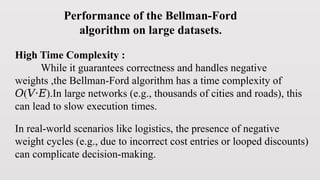
The Bellman-Ford algorithm, developed by Richard Bellman, is a dynamic programming technique used to find the shortest paths from a single source vertex to all other vertices in a weighted graph, capable of handling negative weights and detecting negative cycles. The algorithm operates through edge relaxation and iterates V-1 times, followed by a check for negative cycles. Its applications are critical in scenarios such as logistics for determining optimal delivery paths, though it is considered slow for larger graphs due to its high time complexity.














![Initial distances Array:
distances=[0, ∞, ∞]
distances=float(‘inf’)*V ∞*no of vertices(3)
distances[source] = 0
distances=[∞, ∞, ∞]
distances[0] = 0 (i.e source is 0)
Input:
Enter the number of vertices: 3
Enter the number of edges: 3
Enter edge (source destination weight): 0 1 4
Enter edge (source destination weight): 0 2 1
Enter edge (source destination weight): 1 2 -2
Enter the source vertex: 0
graph=[(0, 1, 4), (0, 2, 1), (1, 2, -2)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordalgorithm-241203173056-b51c0fcd/85/BELLMAN_FORD-_ALGORITHM-IN-DATA-STRUCTURES-15-320.jpg)
![Relaxing the edges v-1 times:
First Iteration (i = 1):
Edge (0 → 1, 4):
∙ Current distances: [0, ∞, ∞]
∙ distances[0] + weight = 0 + 4 = 4
∙ Compare with distances[1] (∞):
Update distances[1] to 4.
∙ Updated distances: [0, 4, ∞]
Edge (0 → 2, 1):
∙ Current distances: [0, 4, ∞]
∙ distances[0] + weight = 0 + 1 = 1
∙ Compare with distances[2] (∞):
Update distances[2] to 1.
∙ Updated distances: [0, 4, 1]
Edge (1 → 2, -2):
∙ Current distances: [0, 4, 1]
∙ distances[1] + weight = 4 + (-2) = 2
Compare with distances[2] (1):
No update, as 2 is greater than 1
After the first iteration:
distances: [0, 4, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordalgorithm-241203173056-b51c0fcd/85/BELLMAN_FORD-_ALGORITHM-IN-DATA-STRUCTURES-16-320.jpg)
![Second Iteration (i = 2):
We process all edges again:
Edge (0 → 1, 4):
∙ Current distances: [0, 4, 1]
∙ distances[0] + weight = 0 + 4 = 4
Compare with distances[1] (4):
No update, as they are equal
Edge (0 → 2, 1):
∙ Current distances: [0, 4, 1]
∙ distances[0] + weight = 0 + 1 = 1
∙ Compare with distances[2] (1):
No update, as they are equal.
Edge (1 → 2, -2):
•Current distances: [0, 4, 1]
•distances[1] + weight = 4 + (-2) = 2
•Compare with distances[2] (1):
No update, as 2 is greater than 1.
After the second iteration:
distances: [0, 4, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordalgorithm-241203173056-b51c0fcd/85/BELLMAN_FORD-_ALGORITHM-IN-DATA-STRUCTURES-17-320.jpg)
![•After relaxing all edges V-1 times, this step checks if any edge can still be
relaxed (which would indicate a negative weight cycle).
•If distances[u] + weight < distances[v] still holds for any edge, it means the
graph contains a negative weight cycle, and the algorithm prints a message and exits
Output:
Shortest distances from source:
Vertex 0: 0
Vertex 1: 4
Vertex 2: 1
Check for negative cycle:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordalgorithm-241203173056-b51c0fcd/85/BELLMAN_FORD-_ALGORITHM-IN-DATA-STRUCTURES-18-320.jpg)


![CASE STUDY CODE
def bellmanFord(V, edges, src):
INF = float('inf')
dist = [INF] * V
dist[src] = 0
for i in range(V):
for edge in edges:
u, v, wt = edge
if dist[u] != INF and dist[u] + wt < dist[v]:
if i == V - 1:
return [-1]
dist[v] = dist[u] + wt
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordalgorithm-241203173056-b51c0fcd/85/BELLMAN_FORD-_ALGORITHM-IN-DATA-STRUCTURES-21-320.jpg)
![print("Welcome to the Logistics Network Optimizer!")
V = int(input("Enter the number of cities: "))
E = int(input("Enter the number of roads: "))
print("nEnter the road details (source, destination, travel
time):")
edges = []
for i in range(E):
print(f"Road {i + 1}:")
u = int(input(" Source city (0-indexed): "))
v = int(input(" Destination city (0-indexed): "))
wt = int(input(" Travel time (can be negative): "))
edges.append([u, v, wt])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordalgorithm-241203173056-b51c0fcd/85/BELLMAN_FORD-_ALGORITHM-IN-DATA-STRUCTURES-22-320.jpg)
![src = int(input("nEnter the source city (central warehouse, 0-
indexed): "))
print("nCalculating shortest paths...")
ans = bellmanFord(V, edges, src)
if ans == [-1]:
print("nError: Negative weight cycle detected in the network!")
else:
print("nShortest distances from the central warehouse:")
for city in range(V):
if ans[city] == float('inf'):
print(f" City {city}: No path available")
else:
print(f" City {city}: {ans[city]} time units")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordalgorithm-241203173056-b51c0fcd/85/BELLMAN_FORD-_ALGORITHM-IN-DATA-STRUCTURES-23-320.jpg)




![▪ Edges: 2,3,4
distances=[0, ∞, ∞]
After 1st
iteration : distances=[-2,5,8]
After 2nd
iteration : distances=[-4,3,6]
▪ Cycle Detection(additional iteration):
Edge in Focus: 2→4.
▪ If distances[2] + w < distances[4]
If -4+5<3
1<3 #returns true
▪ Output: Negative weight cycle detected!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordalgorithm-241203173056-b51c0fcd/85/BELLMAN_FORD-_ALGORITHM-IN-DATA-STRUCTURES-28-320.jpg)