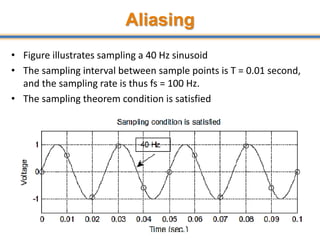
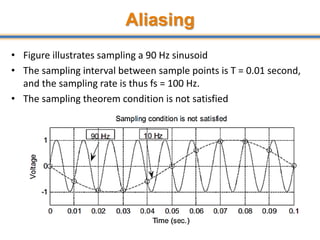
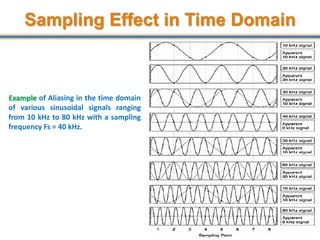
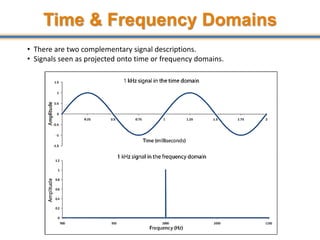
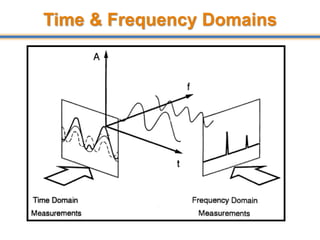
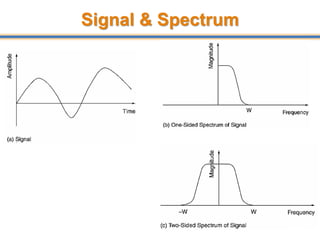
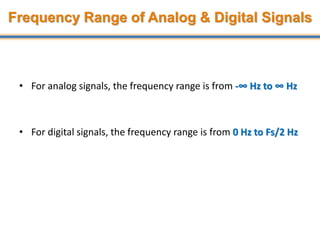
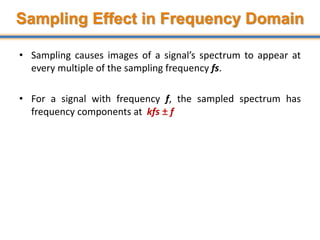
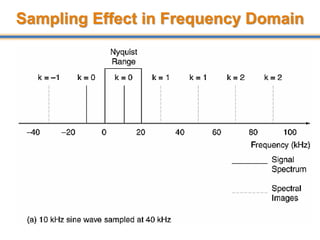
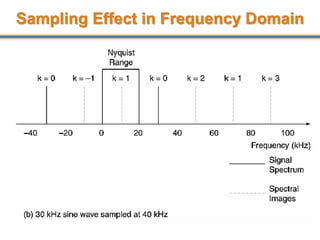
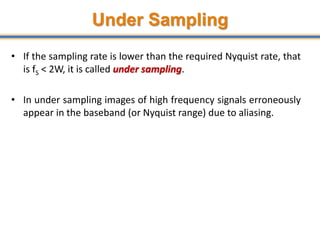
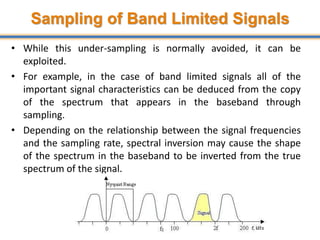
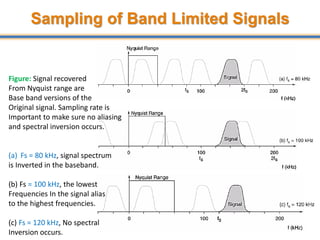
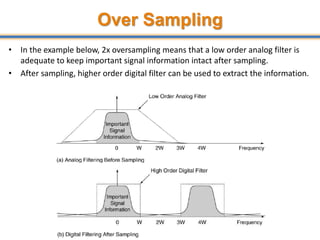
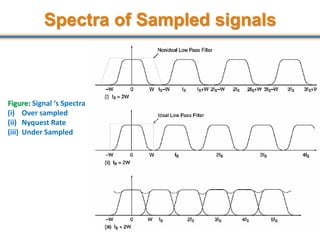
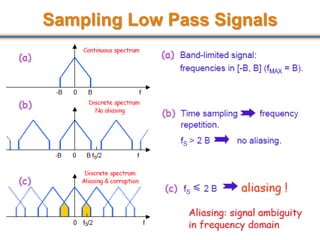
The document discusses aliasing in signal processing and sampling. It defines aliasing as distortion that occurs when the sampling rate is below the minimum required rate. Aliasing causes high frequency signals to appear as lower frequencies. To prevent aliasing, signals must be low-pass filtered before sampling to remove frequencies above half the sampling rate. The sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency component in the original signal as per the Nyquist sampling theorem. Oversampling can help reduce demands on anti-aliasing filters.