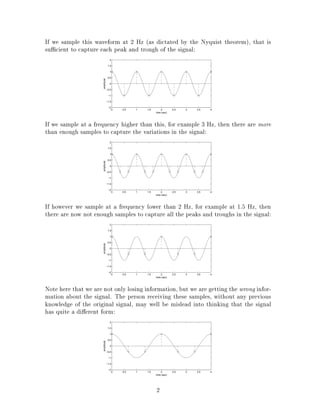
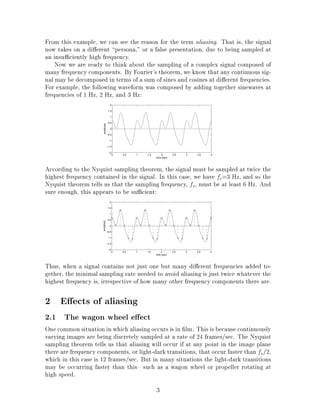
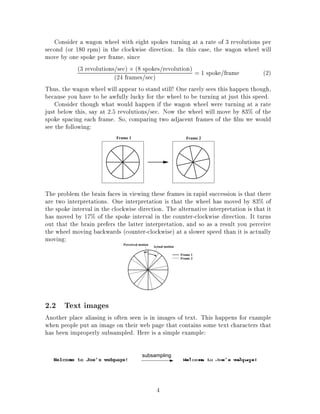
The document discusses the concept of aliasing which occurs when a signal is discretely sampled at too low of a rate. It describes how aliasing can cause signals to take on a false presentation and provide misleading information. The Nyquist sampling theorem states that the sampling frequency must be at least twice the highest frequency contained in the signal to avoid aliasing. The document then provides examples of how aliasing occurs with things like filmed wagon wheels and subsampled text images. It explains that aliasing can be avoided by low-pass filtering or blurring the signal before sampling to reduce the highest frequency.