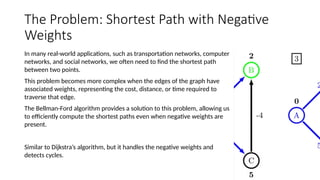
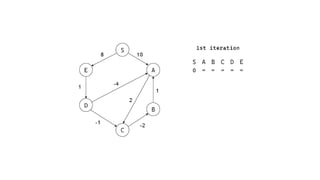
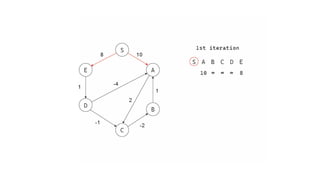
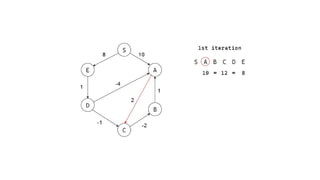
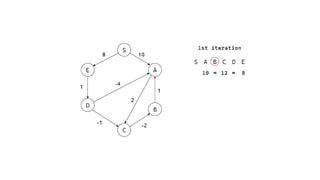
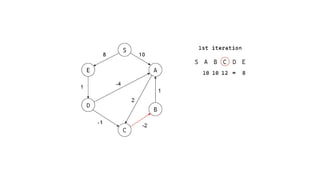
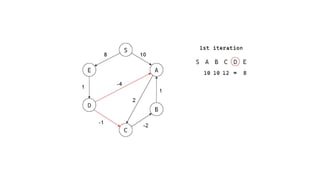
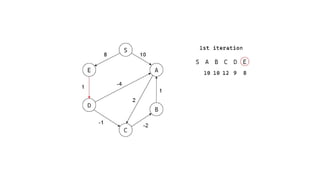
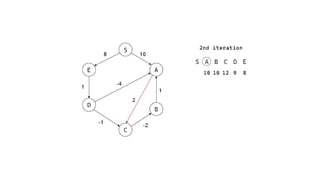
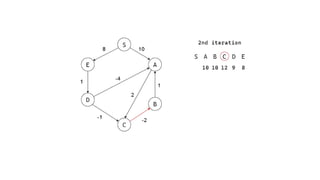
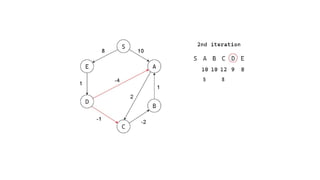
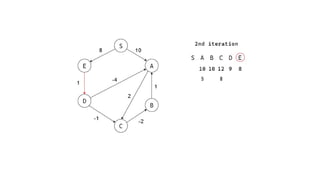
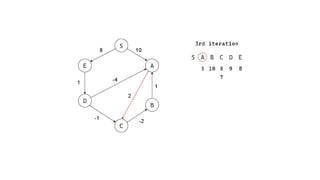
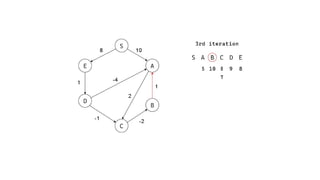
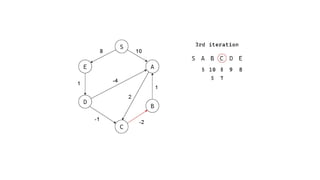
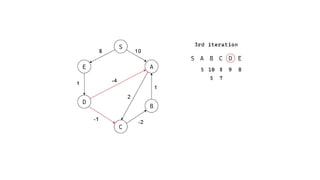
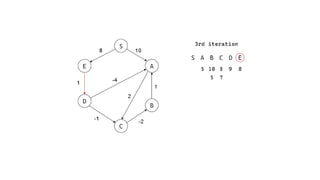
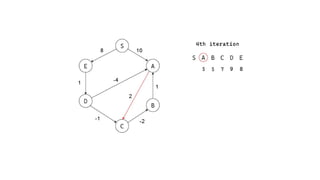
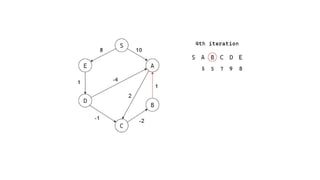
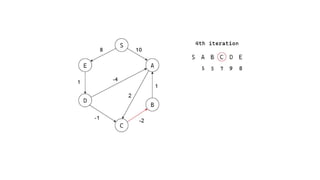
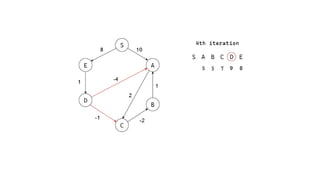
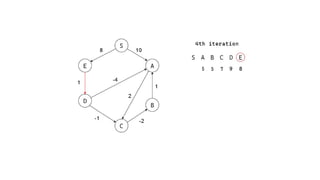
The Bellman-Ford algorithm is a key method in computer science for finding the shortest paths in weighted directed graphs, even when negative weights are present. It operates through initialization, relaxation of edges, and optimization of paths, with a time complexity of O(ve), which is higher than Dijkstra's algorithm that is more efficient for non-negative weights. The algorithm's ability to detect negative cycles makes it suitable for various real-world applications, including transportation and computer networks.