This document describes Bellman Ford's algorithm for finding the shortest paths in a graph. It begins with an introduction comparing Bellman Ford to Dijkstra's algorithm. It then explains the working mechanism, provides an example problem, and outlines the pseudocode. Key points are that Bellman Ford can handle graphs with negative edge weights, works by iteratively relaxing path estimates, and has a worst case time complexity of O(VE) where V is the number of vertices and E is the number of edges. Applications include distance vector routing protocols and finding shortest paths. The conclusion compares Bellman Ford to Dijkstra's algorithm.












![Click to edit Master title style
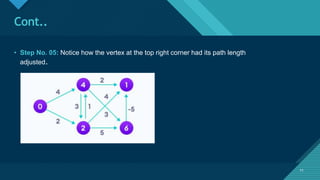
14
Pseudocode
14
function bellmanFord(G, S)
for each vertex V in G
distance[V] <- infinite
previous[V] <- NULL
distance[S] <- 0
for each vertex V in G
for each edge (U,V) in G
tempDistance <- distance[U] +
edge_weight(U, V)
if tempDistance < distance[V]
distance[V] <- tempDistance
previous[V] <- U
for each edge (U,V) in G
If distance[U] + edge_weight(U, V) <
distance[V}
Error: Negative Cycle Exists
return distance[ ], previous[ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hasnainkhaliddaappt-221024145418-74a6e84f/85/Hasnain_Khalid_DAA_ppt-pptx-14-320.jpg)



