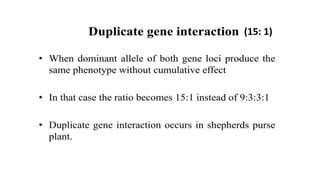
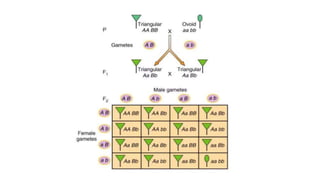

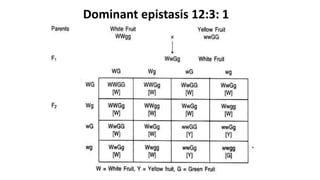

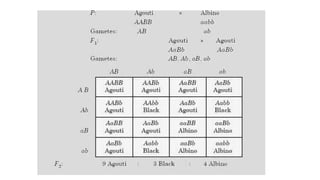
Two or more independent genes can work together to create a specific phenotype, which is known as complementary gene interaction. Bateson and Punnett crossed white and purple flowered Lathyrus plants and observed both flower colors in a 9:7 ratio in the F2 generation, showing complementary gene action. When recessive alleles at one gene locus prevent expression of alleles at another locus, it is known as dominant epistasis, which results in a phenotypic ratio of 12:3:1.













