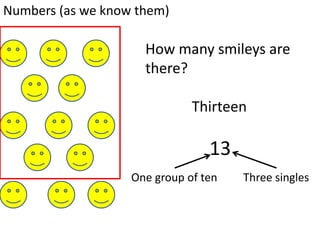
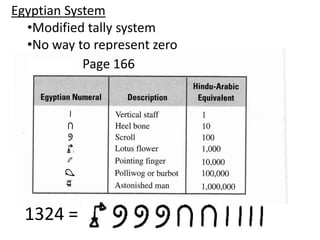
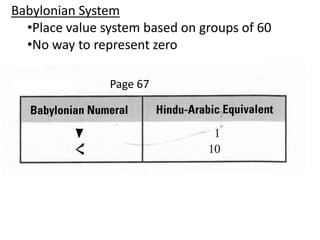
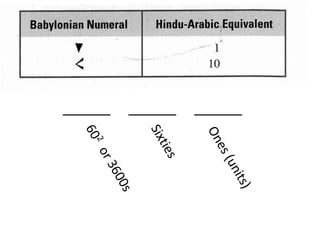
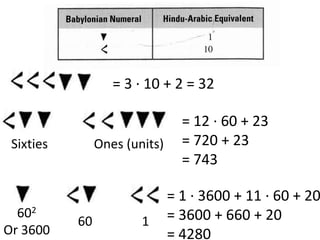
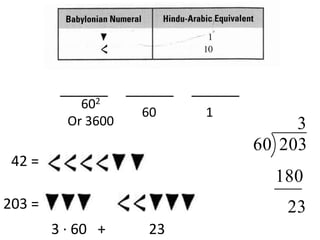
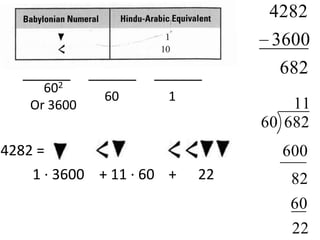
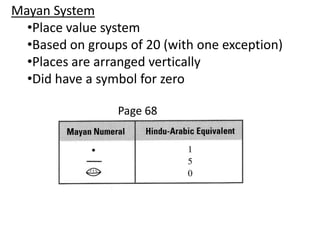
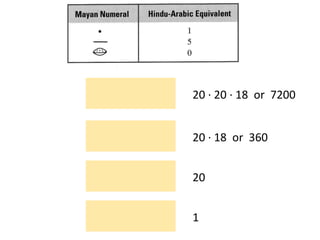
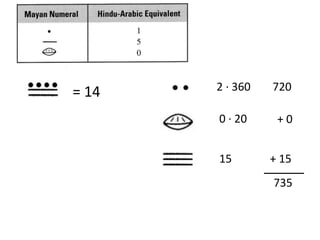
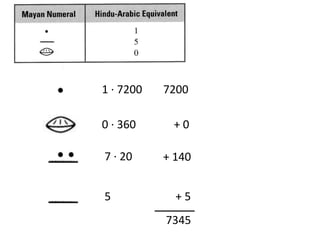
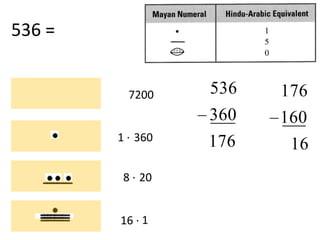
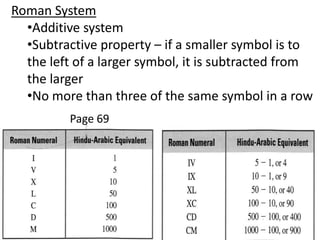
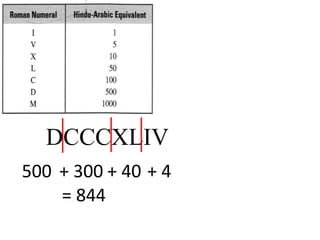
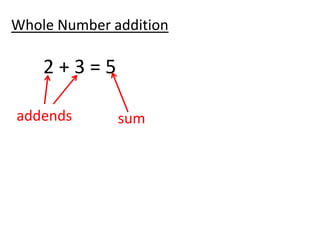
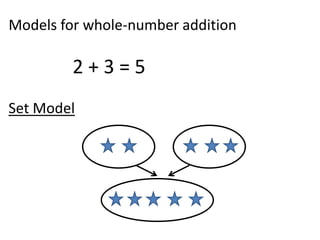
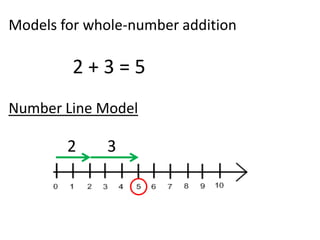
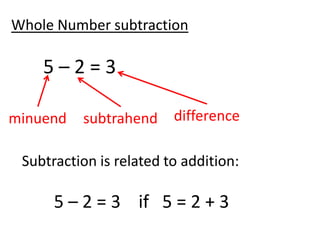
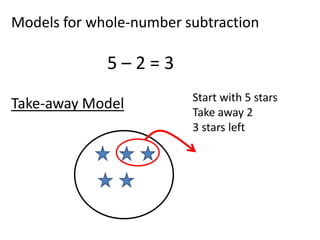
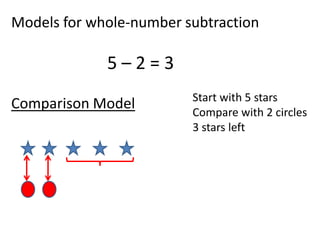
The document discusses different number systems used throughout history including Hindu-Arabic, Egyptian, Babylonian, Mayan, and Roman systems. It also covers basic concepts of whole numbers such as addition, subtraction, and their properties. Different models are presented to demonstrate whole number operations including set, number line, take-away, comparison, and missing addend models.