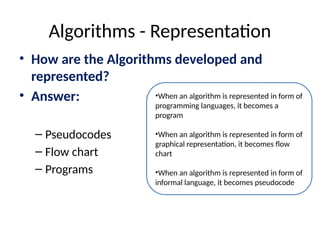
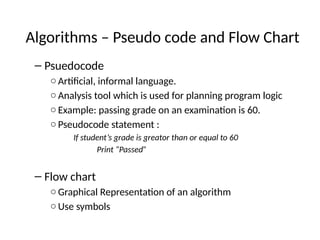
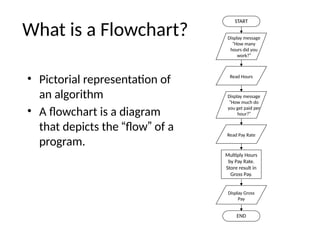
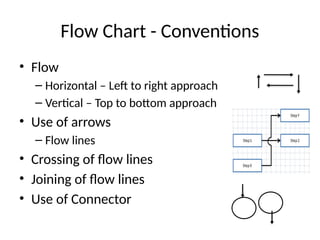
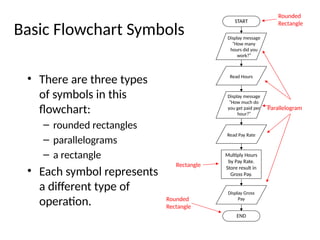
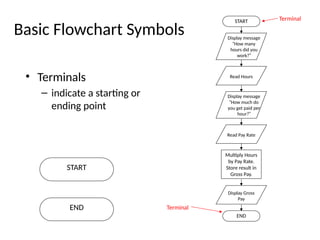
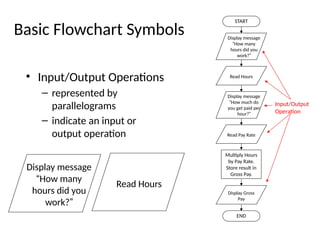
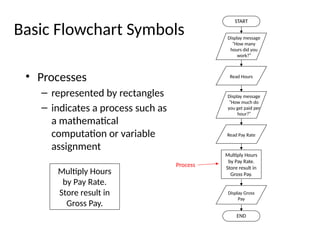
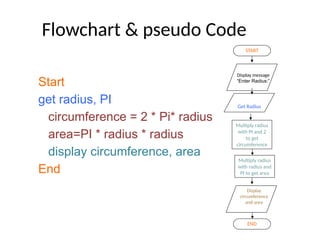
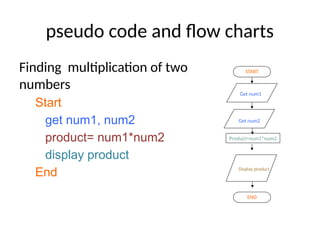
The document introduces algorithms in computer programming, highlighting their step-by-step logic and representation forms such as pseudocode and flowcharts. It outlines basic flowchart symbols, including terminals, input/output operations, and processes, along with examples and advantages/disadvantages of using flowcharts and pseudocode for programming. Additionally, it provides specific examples for writing pseudocode and creating flowcharts for simple mathematical operations.