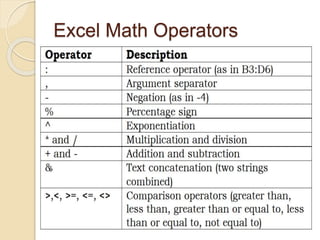
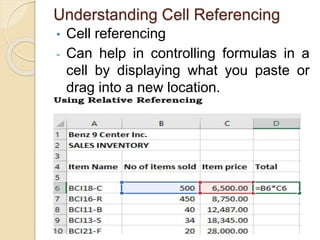
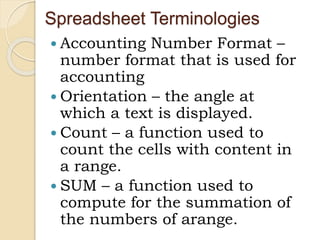
This document discusses advanced spreadsheet functions and formulas in Excel. It explains that spreadsheets are used for tasks like budgets and forecasting using columns and cells. Advanced functions covered include data entry, filtering, protecting data, pivot tables, macros, combining functions, and calculations. Formulas in Excel use operators and functions to analyze and calculate worksheet data. The document demonstrates how to enter formulas, use cell referencing and absolute referencing, and covers common spreadsheet terminology like ranges, criteria, formatting, and functions like COUNT, SUM, AVERAGE.