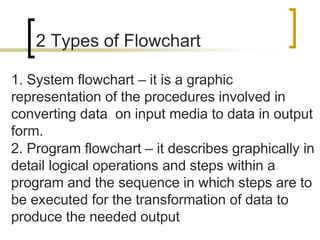
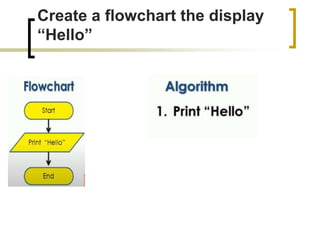
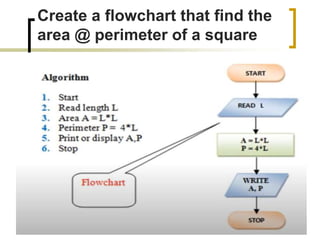
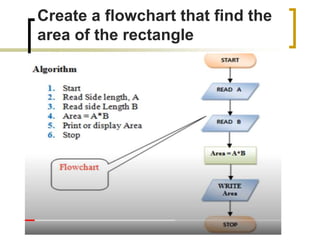
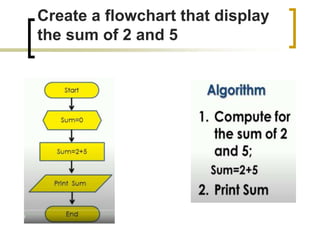
The document provides information about flowcharts including:
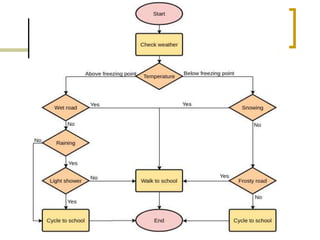
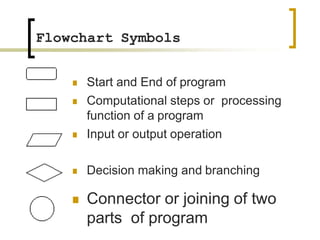
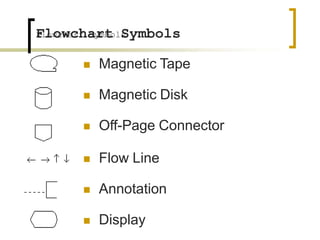
- Flowcharts use symbols to represent steps in a process or program and the flow from one to the next.
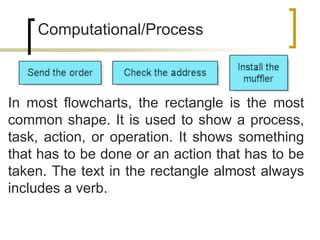
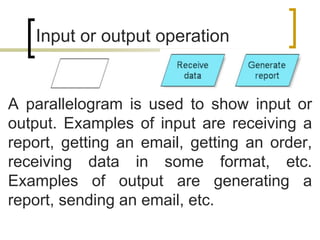
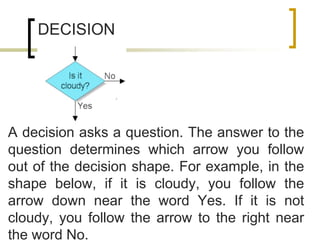
- Common symbols include shapes for processes, decisions, inputs/outputs, and connecting arrows.
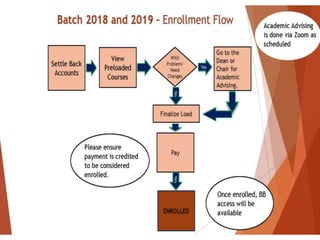
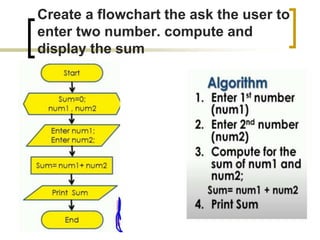
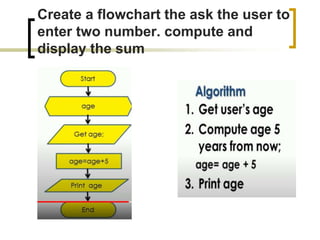
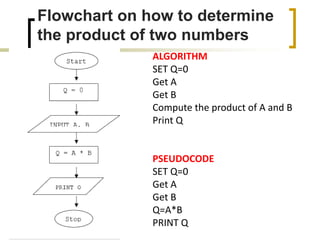
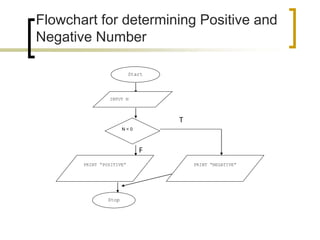
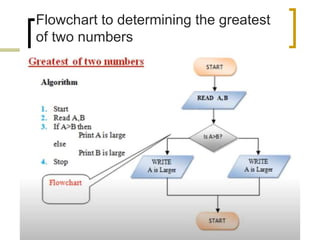
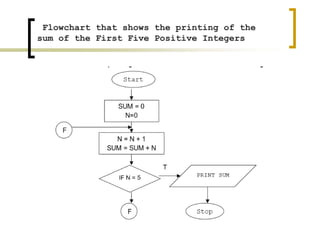
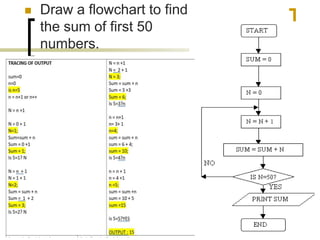
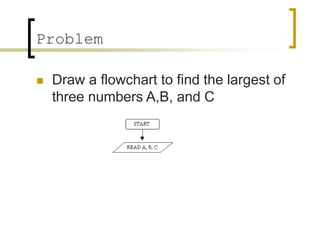
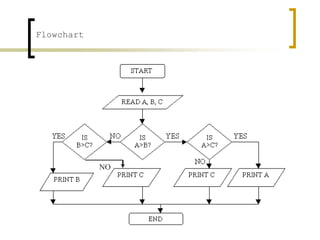
- Examples of flowcharts are given for finding the sum of two numbers, determining if a number is positive or negative, and finding the greatest of two numbers.
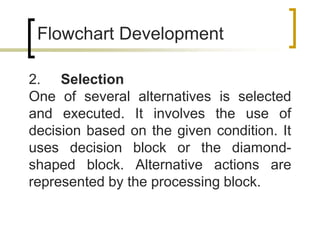
- Flowcharts can model sequential, selection, and repetitive program logic.